|
BL 13.5-inch Mk VI Naval Gun
The BL 13.5-inch Mk VI gun was a British heavy naval gun, originally ordered by the Ottoman Navy to equip its dreadnoughts around 1911. The one ship completed was seized by the British Government when World War I began in August 1914 and became . Only 10 guns were built, to a design similar to that of their 45-calibre BL 13.5-inch Mk V naval gun. The smaller chamber Chamber or the chamber may refer to: In government and organizations *Chamber of commerce, an organization of business owners to promote commercial interests *Legislative chamber, in politics *Debate chamber, the space or room that houses deliber ... in the Mk VI gun meant that less propellant could be used which reduced muzzle velocity by and range by . Designed by Vickers, they manufactured the guns of X and Y turrets, while Elswick Ordnance Company manufactured the guns of A, B, and Q turrets. Weapons of comparable role, performance and era * 340mm/45 Modèle 1912 gun French equivalent References Bibli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising France, Russia, and Britain) and the Triple Alliance (containing Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy). Tensions in the Balkans came to a head on 28 June 1914, following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
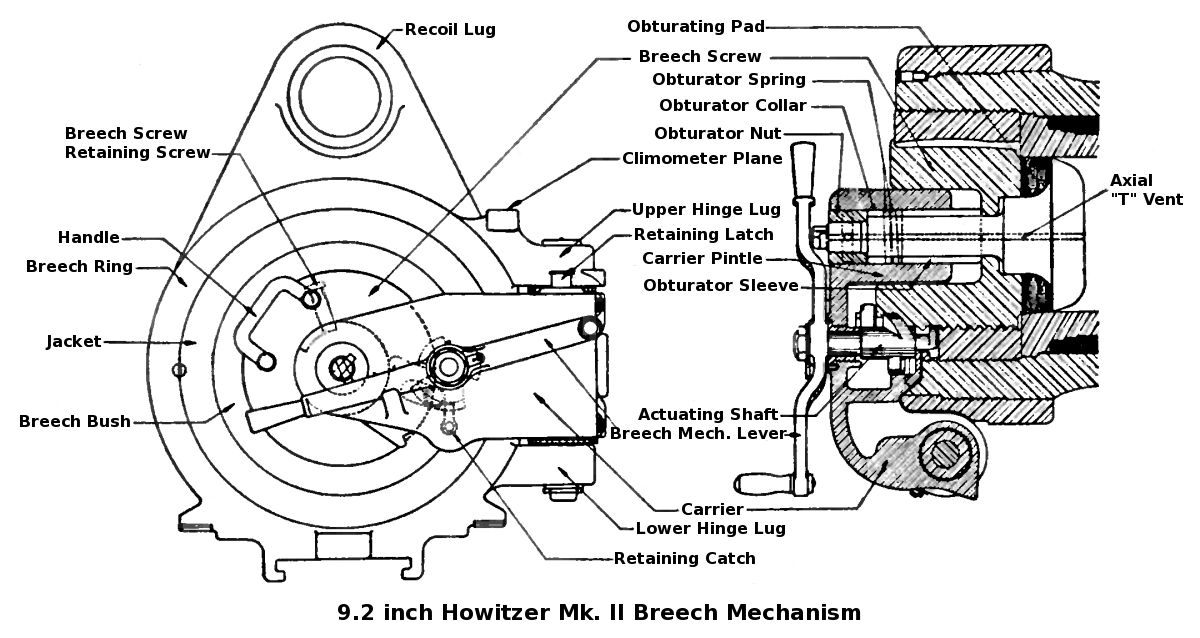
Vickers, Sons & Maxim, Ltd
Vickers Limited was a British engineering conglomerate. The business began in Sheffield in 1828 as a steel foundry and became known for its church bells, going on to make shafts and propellers for ships, armour plate and then artillery. Entire large ships, cars, tanks and torpedoes followed. Airships and aircraft were added, and Vickers jet airliners were to remain in production until 1965. Financial problems following the death of the Vickers brothers were resolved in 1927 by separating Metropolitan Carriage Wagon and Finance Company and Metropolitan-Vickers, then merging the remaining bulk of the original business with Armstrong Whitworth to form Vickers-Armstrongs. The Vickers name resurfaced as Vickers plc between 1977 and 1999. History Foundry Vickers was formed in Sheffield as a steel foundry by the miller Edward Vickers and his father-in-law George Naylor in 1828. Naylor was a partner in the foundry Naylor & Sanderson, and Vickers' brother William owned a steel roll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elswick Ordnance Company
The Elswick Ordnance Company (sometimes referred to as Elswick Ordnance Works, but usually as "EOC") was a British armaments manufacturing company of the late 19th and early 20th century History Originally created in 1859 to separate William Armstrong's armaments business from his other business interests, to avoid a conflict of interest as Armstrong was then Engineer of Rifled Ordnance for the War Office and the company's main customer was the British Government. Armstrong held no financial interest in the company until 1864 when he left Government service, and Elswick Ordnance was re-united with the main Armstrong businesses to form Sir W.G. Armstrong & Company. EOC was then the armaments branch of W.G. Armstrong & Company and later of Armstrong Whitworth. EOC's main customer in its early years was the British Government, but the Government abandoned "Armstrong guns" in the mid-1860s due to dissatisfaction with Armstrong's breech mechanism, and instead built its own rifled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caliber (artillery)
In artillery, caliber or calibredifference in British English and American English spelling is the internal diameter of a gun barrel, or - by extension - a relative measure of the barrel length. Rifled barrels Rifled barrels introduce ambiguity to measurement of caliber. A rifled bore consists of alternating grooves and lands. The distance across the bore from groove to groove is greater than the distance from land to land. Projectiles fired from rifled barrels must be of the full groove to groove diameter to be effectively rotated by the rifling, but the caliber has sometimes been specified as the land to land diameter before rifling grooves were cut. The depth of rifling grooves (and the consequent ambiguity) increases in larger calibers. Steel artillery projectiles may have a forward bourrelet section machined to a diameter slightly smaller than the original land to land dimension of the barrel and a copper driving band somewhat larger than the groove to groove diameter t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Ordnance Terms
This article explains terms used for the British Armed Forces' ordnance (i.e.: weapons) and also ammunition. The terms may have slightly different meanings in the military of other countries. BD Between decks: applies to a naval gun mounting in which part of the rotating mass is below the deck, and part of it is above the deck. This allows for a lower profile of turret, meaning that turrets need not be superfiring (i.e. they can be mounted on the same deck and not obstruct each other at high angles of elevation.) BL The term BL, in its general sense, stood for breech loading, and contrasted with muzzle loading. The shell was loaded via the breech (i.e. the gunner's end of the barrel, which opened) followed by the propellant charge, and the breech mechanism was closed to seal the chamber. Breech loading, in its formal British ordnance sense, served to identify the gun as the type of rifled breechloading gun for which the powder charge was loaded in a silk or cloth bag and the br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Gun
Naval artillery is artillery mounted on a warship, originally used only for naval warfare and then subsequently used for naval gunfire support, shore bombardment and anti-aircraft roles. The term generally refers to tube-launched projectile-firing weapons and excludes self-propelled projectiles such as torpedoes, rockets, and missiles and those simply dropped overboard such as depth charges and naval mines. Origins The idea of ship-borne artillery dates back to the classical era. Julius Caesar indicates the use of ship-borne catapults against Britons ashore in his ''Commentarii de Bello Gallico''. The dromons of the Byzantine Empire carried catapults and Greek fire, fire-throwers. From the late Middle Ages onwards, warships began to carry cannon, cannons of various calibres. The Mongol invasion of Java introduced cannons to be used in naval warfare (e.g. Cetbang by the Majapahit). The Battle of Arnemuiden, fought between England and France in 1338 at the start of the Hundred Y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dreadnought
The dreadnought (alternatively spelled dreadnaught) was the predominant type of battleship in the early 20th century. The first of the kind, the Royal Navy's , had such an impact when launched in 1906 that similar battleships built after her were referred to as "dreadnoughts", and earlier battleships became known as pre-dreadnoughts. Her design had two revolutionary features: an "all-big-gun" armament scheme, with an unprecedented number of heavy-calibre guns, and steam turbine propulsion. As dreadnoughts became a crucial symbol of national power, the arrival of these new warships renewed the naval arms race between the United Kingdom and Germany. Dreadnought races sprang up around the world, including in South America, lasting up to the beginning of World War I. Successive designs increased rapidly in size and made use of improvements in armament, armour and propulsion throughout the dreadnought era. Within five years, new battleships outclassed ''Dreadnought'' herself. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BL 13
BL (or similar) may refer to: Arts and entertainment * BL Publishing, a division of the wargames manufacturing company, Games Workshop * ''Boston Legal'', a US legal comedy drama * Boys' love, Japanese term for female-oriented fiction featuring idealized romantic relationships between two males Businesses and organizations * Bell Labs, an audio-technology research and design enterprise * Boys' Latin School of Maryland, a US private school * Brisbane Lions, an Australian rules football team in the Australian Football League * British Library, the UK's national library * British Leyland, a former UK vehicle manufacturing company * Pacific Airlines (IATA code BL), a low-cost airline * Lytvyn Bloc, a Ukrainian political party Food and drink * Bitter lemon, a carbonated soft drink * Bud Light, an American lager beer In law * Bachelor of Laws (B.L.), an undergraduate degree in law * Barrister-at-Law, a degree and professional qualification in Ireland, Northern Ireland and Nigeria. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chamber (firearms)
In firearms, the chamber is the cavity at the back end of a breechloader's barrel or cylinder, where the cartridge is inserted before being fired. The rear opening of the chamber is the breech, and is sealed by the breechblock or the bolt. Function Rifles and pistols generally have a single chamber integral to their barrels, but revolvers have multiple chambers in their cylinder, and no chamber in their barrel. Thus, rifles and pistols can usually still be fired with the magazine removed as long as a cartridge is inserted into the chamber, while a revolver cannot be fired at all with its cylinder swung out. The act of ''chambering'' a cartridge means the insertion of a round into the chamber, either manually or through the action of the weapon, e.g., pump-action, lever-action, bolt action, or Autoloading operation generally in anticipation of firing the weapon, without need to "load" the weapon upon decision to use it (reducing the number of ''actions'' needed to disch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
340mm/45 Modèle 1912 Gun
The 340mm/45 Modèle 1912 gun (13.4 in) was a heavy naval gun of the French Navy. While the calibres of the naval guns of the French Navy were usually very close to those of their British counterparts, the calibre of 340 mm is specific to the French Navy. The built-up gun was designed to be carried by the and classes in quadruple gun turrets, but no ship of these types was completed as a battleship. They were carried by the s in twin turrets. Some of these guns were used as railway guns and coastal artillery in World War I, also serving in World War II. Railway gun Due to the cancellation or conversion of most of the ships these guns were made for, the relatively large number of spare guns available facilitated their use as railway guns in both World Wars. Two batteries of 340 mm guns, with an authorized strength of one gun per battery, were operated by the 53rd Coast Artillery, U. S. Army, in World War I. As with most French railway guns, after the Fall of Fran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Guns Of The United Kingdom
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval warfare, naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral zone, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It includes anything conducted by surface Naval ship, ships, amphibious warfare, amphibious ships, submarines, and seaborne naval aviation, aviation, as well as ancillary support, communications, training, and other fields. The strategic offensive role of a navy is Power projection, projection of force into areas beyond a country's shores (for example, to protect Sea lane, sea-lanes, deter or confront piracy, ferry troops, or attack other navies, ports, or shore installations). The strategic defensive purpose of a navy is to frustrate seaborne projection-of-force by enemies. The strategic task of the navy also may incorporate nuclear deterrence by use of submarine-launched ballistic missiles. Naval operations can be broa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |