|
BL 12-inch Mk I – VII Naval Gun
The BL 12 inch naval gun Mk I was a British rifled breech-loading naval gun of the early 1880s intended for the largest warships such as battleships and also coastal defence. It was Britain's first attempt to match the large guns being installed in rival European navies, particularly France, after Britain transitioned from rifled muzzle-loading guns to the modern rifled breech-loaders somewhat later than the European powers. Mks I - VIIMk I = Mark 1, Mk VII = Mark 7. Britain used Roman numerals to designate marks (i.e. models) of ordnance until after World War II. Hence this article describes the first seven models of British BL 12-inch guns all had a barrel of approximately 303 inches in length (25.25 calibres) and similar performance. Naval service Mk II was installed on battleships from 1882, and the coastal service ironclad . Mk II guns failed in service and were quickly replaced by Mks III. IV and V, with many changes and improvements. The later marks were also mounted on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Gun
Naval artillery is artillery mounted on a warship, originally used only for naval warfare and then subsequently used for naval gunfire support, shore bombardment and anti-aircraft roles. The term generally refers to tube-launched projectile-firing weapons and excludes self-propelled projectiles such as torpedoes, rockets, and missiles and those simply dropped overboard such as depth charges and naval mines. Origins The idea of ship-borne artillery dates back to the classical era. Julius Caesar indicates the use of ship-borne catapults against Britons ashore in his ''Commentarii de Bello Gallico''. The dromons of the Byzantine Empire carried catapults and Greek fire, fire-throwers. From the late Middle Ages onwards, warships began to carry cannon, cannons of various calibres. The Mongol invasion of Java introduced cannons to be used in naval warfare (e.g. Cetbang by the Majapahit). The Battle of Arnemuiden, fought between England and France in 1338 at the start of the Hundred Y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
No Man's Land Fort
No Man's Land Fort, also referred to as No Man's Fort, is a sea fort in the Solent, near Portsmouth, England. It is one of the Palmerston Forts built between 1867 and 1880 after the recommendations of the 1859 Royal Commission. It is 200 feet in diameter, and lies off the coast of the Isle of Wight. History The fort was designed by Captain E. H. Stewart, overseen by Assistant Inspector General of Fortifications, Colonel W. F. D. Jervois. Construction work began in 1865, and the fort was completed in 1880, long after the threat of a seaborne invasion from France had passed, at a cost of £462,500. A 2020 report stated that during the Second World War, "the forts were used to defend the Portsmouth dockyards. Life on site was grim; those serving were deliberately chosen for their inability to swim, to avoid any attempt to escape". No Man's Land Fort is almost identical to Horse Sand Fort. It has been used as a luxury home/hospitality centre for high-paying guests – due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
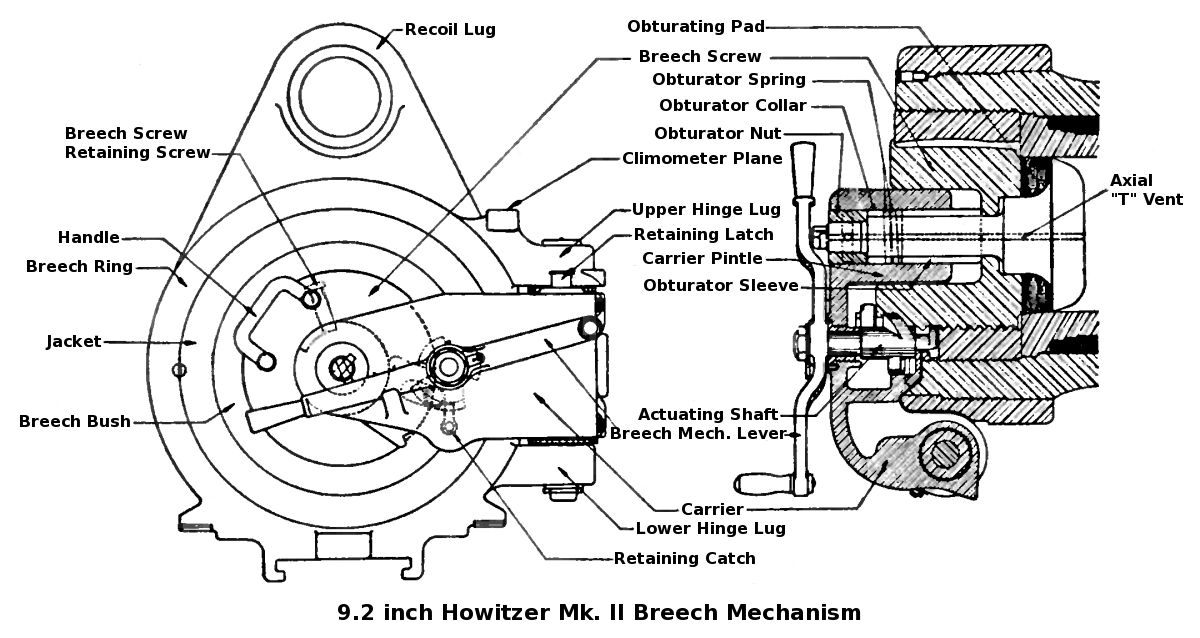
305 Mm Artillery
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious or cultural significance in many societies. Evolution of the Arabic digit The use of three lines to denote the number 3 occurred in many writing systems, including some (like Roman and Chinese numerals) that are still in use. That was also the original representation of 3 in the Brahmic (Indian) numerical notation, its earliest forms aligned vertically. However, during the Gupta Empire the sign was modified by the addition of a curve on each line. The Nāgarī script rotated the lines clockwise, so they appeared horizontally, and ended each line with a short downward stroke on the right. In cursive script, the three strokes were eventually connected to form a glyph resembling a with an additional stroke at the bottom: ३. The Indian digits spread to the Caliphate in the 9th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Guns Of The United Kingdom
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval warfare, naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral zone, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It includes anything conducted by surface Naval ship, ships, amphibious warfare, amphibious ships, submarines, and seaborne naval aviation, aviation, as well as ancillary support, communications, training, and other fields. The strategic offensive role of a navy is Power projection, projection of force into areas beyond a country's shores (for example, to protect Sea lane, sea-lanes, deter or confront piracy, ferry troops, or attack other navies, ports, or shore installations). The strategic defensive purpose of a navy is to frustrate seaborne projection-of-force by enemies. The strategic task of the navy also may incorporate nuclear deterrence by use of submarine-launched ballistic missiles. Naval operations can be broa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ian V
Ian or Iain is a name of Scottish Gaelic origin, derived from the Hebrew given name (Yohanan, ') and corresponding to the English name John. The spelling Ian is an Anglicization of the Scottish Gaelic forename ''Iain''. It is a popular name in Scotland, where it originated, as well as other English-speaking countries. The name has fallen out of the top 100 male baby names in the United Kingdom, having peaked in popularity as one of the top 10 names throughout the 1960s. In 1900, Ian was the 180th most popular male baby name in England and Wales. , the name has been in the top 100 in the United States every year since 1982, peaking at 65 in 2003. Other Gaelic forms of "John" include "Seonaidh" ("Johnny" from Lowland Scots), "Seon" (from English), "Seathan", and "Seán" and "Eoin" (from Irish). Its Welsh counterpart is Ioan, its Cornish equivalent is Yowan and Breton equivalent is Yann. Notable people named Ian As a first name (alphabetical by family name) *Ian Agol (born 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Naval Guns ...
List of Naval Guns by country of origin in decreasing caliber size List of naval guns by caliber size, all countries Naval anti-aircraft guns See also *List of artillery *List of the largest cannon by caliber *Glossary of British ordnance terms References {{reflist External links NAVWEAPS – Naval weapons of the world, 1880 to today(retrieved 2010-02-01) Naval A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval warfare, naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral zone, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palliser Shot
upPalliser shot, Mark I, for 9-inch Rifled Muzzle Loading (RML) gun Palliser shot is an early British armour-piercing artillery projectile, intended to pierce the armour protection of warships being developed in the second half of the 19th century. It was invented by Sir William Palliser, after whom it is named. History Major Palliser's shot, approved 21 October 1867, was an improvement over the ordinary elongated shot of the time. It was adopted for the larger types of rifled muzzle-loading guns rifled on the Woolwich principle (with three rifling grooves). Palliser shot in many calibers stayed in service in the armour-piercing role until phased out of (British) service in 1909 for naval and fortress use, and 1921 for land service. At the Battle of Angamos (8 October 1879) the Chilean ironclad warships fired twenty 250-pound Palliser gunshots against the Peruvian monitor ''Huáscar'', with devastating results. It was the first time that such piercing shells were used in act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse Sand Fort
Horse Sand Fort is one of the larger Royal Commission sea forts in the Solent off Portsmouth, Hampshire, England. The fort is one of four built as part of the Palmerston Forts constructions. It is across, built between 1865 and 1880, with two floors and a basement and armour-plated all round. History Horse Sand Fort was designed by Captain E. H. Stewart, overseen by Assistant Inspector General of Fortifications, Colonel W. F. D. Jervois. Construction work began in 1865, and the fort was completed in 1880, long after the threat of a seaborne invasion from France had passed, at a cost of £424,694. The original armament was to have been forty five 10-inch and 44 12.5-inch rifled muzzle-loading (RML) guns on the gun floors with 10 12-inch RMLs mounted on the roof in five turrets. In fact the turrets were never built and the limited space meant the 12.5-inch guns had to be operated with less than full charges of powder. In 1882, 12-inch rifled breech-loading guns were plac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spitbank Fort
Spitbank Fort or Spitsand Fort or Spit Sand Fort or simply Spit Fort is a sea fort built as a result of the 1859 Royal Commission. The fort is one of four built as part of the Palmerston Forts constructions. Located in the Solent, near Portsmouth, England, and is now a luxury hotel. History Active naval installation, 1878-1956 The four armour-plated forts were designed by Captain E. H. Stewart overseen by Assistant Inspector General of Fortifications, Colonel W. F. D. Jervois. Construction started in 1867, and was completed in 1878, at a cost of £167,300 STG. Spitbank is smaller than the two main Solent forts, Horse Sand Fort and No Man's Land Fort. Its main purpose was as a further line of defence for ships that made it past the two main forts. It is in diameter across at its base, with one floor and a basement and armour plating only on the seaward side. It was originally planned to have been armed with nine 10" 18-ton rifled muzzle loader (RML) guns on the seaward side ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coastal Gun
Coastal artillery is the branch of the armed forces concerned with operating anti-ship artillery or fixed gun batteries in coastal fortifications. From the Middle Ages until World War II, coastal artillery and naval artillery in the form of cannons were highly important to military affairs and generally represented the areas of highest technology and capital cost among materiel. The advent of 20th-century technologies, especially military aviation, naval aviation, jet aircraft, and guided missiles, reduced the primacy of cannons, battleships, and coastal artillery. In countries where coastal artillery has not been disbanded, these forces have acquired amphibious capabilities. In littoral warfare, mobile coastal artillery armed with surface-to-surface missiles can still be used to deny the use of sea lanes. It was long held as a rule of thumb that one shore-based gun equaled three naval guns of the same caliber, due to the steadiness of the coastal gun which allowed for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Numerals
Roman numerals are a numeral system that originated in ancient Rome and remained the usual way of writing numbers throughout Europe well into the Late Middle Ages. Numbers are written with combinations of letters from the Latin alphabet, each letter with a fixed integer value, modern style uses only these seven: The use of Roman numerals continued long after the decline of the Roman Empire. From the 14th century on, Roman numerals began to be replaced by Arabic numerals; however, this process was gradual, and the use of Roman numerals persists in some applications to this day. One place they are often seen is on clock faces. For instance, on the clock of Big Ben (designed in 1852), the hours from 1 to 12 are written as: The notations and can be read as "one less than five" (4) and "one less than ten" (9), although there is a tradition favouring representation of "4" as "" on Roman numeral clocks. Other common uses include year numbers on monuments and buildings and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Ordnance Terms
This article explains terms used for the British Armed Forces' ordnance (i.e.: weapons) and also ammunition. The terms may have slightly different meanings in the military of other countries. BD Between decks: applies to a naval gun mounting in which part of the rotating mass is below the deck, and part of it is above the deck. This allows for a lower profile of turret, meaning that turrets need not be superfiring (i.e. they can be mounted on the same deck and not obstruct each other at high angles of elevation.) BL The term BL, in its general sense, stood for breech loading, and contrasted with muzzle loading. The shell was loaded via the breech (i.e. the gunner's end of the barrel, which opened) followed by the propellant charge, and the breech mechanism was closed to seal the chamber. Breech loading, in its formal British ordnance sense, served to identify the gun as the type of rifled breechloading gun for which the powder charge was loaded in a silk or cloth bag and the br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |