|
BAT2
Large proline-rich protein BAT2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BAT2'' gene. Function A cluster of genes, BAT1-BAT5, has been localized in the vicinity of the genes for TNF alpha and TNF beta. These genes are all within the human major histocompatibility complex class III region. This gene has microsatellite repeats which are associated with the age-at-onset of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) and possibly thought to be involved with the inflammatory process of pancreatic beta-cell destruction during the development of IDDM. This gene is also a candidate gene for the development of rheumatoid arthritis. There are two alternatively spliced transcripts encoding different isoforms described for this gene. Interactions BAT2 has been shown to interact with: * C1QBP, * EIF3S6, * HNRNPA1, * IFT88, * IMMT, and * UBAP2L Ubiquitin-associated protein 2-like is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''UBAP2L'' gene. Interactions UBAP2L has been show ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EIF3S6
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 subunit E (eIF3e) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''EIF3E'' gene. Interactions EIF3S6 has been shown to interact with: * BAT2, * COPS6 * CSN3, * EIF3A Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 subunit A (eIF3a) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''EIF3A'' gene. It is one of the subunits of Eukaryotic initiation factor 3 (eIF3) a multiprotein complex playing major roles in translatio ..., and * TRIM27. See also * Eukaryotic initiation factor 3 (eIF3) References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-8-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C1QBP
Complement component 1 Q subcomponent-binding protein, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''C1QBP'' gene. The human complement subcomponent C1q associates with C1r and C1s in order to yield the first component of the serum complement system. The protein encoded by this gene is known to bind to the globular heads of C1q molecules and inhibit C1 activation. This protein has also been identified as the p32 subunit of pre-mRNA splicing factor SF2, as well as a hyaluronic acid-binding protein. Protein subunit C1QBP is 282 amino acid in length and has three homologous subunit with its N-terminal 73 amino acid residues cleaved off to produce mature C1QBP. C1QBP appears as a monomer around 33 kDa on SDS-PAGE gel under both reducing and nonreducing condition but migrates as a trimer on size-exclusion chromatography (gel filtration). Protein structure The crystal structure of C1QBP at 2.25 Å resolution shows a homotrimeric ring displaying symmetry. The individ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterogeneous Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein A1
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HNRNPA1'' gene. Mutations in hnRNP A1 are causative of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and the syndrome multisystem proteinopathy. Function This gene belongs to the A/B subfamily of ubiquitously expressed heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPs). The hnRNPs are RNA binding proteins and they complex with heterogeneous nuclear RNA (hnRNA). These proteins are associated with pre-mRNAs in the nucleus and appear to influence pre-mRNA processing and other aspects of mRNA metabolism and transport. While all of the hnRNPs are present in the nucleus, some seem to shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The hnRNP proteins have distinct nucleic acid binding properties. The protein encoded by this gene has two repeats of quasi-RRM domains that bind to RNAs in the N-terminal domain which are pivotal for RNA specificity and binding. The protein also has a glycine rich arginine-glyci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IFT88
Intraflagellar transport protein 88 homolog is a protein that is encoded by the ''IFT88'' gene. Function This gene encodes a member of the tetratrico peptide repeat (TPR) family. Mutations of a similar gene in mouse can cause polycystic kidney disease. Two transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been identified for this gene. In 2012 a mutation was found to be responsible for a novel form of ciliopathy and anosmia in humans capable of remedy in mice by adenoviral mediated gene therapy. Interactions IFT88 has been shown to interact with BAT2 and WDR62. WDR62 is required for IFT88 localization to the cilia basal body and the cilia axoneme An axoneme, also called an axial filament is the microtubule-based cytoskeletal structure that forms the core of a cilium or flagellum. Cilia and flagella are found on many cells, organisms, and microorganisms, to provide motility. The axo .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * {{ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IMMT
Mitochondrial inner membrane protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IMMT'' gene.) ''IMMT'' encodes an inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM) protein in the nucleus. It is posttranslational transported to the IMM. Mic60/Mitofilin (encoded by the ''IMMT'' gene) is a core subunit of the MICOS-complex, directly located next to cristae junctions (CJ). Human Mic60 exists in two isoforms of different size, anchored to the IMM via its N-terminus, while most of the protein is located to the inner mitochondrial space (IMS). Function Mic60 is evolutionary one of the oldest MICOS subunits as homologous were found in anaerobic prokaryotes. It is mainly present in two isoforms (ca. 88 and 90 kDa). In the brain, four isoforms are known, which differ in their isoelectric point due to different post-translational modifications. The amino terminus of Mic60 is anchored in the IM, while most of the protein is extended to the IMS. C-terminal Mic60 has a conserved mitofilin domain which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TNF Alpha
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF, cachexin, or cachectin; formerly known as tumor necrosis factor alpha or TNF-α) is an adipokine and a cytokine. TNF is a member of the TNF superfamily, which consists of various transmembrane proteins with a homologous TNF domain. As an adipokine, TNF promotes insulin resistance, and is associated with obesity-induced type 2 diabetes. As a cytokine, TNF is used by the immune system for cell signaling. If macrophages (certain white blood cells) detect an infection, they release TNF to alert other immune system cells as part of an inflammatory response. TNF signaling occurs through two receptors: TNFR1 and TNFR2. TNFR1 is constituitively expressed on most cell types, whereas TNFR2 is restricted primarily to endothelial, epithelial, and subsets of immune cells. TNFR1 signaling tends to be pro-inflammatory and apoptotic, whereas TNFR2 signaling is anti-inflammatory and promotes cell proliferation. Suppression of TNFR1 signaling has been important ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphotoxin
Lymphotoxin is a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily of cytokines, whose members are responsible for regulating the growth and function of lymphocytes and are expressed by a wide variety of cells in the body. Lymphotoxin plays a critical role in developing and preserving the framework of lymphoid organs and of gastrointestinal immune responses, as well as in the activation signaling of both the innate and adaptive immune responses. Lymphotoxin alpha (LT-α, previously known as TNF-beta) and lymphotoxin beta (LT-β), the two forms of lymphotoxin, each have distinctive structural characteristics and perform specific functions. Structure and function Each LT-α/LT-β subunit is a trimer and assembles into homotrimers or heterotrimers. LT-α binds with LT-β to form membrane-bound heterotrimers LT-α1-β2 and LT-α2-β1, which are commonly referred to as lymphotoxin beta. LT-α1-β2 is the most prevalent form of lymphotoxin beta. LT-α also forms a homotrimer, LT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
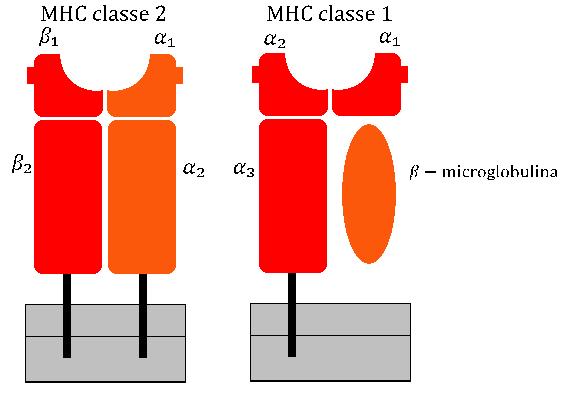
Major Histocompatibility Complex
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a large locus on vertebrate DNA containing a set of closely linked polymorphic genes that code for cell surface proteins essential for the adaptive immune system. These cell surface proteins are called MHC molecules. This locus got its name because it was discovered via the study of transplanted tissue compatibility. Later studies revealed that tissue rejection due to incompatibility is only a facet of the full function of MHC molecules: binding an antigen derived from self-proteins, or from pathogens, and bringing the antigen presentation to the cell surface for recognition by the appropriate T-cells. MHC molecules mediate the interactions of leukocytes, also called white blood cells (WBCs), with other leukocytes or with body cells. The MHC determines donor compatibility for organ transplant, as well as one's susceptibility to autoimmune diseases. In a cell, protein molecules of the host's own phenotype or of other biologic entities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes (T1D), formerly known as juvenile diabetes, is an autoimmune disease that originates when cells that make insulin (beta cells) are destroyed by the immune system. Insulin is a hormone required for the cells to use blood sugar for energy and it helps regulate glucose levels in the bloodstream. Before treatment this results in high blood sugar levels in the body. The common symptoms of this elevated blood sugar are frequent urination, increased thirst, increased hunger, weight loss, and other serious complications. Additional symptoms may include blurry vision, tiredness, and slow wound healing. Symptoms typically develop over a short period of time, often a matter of weeks. The cause of type 1 diabetes is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The underlying mechanism involves an autoimmune destruction of the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. Diabetes is diagnosed by testing the level of sugar or gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |