|
B330
The B330 (previously known as the Nautilus space complex module and BA 330) was an inflatable space habitat being privately developed by Bigelow Aerospace from 2010 until 2020. The design was evolved from NASA's TransHab habitat concept. B330 will have of internal volume, hence its numeric designation. The craft is intended to support zero-gravity research including scientific missions and manufacturing processes. Beyond its industrial and scientific purposes, however, it has potential as a destination for space tourism and a craft for missions destined for the Moon and Mars. Several test articles were built and tested in various conditions in ground test facilities, but no flight versions were built. Features Compared to their volume-mass ratio, expandable modules offer more living space than traditional rigid modules. For example, the pressurised volume of a B330 module is , compared to of the 15-tonne ISS Destiny module. Thus B330 offers 210% more habitable space, wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bigelow Aerospace
Bigelow Aerospace is an American aeronautics and outer space technology company which manufactures and develops expandable space station modules. Bigelow Aerospace was founded by Robert Bigelow in 1998, and is based in North Las Vegas, Nevada. It is funded in large part by the profit Bigelow gained through his ownership of the hotel chain, Budget Suites of America. By 2013, Bigelow had invested US$250 million in the company. Bigelow stated on a number of occasions that he was prepared to fund Bigelow Aerospace with about US$500 million through 2015 in order to achieve launch of full-scale hardware. Bigelow Aerospace announced in 2010 that they intended to create a modular set of space habitats for creating or expanding space stations but despite many concepts and models, never completed a working space station beyond two small prototypes that flew in 2006 and 2007. In March 2020, the company laid off all 88 of its employees due to the COVID-19 pandemic, and planned to rehire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflatable Space Habitat
Inflatable habitats or expandable habitats are pressurized tent-like structures capable of supporting life in outer space whose internal volume increases after launch. They have frequently been proposed for use in space applications to provide a greater volume of living space for a given mass. The first formal design and manufacture of an inflatable space habitat was in 1961 with a space station design produced by Goodyear (although this design was never flown). A proposal released in 1989 by Johnson Space Center's Man Systems Division outlined a diameter spherical habitat lunar outpost which was partially buried in the lunar surface. An inflatable module called TransHab (a portmanteau of ''Trans Habitation'') was proposed for the International Space Station, and later the private company Bigelow Aerospace revived the design for use in a number of potential civil and commercial applications. Construction The construction of an inflatable space habitat is determined by its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Tourism
Space tourism is human space travel for recreational purposes. There are several different types of space tourism, including orbital, suborbital and lunar space tourism. During the period from 2001 to 2009, seven space tourists made eight space flights aboard a Russian Soyuz spacecraft to the International Space Station, brokered by Space Adventures in conjunction with Roscosmos and RSC Energia. The publicized price was in the range of US$20–25 million per trip. Some space tourists have signed contracts with third parties to conduct certain research activities while in orbit. By 2007, space tourism was thought to be one of the earliest markets that would emerge for commercial spaceflight. Russia halted orbital space tourism in 2010 due to the increase in the International Space Station crew size, using the seats for expedition crews that would previously have been sold to paying spaceflight participants. Orbital tourist flights were set to resume in 2015 but the planned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA (Japan), ESA (Europe), and CSA (Canada). The ownership and use of the space station is established by intergovernmental treaties and agreements. The station serves as a microgravity and space environment research laboratory in which scientific research is conducted in astrobiology, astronomy, meteorology, physics, and other fields. The ISS is suited for testing the spacecraft systems and equipment required for possible future long-duration missions to the Moon and Mars. The ISS programme evolved from the Space Station ''Freedom'', a 1984 American proposal to construct a permanently crewed Earth-orbiting station, and the contemporaneous Soviet/Russian '' Mir-2'' proposal from 1976 with similar aims. The ISS is the ninth space station to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orion Spacecraft
Orion (officially Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle or Orion MPCV) is a Reusable spacecraft, partially reusable crewed spacecraft used in NASA's Artemis program. The spacecraft consists of a Crew Module (CM) space capsule designed by Lockheed Martin and the European Service Module (ESM) manufactured by Airbus Defence and Space. Capable of supporting a crew of six beyond low Earth orbit, Orion can last up to 21 days undocked and up to six months docked. It is equipped with Solar panels on spacecraft, solar panels, an NASA Docking System, automated docking system, and glass cockpit interfaces modeled after those used in the Boeing 787 Dreamliner. A single AJ10 engine provides the spacecraft's primary propulsion, while eight R-4D, R-4D-11 engines, and six pods of custom reaction control system engines developed by Airbus, provide the spacecraft's secondary propulsion. Although compatible with other launch vehicles, Orion is primarily intended to launch atop a Space Launch System (S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Docking And Berthing Of Spacecraft
Docking and berthing of spacecraft is the joining of two space vehicles. This connection can be temporary, or partially permanent such as for space station modules. ''Docking'' specifically refers to joining of two separate free-flying space vehicles. ''Berthing'' refers to mating operations where a passive module/vehicle is placed into the mating interface of another space vehicle by using a robotic arm. Because the modern process of un-berthing requires more crew labor and is time-consuming, berthing operations are unsuited for rapid crew evacuations in the event of an emergency. History Docking Spacecraft docking capability depends on space rendezvous, the ability of two spacecraft to find each other and station-keep in the same orbit. This was first developed by the United States for Project Gemini. It was planned for the crew of Gemini 6 to rendezvous and manually dock under the command of Wally Schirra, with an uncrewed Agena Target Vehicle in October 1965, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Maneuver
In spaceflight, an orbital maneuver (otherwise known as a burn) is the use of propulsion systems to change the orbit of a spacecraft. For spacecraft far from Earth (for example those in orbits around the Sun) an orbital maneuver is called a ''deep-space maneuver (DSM)''. The rest of the flight, especially in a transfer orbit, is called ''coasting''. General Rocket equation The Tsiolkovsky rocket equation, or ideal rocket equation is an equation that is useful for considering vehicles that follow the basic principle of a rocket: where a device that can apply acceleration to itself (a thrust) by expelling part of its mass with high speed and moving due to the conservation of momentum. Specifically, it is a mathematical equation that relates the delta-v (the maximum change of speed of the rocket if no other external forces act) with the effective exhaust velocity and the initial and final mass of a rocket (or other reaction engine.) For any such maneuver (or journey involvin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
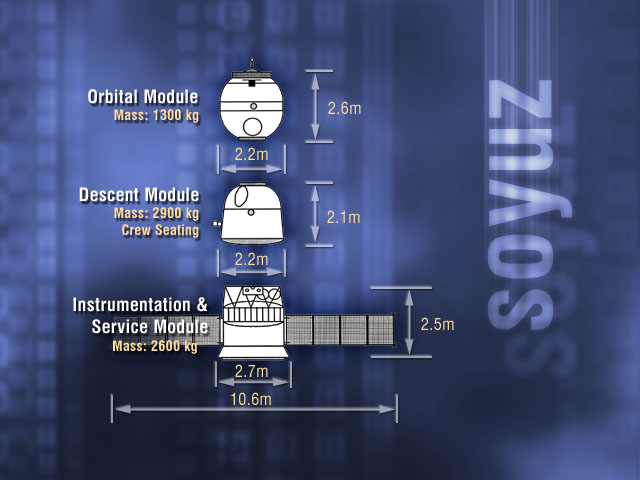
Soyuz Spacecraft
Soyuz () is a series of spacecraft which has been in service since the 1960s, having made more than 140 flights. It was designed for the Soviet space program by the Korolev Design Bureau (now Energia). The Soyuz succeeded the Voskhod spacecraft and was originally built as part of the Soviet crewed lunar programs. It is launched on a Soyuz rocket from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Between the 2011 retirement of the Space Shuttle and the 2020 demo flight of SpaceX Crew Dragon, the Soyuz served as the only means to ferry crew to or from the International Space Station, for which it remains heavily used. Although China did launch crewed Shenzhou flights during this time, none of them docked with the ISS. History The first Soyuz flight was uncrewed and started on 28 November 1966. The first Soyuz mission with a crew, Soyuz 1, launched on 23 April 1967 but ended with a crash due to a parachute failure, killing cosmonaut Vladimir Komarov. The following flight was uncrew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dragon V2
Dragon 2 is a class of partially reusable spacecraft developed and manufactured by American aerospace manufacturer SpaceX, primarily for flights to the International Space Station (ISS). SpaceX has also launched private missions such as Inspiration4 and Axiom Mission 1. There are two variants: Crew Dragon, a spacecraft capable of ferrying four crew, and Cargo Dragon, an updated replacement for the original Dragon 1. The spacecraft consists of a reuseable space capsule and an expendable trunk module. The spacecraft launches atop a Falcon 9 Block 5 rocket and the capsule returns to Earth via splashdown. Cargo Dragon supplies cargo to the ISS under a Commercial Resupply Services-2 contract with NASA. The first flight of Dragon 2 in a cargo configuration launched in December 2020. It shares this duty with Northrop Grumman Innovation Systems' Cygnus spacecraft, and Sierra Nevada Corporation's Dream Chaser spacecraft is expected to join them . , Crew Dragon is the only U.S. hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
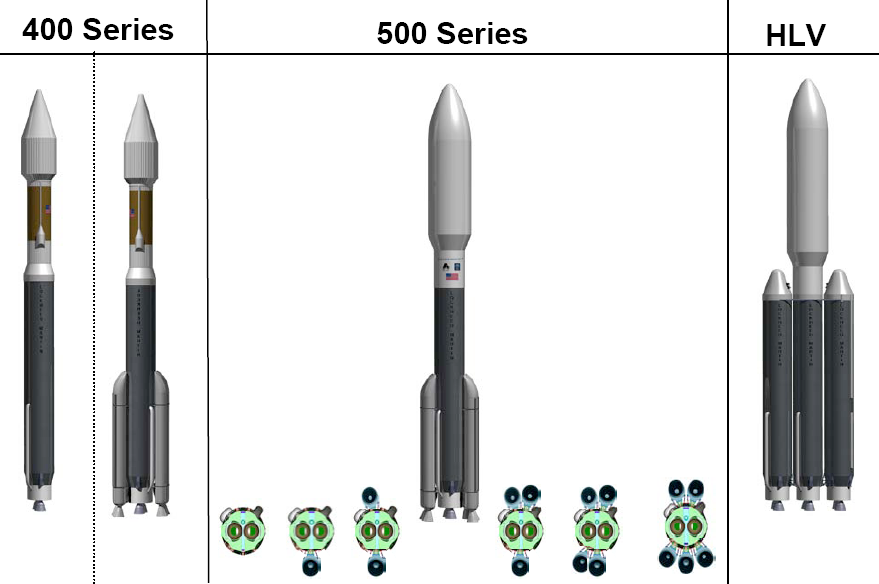
Atlas V
Atlas V is an expendable launch system and the fifth major version in the Atlas (rocket family), Atlas launch vehicle family. It was originally designed by Lockheed Martin, now being operated by United Launch Alliance (ULA), a joint venture between Lockheed Martin and Boeing. Atlas V is also a major NASA launch vehicle. It is America's longest-serving active rocket. In August 2021, ULA announced that Atlas V would be retired, and all 29 remaining launches had been sold. , 19 launches remain. Each Atlas V launch vehicle consists of two main stages. The first stage (rocketry), first stage is powered by a Russian RD-180 engine manufactured by NPO Energomash, Energomash and burning kerosene and liquid oxygen. The Centaur (rocket stage), Centaur upper stage is powered by one or two American RL10 engine(s) manufactured by Aerojet Rocketdyne and burns liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen. The Star 48 upper stage was used on the ''New Horizons'' mission as a third stage. strap-on booster, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
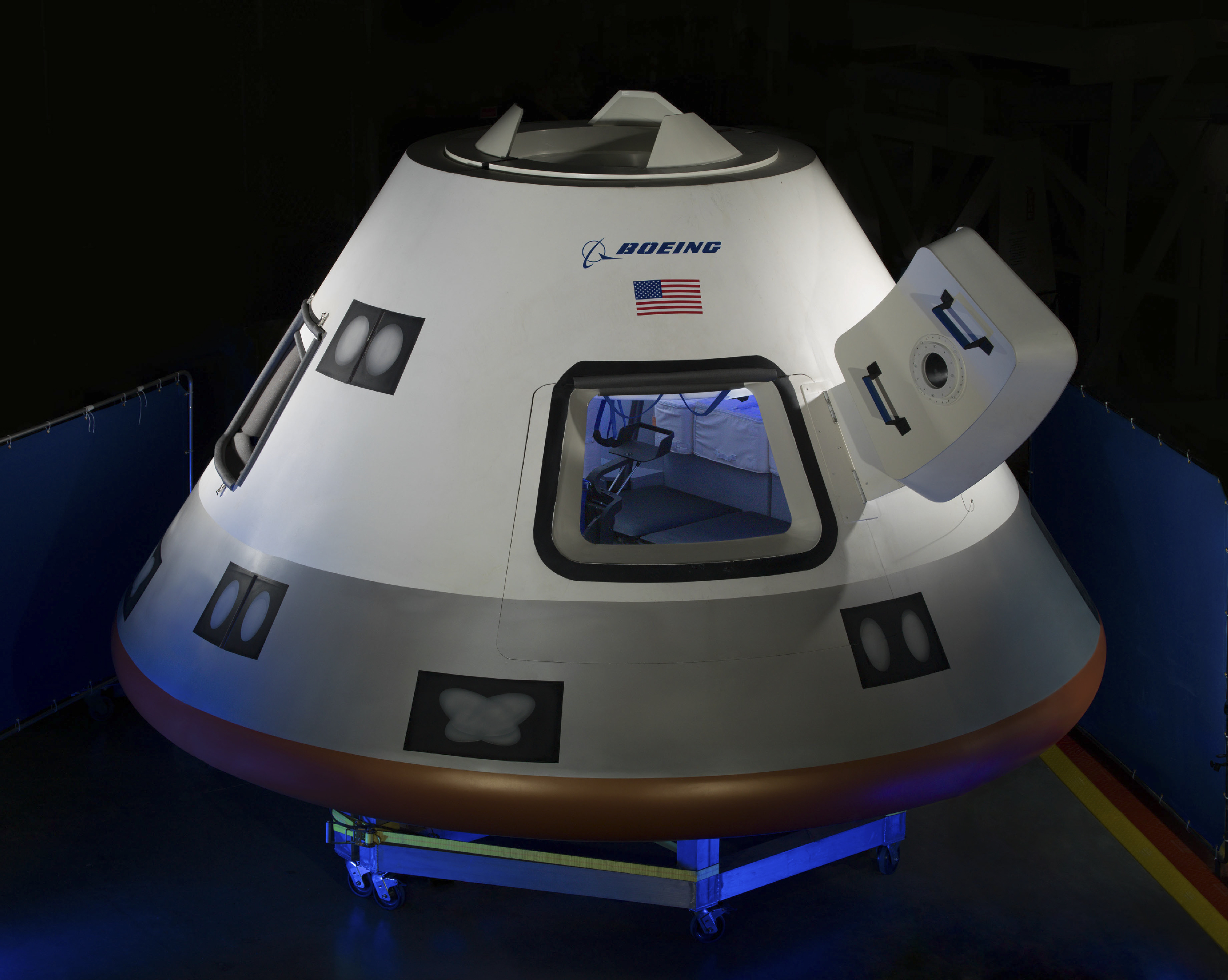
CST-100 Starliner
The Boeing CST-100 Starliner is a class of two partially designed to transport crew to the (ISS) and other low-Earth-orbit destinations. It is manufactured by for its participation in 's |
Spacecraft Propulsion
Spacecraft propulsion is any method used to accelerate spacecraft and artificial satellites. In-space propulsion exclusively deals with propulsion systems used in the vacuum of space and should not be confused with space launch or atmospheric entry. Several methods of pragmatic spacecraft propulsion have been developed each having its own drawbacks and advantages. Most satellites have simple reliable chemical thrusters (often monopropellant rockets) or resistojet rockets for orbital station-keeping and some use momentum wheels for attitude control. Soviet bloc satellites have used electric propulsion for decades, and newer Western geo-orbiting spacecraft are starting to use them for north–south station-keeping and orbit raising. Interplanetary vehicles mostly use chemical rockets as well, although a few have used ion thrusters and Hall-effect thrusters (two different types of electric propulsion) to great success. Hypothetical in-space propulsion technologies describe the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |