|
Buried Rupture Earthquake
In seismology, a buried rupture earthquake, or blind earthquake, is an earthquake which does not produce a visible offset in the ground along the fault (as opposed to a surface rupture earthquake, which does). When the fault in question is a thrust fault, the earthquake is known as a blind thrust earthquake. Ground motion Recorded ground motions of large surface-rupture earthquakes are weaker than the ground motions from buried rupture earthquakes. Depth The asperity for a buried rupture earthquakes is in area deeper than roughly . Examples are the Loma Prieta earthquake, Northridge earthquake, and the Noto Hanto earthquake. Tsunamis As compared to the seabed surface rupture case, uplifted water outside the fault plane in buried rupture earthquakes makes for large tsunami waves. See also * Aseismic creep In geology, aseismic creep or fault creep is measurable surface displacement along a fault in the absence of notable earthquakes. Aseismic creep may also occur as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaiser Permanente Building After Northridge Earthquake
''Kaiser'' is the German word for "emperor" (female Kaiserin). In general, the German title in principle applies to rulers anywhere in the world above the rank of king (''König''). In English, the (untranslated) word ''Kaiser'' is mainly applied to the emperors of the unified German Empire (1871–1918) and the emperors of the Austrian Empire (1804–1918). During the First World War, anti-German sentiment was at its zenith; the term ''Kaiser''—especially as applied to Wilhelm II, German Emperor—thus gained considerable negative connotations in English-speaking countries. Especially in Central Europe, between northern Italy and southern Poland, between western Austria and western Ukraine and in Bavaria, Emperor Franz Joseph I is still associated with "Der Kaiser (the emperor)" today. As a result of his long reign from 1848 to 1916 and the associated Golden Age before the First World War, this title often has still a very high historical respect in this geographical area. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loma Prieta Earthquake
The 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake occurred on California's Central Coast on October 17 at local time. The shock was centered in The Forest of Nisene Marks State Park in Santa Cruz County, approximately northeast of Santa Cruz on a section of the San Andreas Fault System and was named for the nearby Loma Prieta Peak in the Santa Cruz Mountains. With an magnitude of 6.9 and a maximum Modified Mercalli intensity of IX (''Violent''), the shock was responsible for 63 deaths and 3,757 injuries. The Loma Prieta segment of the San Andreas Fault System had been relatively inactive since the 1906 San Francisco earthquake (to the degree that it was designated a seismic gap) until two moderate foreshocks occurred in June 1988 and again in August 1989. Damage was heavy in Santa Cruz County and less so to the south in Monterey County, but effects extended well to the north into the San Francisco Bay Area, both on the San Francisco Peninsula and across the bay in Oakland. No surface faulting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buried Rupture Earthquakes
In seismology, a buried rupture earthquake, or blind earthquake, is an earthquake which does not produce a visible offset in the ground along the fault (as opposed to a surface rupture earthquake, which does). When the fault in question is a thrust fault, the earthquake is known as a blind thrust earthquake. Ground motion Recorded ground motions of large surface-rupture earthquakes are weaker than the ground motions from buried rupture earthquakes. Depth The asperity for a buried rupture earthquakes is in area deeper than roughly . Examples are the Loma Prieta earthquake, Northridge earthquake, and the Noto Hanto earthquake. Tsunamis As compared to the seabed surface rupture case, uplifted water outside the fault plane in buried rupture earthquakes makes for large tsunami waves. See also * Aseismic creep In geology, aseismic creep or fault creep is measurable surface displacement along a fault in the absence of notable earthquakes. Aseismic creep may also occur as "aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aseismic Creep
In geology, aseismic creep or fault creep is measurable surface displacement along a fault in the absence of notable earthquakes. Aseismic creep may also occur as "after-slip" days to years after an earthquake. Notable examples of aseismic slip include faults in California (e.g. Calaveras Fault, Hayward Fault, and San Andreas Fault). Causes Aseismic creep accommodates far-field motions on localized zones of deformation at tectonic plate boundaries. The underlying causes of aseismic creep are primarily attributed to poor frictional strength of the fault, low normal stress acting on the fault in the shallow crust, and excessive pore-fluid pressures, which limit the viable amount of normal stress on a fault. The frictional reaction of geologic materials can explain the transition from seismic to aseismic deformation with depth. Friction along faults can cause sudden slips with associated stress drops (earthquakes), along with phases of no motion as stress recharges. Measurements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
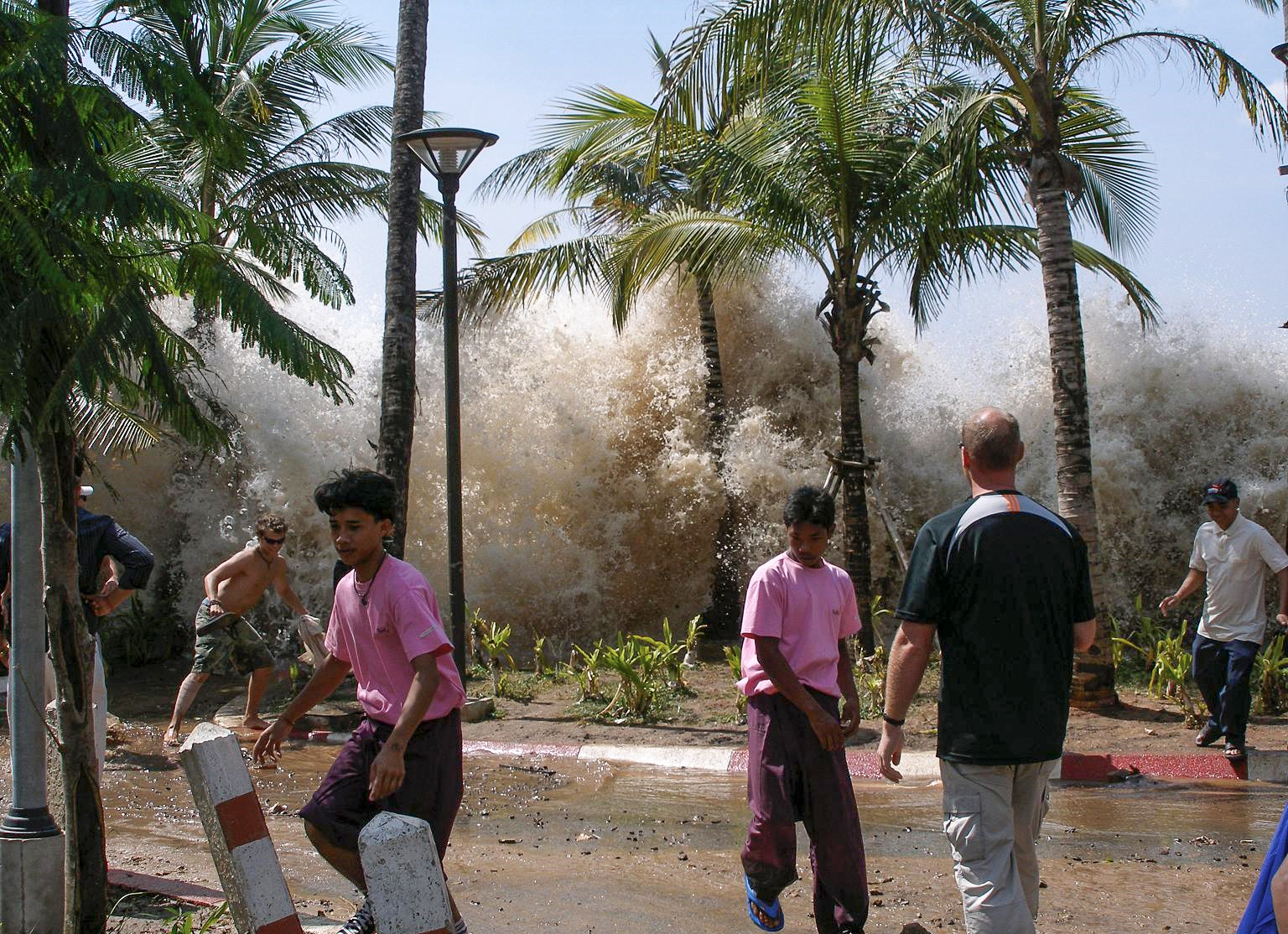
Tsunami Waves
A tsunami ( ; from ja, 津波, lit=harbour wave, ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater explosions (including detonations, landslides, glacier calvings, meteorite impacts and other disturbances) above or below water all have the potential to generate a tsunami. Unlike normal ocean waves, which are generated by wind, or tides, which are in turn generated by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun, a tsunami is generated by the displacement of water from a large event. Tsunami waves do not resemble normal undersea currents or sea waves because their wavelength is far longer. Rather than appearing as a breaking wave, a tsunami may instead initially resemble a rapidly rising tide. For this reason, it is often referred to as a tidal wave, although this usage is not favoured by the scientific community because it might give ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Rupture
In seismology, surface rupture (or ground rupture, or ground displacement) is the visible offset of the ground surface when an earthquake rupture along a fault affects the Earth's surface. Surface rupture is opposed by buried rupture, where there is no displacement at ground level. This is a major risk to any structure that is built across a fault zone that may be active, in addition to any risk from ground shaking. Surface rupture entails vertical or horizontal movement, on either side of a ruptured fault. Surface rupture can affect large areas of land. __TOC__ Lack of surface rupture Not every earthquake results in surface rupture, particularly for smaller and deeper earthquakes. In some cases, however, the lack of surface effects is because the fault that moved does not reach the surface. For example, the 1994 Northridge earthquake had a moment magnitude of 6.7, caused major damage in the Los Angeles area, occurred at below the Earth's surface, but did not cause surface ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
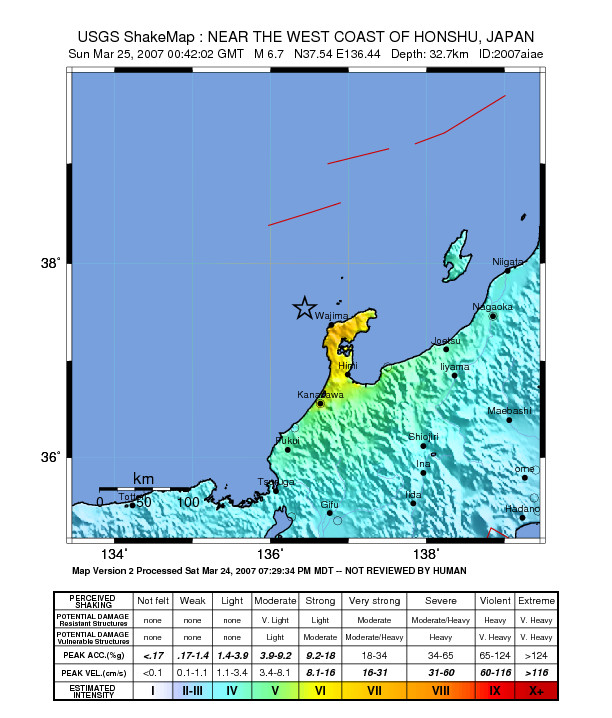
Noto Hanto Earthquake
The occurred on March 25, 2007, in the Hokuriku region of Japan. Overview At 9:41:58 a.m. on March 25, 2007, a magnitude 6.9 earthquake struck the Hokuriku region of Japan, near the Noto Peninsula. The earthquake shook the city of Wajima, the city of Nanao, and the town of Anamizu with a seismic intensity of 6+ on Japan's ''shindo'' scale.http://www.seisvol.kishou.go.jp/cgi-tmp/shindo_db/27680.html One death, in the city of Wajima, and at least 356 injuries have been reported. Geology This earthquake was the result of oblique-slip faulting. According to the Geospatial Information Authority of Japan, the fault was 21 km long, 14 km wide and shifted 1.4 m. By using sound waves, the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology also found a fault 18~ km long that is supposed to have caused this earthquake. This earthquake was an intraplate earthquake that occurred within the Eurasia Plate, near the boundary with the North American Pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northridge Earthquake
The 1994 Northridge earthquake was a moment 6.7 (), blind thrust earthquake that occurred on January 17, 1994, at 4:30:55 a.m. PST in the San Fernando Valley region of the City of Los Angeles. The quake had a duration of approximately 10–20 seconds, and its peak ground acceleration of 1.82 ''g'' was the highest ever instrumentally recorded in an urban area in North America. Shaking was felt as far away as San Diego, Turlock, Las Vegas, Richfield, Phoenix and Ensenada. The peak ground velocity at the Rinaldi Receiving Station was , the fastest ever recorded. Two 6.0 aftershocks followed, the first about one minute after the initial event and the second approximately 11 hours later, the strongest of several thousand aftershocks in all. The death toll was 57, with more than 9,000 injured. In addition, property damage was estimated to be $13–50 billion (equivalent to $24–93 billion in 2021), making it one of the costliest natural disasters in U.S. history. Epi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asperity (faults)
An asperity is an area on an active fault where there is increased friction, such that the fault may become locked, rather than continuously slipping as in aseismic creep. Earthquake rupture generally begins with the failure of an asperity, allowing the fault to move. See also * Asperity (materials science) * Asperity (geotechnical engineering) * Earthquake * Fault friction * Fault mechanics Fault mechanics is a field of study that investigates the behavior of geologic faults. Behind every good earthquake is some weak rock. Whether the rock remains weak becomes an important point in determining the potential for bigger earthquakes. ... References External links IRIS page on fault asperities with simple cartoon video of an asperity on an active faultIRIS page on "Modeling Asperities on a Strike-Slip Fault with Spaghetti" {{geology-stub Seismology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismology
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other planet-like bodies. It also includes studies of earthquake environmental effects such as tsunamis as well as diverse seismic sources such as volcanic, tectonic, glacial, fluvial, oceanic, atmospheric, and artificial processes such as explosions. A related field that uses geology to infer information regarding past earthquakes is paleoseismology. A recording of Earth motion as a function of time is called a seismogram. A seismologist is a scientist who does research in seismology. History Scholarly interest in earthquakes can be traced back to antiquity. Early speculations on the natural causes of earthquakes were included in the writings of Thales of Miletus (c. 585 BCE), Anaximenes of Miletus (c. 550 BCE), Aristotle (c. 340 BCE), and Zha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground Motion
Ground motion is the movement of the earth's surface from earthquakes or explosions. Ground motion is produced by seismic waves that are generated by sudden slip on a fault or sudden pressure at the explosive source and travel through the earth and along its surface. This can be due to natural events, such as earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, or human activities, such as the detonation of nuclear weapons. There are two main types of seismic waves: body waves and surface waves. Body waves travel through the interior of the earth, while surface waves travel along the earth's surface. Ground motion is typically caused by surface waves, which are the most destructive type of seismic waves. Ground motion is measured using a seismometer, a device that detects and records the movement of the earth's surface. Seismometers are used by seismologists to study earthquakes and other types of ground motion. The recordings produced by a seismometer are known as seismograms, and they can be use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
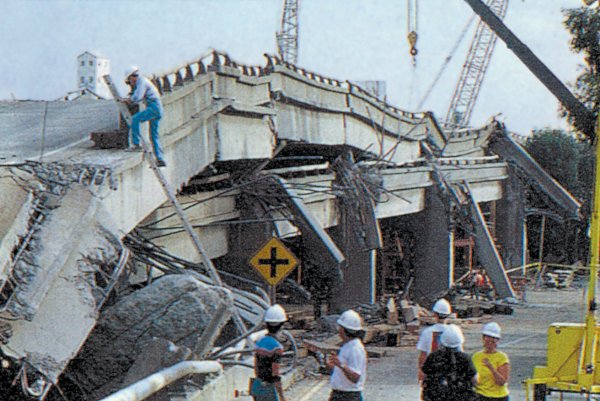
Cypress Collapsed
Cypress is a common name for various coniferous trees or shrubs of northern temperate regions that belong to the family Cupressaceae. The word ''cypress'' is derived from Old French ''cipres'', which was imported from Latin ''cypressus'', the latinisation of the Greek κυπάρισσος (''kyparissos''). Cypress trees are a large classification of conifers, encompassing the trees and shrubs from the cypress family (Cupressaceae) and many others with the word “cypress” in their common name. Many cypress trees have needle-like, evergreen foliage and acorn-like seed cones. Species Species that are commonly known as cypresses include: Most prominently: *Cypress (multiple species within the genus '' Cupressus'') Otherwise: *African cypress (''Widdringtonia'' species), native to Southern Africa *Bald, Pond, and Montezuma cypresses (''Taxodium'' species), native to North America *Chinese swamp cypress (''Glyptostrobus pensilis''), Vietnam, critically endangered *Cordilleran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |