|
Bund Family Of Wick Episcopi
The Bund (later Willis-Bund, later MacCarthy-Willis-Bund) family of Wick Episcopi owned estates in Worcestershire since the fifteenth century; from this armigerous landed gentry family came (and allied to which through marriage were) several individuals of note in the fields of law, local government and literature. History According to the 1925 edition of Burke's Landed Gentry, the earliest mention of the family in current registries is dated 18 January 1559, this being the marriage of Edward Frenche and Jane Bund. At that time the family held the property at Wick that they were still recorded as holding in the twentieth century.Burke's Landed Gentry 14th ed. (reprint of 1921 ed.), ed. A. Winton Thorpe, 1925, p. 238, 'Willis-Bund of Wick Episcopi' pedigree The Bund family were however known to have been landowners in the area since at least 1457. Alongside their property at Wick Episcopi, the Bund family held land at Upper Wick, Laughern Grove (later 'Bunde Grove'; previously pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rushwick
Rushwick is a village and civil parish in the Malvern Hills District in the county of Worcestershire, England. It is situated to the west of Worcester, Rushwick Parish comprises the four villages and hamlets of Broadmore Green, Crown East, Rushwick village and Upper Wick. The River Teme forms the southern boundary of the parish, and the Worcester to Hereford railway line passes through the village. The area of the parish is . In the 2011 census, the population of the parish was 1,155. Rushwick village has been circumvented by the Western By-pass, reducing through traffic, making it much quieter compared with previous times. It has one pub inside the village, and one on the outskirts. An organic meat and vegetable shop can be found in the south of the village. There is also a preschool and a primary school. The parish church, dedicated to St Thomas, was originally built as a private chapel in the 1840s, but was rebuilt on the main Bromyard road, in the village of Crown East, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedgeberrow
Sedgeberrow is a village and civil parish in the Wychavon district of Worcestershire, England, about south of Evesham. It stands beside the River Isbourne, a tributary of the River Avon. History The Toponymy has evolved through forms including ''Secgesbearawe'' in the 10th century, ''Seggesbereg'' or ''Shegeberwe'' in the 13th century and ''Seggeberugh'' in the 14th century. Other forms of the name from different periods are cited in the course of the history of the manor.A History of the County of Worcester: Volume 3, pp. 518-521 Sedgeberrow is an ancient manor. In AD 777 King Offa of Mercia granted ''Segcgesbearuue'' or ''Secgesbearuue'' to King Ealdred, of Hwicce, which was part of the Kingdom of Mercia. Ealdred in turn granted Sedgeberrow to the Bishop of Worcester. In 1086 the Domesday Book recorded that ''Seggesbarwe'' was held by the monks of Worcester Priory. In 1539-40 the Crown dissolved the Priory and in 1542 it granted ''Segebarowe'' to the Dean and Chapter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goldington
Goldington is an electoral ward within the town of Bedford, Bedfordshire, England. It encompasses much of the historic village and parish of Goldington that was merged with Bedford in 1934, although some parts of the old village are within the neighbouring Newnham ward. It also includes two modern estates that are part of Renhold Parish. The boundaries of Goldington are approximately The Spires and Aspire estates to the north, Norse Road to the east, Goldington Road to the south, with Church Lane and Bow Hill to the west. The northern part of the area is sometimes known as Elms Farm. History Goldington was a village which grew up along the old A428 road between Bedford and Cambridge. St Mary's Church in Goldington has parish registers going back to 1559. In August 1645 Major Walter Baskerville, a Royalist cavalry Officer, was killed in a skirmish in Goldington. Goldington Hall (a small mansion) was built in the 1650s. The Hall was rebuilt in 1874. In 1934 the southern part o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
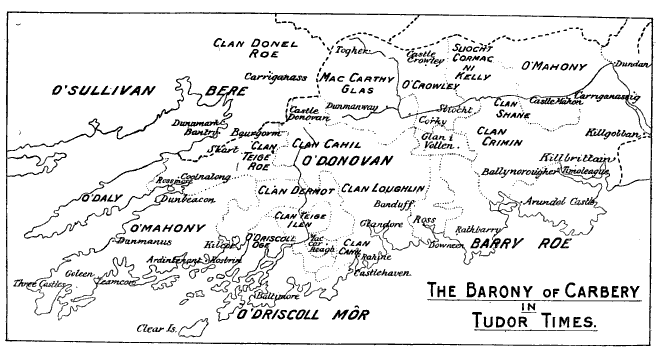
MacCarthy Reagh
The Mac Cárthaigh Riabhach (anglicised ''MacCarthy Reagh'') dynasty are a branch of the MacCarthy dynasty, Kings of Desmond, deriving from the Eóganacht Chaisil sept. History The Mac Cárthaigh Riabhach seated themselves as kings of Carbery in what is now southwestern County Cork including Rosscarbery in the 13th century.Butler, "The Barony of Carbery" Their primary allies in the initially small territory itself were O'Donovans, and members of the Ui Chairpre; both were recent arrivals, gaining their lands from the O'Mahonys of Eóganacht Raithlind and the O'Driscolls of Corcu Loígde. The historical record for this period is very confused and a precise sequence of events cannot be reconstructed. A portion of Carbery was conquered around 1232 by Donal Gott MacCarthy, King of Desmond, from whom the dynasty descend. His son Donal Maol Mac Carthaigh, was the first ruler of the new principality. Their descendants would expand their territories considerably and forge a small, wealthy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tideford
Tideford (; kw, Resteudhi) is a small village in east Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is twinned with Plouguerneau in Brittany, France. Its name derives from its location on the River Tiddy, literally meaning "Ford on the River Tiddy". Tideford is not listed in the Domesday Book but the earliest settlement is thought to have been around 1100AD. The bridge over the River Tiddy at the bottom of Bridge Road dates from the 14th century and this is the earliest surviving structure. Tideford grew in the eighteenth century as the nearby Port Eliot country estate built a number of houses in the village. Many of these have now been sold, but of note is 'Bridge House', located at the bottom of Bridge Road, which remains a gatehouse onto the estate. The village is on the busy A38 between Saltash and Liskeard, one of two main road routes into Cornwall (the other being the A30 which runs into north Cornwall). Tideford does not have a railway station, the nearest being at St Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
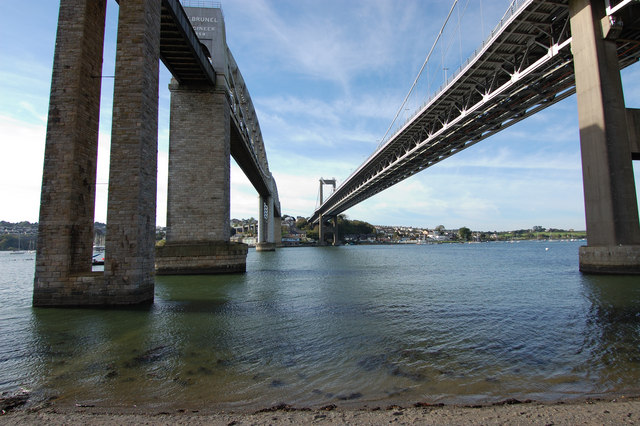
Saltash
Saltash (Cornish: Essa) is a town and civil parish in south Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It had a population of 16,184 in 2011 census. Saltash faces the city of Plymouth over the River Tamar and is popularly known as "the Gateway to Cornwall". Saltash’s landmarks include the Tamar Bridge which connects Plymouth to Cornwall by road, and the Royal Albert Bridge. The area of Latchbrook is part of the town. Description Saltash is the location of Isambard Kingdom Brunel's Royal Albert Bridge, opened by Prince Albert on 2 May 1859. It takes the railway line across the River Tamar. Alongside it is the Tamar Bridge, a toll bridge carrying the A38 trunk road, which in 2001 became the first suspension bridge to be widened whilst remaining open to traffic. Saltash railway station, which has a regular train service, with some routes between London Paddington station is close to the town centre. Stagecoach South West, Plymouth Citybus, and Go Cornwall Bus operate bus service ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Milward & Sons
Henry Milward & Sons is an English manufacturer of sewing needles based in Redditch. Henry Milward and Sons and its employees boast over a quarter of a millennium making needles. History The earliest reference to the Milward family in connection with needle making is a James Milward who was a needle maker on Fish Hill in 1676. Symon Milward created the company of Henry Milward & Sons aka Milward's Needles (Milward's) in 1730 at the age of 40, in Redditch, United Kingdom. It was however, his son Henry who takes credit for the foundation of the company as the company was registered in his name during the first year of his birth. ee Redditch Museum Family tree From the first half of the 18th century, the name of Henry Milward and Sons became well known as the makers of good quality needles. At one point they were the largest manufacturer of its type in the world, producing knitting needles, surgical needles, and fishing tackle, from a number of factories both in the UK and globa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
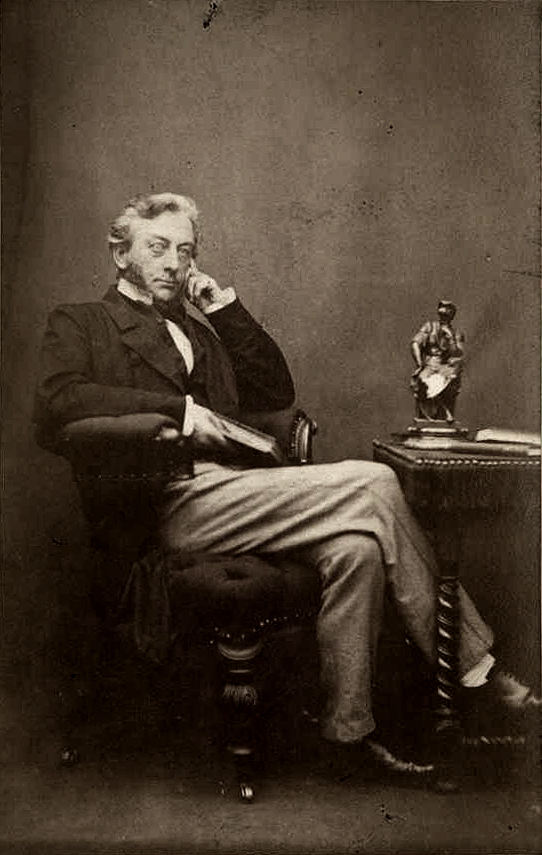
John William Willis-Bund
John William Bund Willis-Bund (8 August 1843 – 7 June 1928) was a British lawyer, legal writer and professor of constitutional law and history at King's College London, a historian who wrote on the Welsh church and other subjects, and a local Worcestershire politician. An electronic version of a publication by the Honourable Society of Cymmrodorion Biography Willis-Bund was born in 1843 at sea, his parents returning from his father's judicial posting in Australia. He was baptized at Bahia, South America.The Times, 9 January 1928, p. 19Biographical History of Gonville and Caius College 1349-1897 vol. II 1713-1897, John Venn, Cambridge University Press/ C. J. Clay and Sons, 1898, pg 354 He was the son of John Walpole Willis and his second wife Ann Susanna Kent Bund, of Wick Episcopi, Worcestershire. The adoption of his mother's surname (in 1864) was necessary in order to succeed his maternal grandfather as heir to the Bund family's Worcestershire properties. He was educated at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jure Uxoris
''Jure uxoris'' (a Latin phrase meaning "by right of (his) wife"), citing . describes a title of nobility used by a man because his wife holds the office or title ''suo jure'' ("in her own right"). Similarly, the husband of an heiress could become the legal possessor of her lands. For example, married women in England and Wales were legally incapable of owning real estate until the Married Women's Property Act 1882. Kings who ruled ''jure uxoris'' were regarded as co-rulers with their wives and are not to be confused with king consort, who were merely consorts of their wives. Middle Ages During the feudal era, the husband's control over his wife's real property, including titles, was substantial. On marriage, the husband gained the right to possess his wife's land during the marriage, including any acquired after the marriage. Whilst he did not gain the formal legal title to the lands, he was able to spend the rents and profits of the land and sell his right, even if the wife pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Walpole Willis
John Walpole Willis (4 January 1793 – 10 September 1877) was a British judge of Upper Canada, British Guiana (as acting Chief Justice), the Supreme Court of New South Wales, and resident judge at Port Phillip, Melbourne. Early life The second son of Captain William Willis (of the 13th Light Dragoons) and his wife Mary Hamilton Smyth (of the family of the Viscounts Strangford), Willis was born at Holyhead, Anglesey, where his father was stationed. He was a descendant of the Willises of Suffolk and Cambridgeshire – from whom descended the Willys baronets of Fen Ditton – through his grandfather, Joseph Willis of Wakefield, Yorkshire, where the family had been settled since the seventeenth century. Willis was educated at Rugby (alongside his elder brother, William Downes Willis), Charterhouse (whence he was expelled for taking a leading part in a school rebellion alongside a fellow student, Wood), and as a fellow-commoner at Trinity Hall, Cambridge, where he took an MA. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assizes
The courts of assize, or assizes (), were periodic courts held around England and Wales until 1972, when together with the quarter sessions they were abolished by the Courts Act 1971 and replaced by a single permanent Crown Court. The assizes exercised both civil and criminal jurisdiction, though most of their work was on the criminal side. The assizes heard the most serious cases, which were committed to it by the quarter sessions (local county courts held four times per year), while the more minor offences were dealt with summarily by justices of the peace in petty sessions (also known as magistrates' courts). The word ''assize'' refers to the sittings or sessions (Old French ''assises'') of the judges, known as "justices of assize", who were judges who travelled across the seven circuits of England and Wales on commissions of "oyer and terminer", setting up court and summoning juries at the various assize towns. Etymology Middle English < |
Inner Temple
The Honourable Society of the Inner Temple, commonly known as the Inner Temple, is one of the four Inns of Court and is a professional associations for barristers and judges. To be called to the Bar and practise as a barrister in England and Wales, a person must belong to one of these Inns. It is located in the wider Temple area, near the Royal Courts of Justice, and within the City of London. The Inn is a professional body that provides legal training, selection, and regulation for members. It is ruled by a governing council called "Parliament", made up of the Masters of the Bench (or "Benchers"), and led by the Treasurer, who is elected to serve a one-year term. The Temple takes its name from the Knights Templar, who originally (until their abolition in 1312) leased the land to the Temple's inhabitants (Templars). The Inner Temple was a distinct society from at least 1388, although as with all the Inns of Court its precise date of founding is not known. After a disrupted early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |