|
Built-in Test Equipment
Built-in test equipment (BITE) for avionics primarily refers to passive fault management and diagnosis equipment built into airborne systems to support maintenance processes. Built-in test equipment includes multimeter A multimeter (also known as a multi-tester, volt-ohm-milliammeter, volt-ohmmeter or VOM, avometer or ampere-volt-ohmmeter) is a measuring instrument that can measure multiple electrical properties. A typical multimeter can measure voltage, elec ...s, oscilloscopes, discharge probes, and frequency generators that are provided as part of the system to enable testing and perform diagnostics. The acronym BIT is often used for this same function or, more specifically, in reference to the individual tests. BIT often includes: * The detection of the fault * The accommodation of the fault (how the system actively responds to the fault) * The annunciation or logging of the fault to warn of possible effects and/or aid in troubleshooting the faulty equipment. Functiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avionics
Avionics (a portmanteau of ''aviation'' and ''electronics'') are the Electronics, electronic systems used on aircraft. Avionic systems include communications, Air navigation, navigation, the display and management of multiple systems, and the hundreds of systems that are fitted to aircraft to perform individual functions. These can be as simple as a searchlight for a police helicopter or as complicated as the tactical system for an airborne early warning platform. History The term "avionics" was coined in 1949 by Philip J. Klass, senior editor at ''Aviation Week & Space Technology'' magazine as a portmanteau of "aviation electronics". Radio communication was first used in aircraft just prior to World War I. The first Airborne radio relay, airborne radios were in zeppelins, but the military sparked development of light radio sets that could be carried by heavier-than-air craft, so that aerial reconnaissance biplanes could report their observations immediately in case they we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fault Management
In network management, fault management is the set of functions that detect, isolate, and correct malfunctions in a telecommunications network, compensate for environmental changes, and include maintaining and examining error logs, accepting and acting on error detection notifications, tracing and identifying faults, carrying out sequences of diagnostics tests, correcting faults, reporting error conditions, and localizing and tracing faults by examining and manipulating database information. When a fault or event occurs, a network component will often send a notification to the network operator using a protocol such as SNMP. An alarm is a persistent indication of a fault that clears only when the triggering condition has been resolved. A current list of problems occurring on the network component is often kept in the form of an active alarm list such as is defined in RFC 3877, the Alarm MIB. A list of cleared faults is also maintained by most network management systems. Fault m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
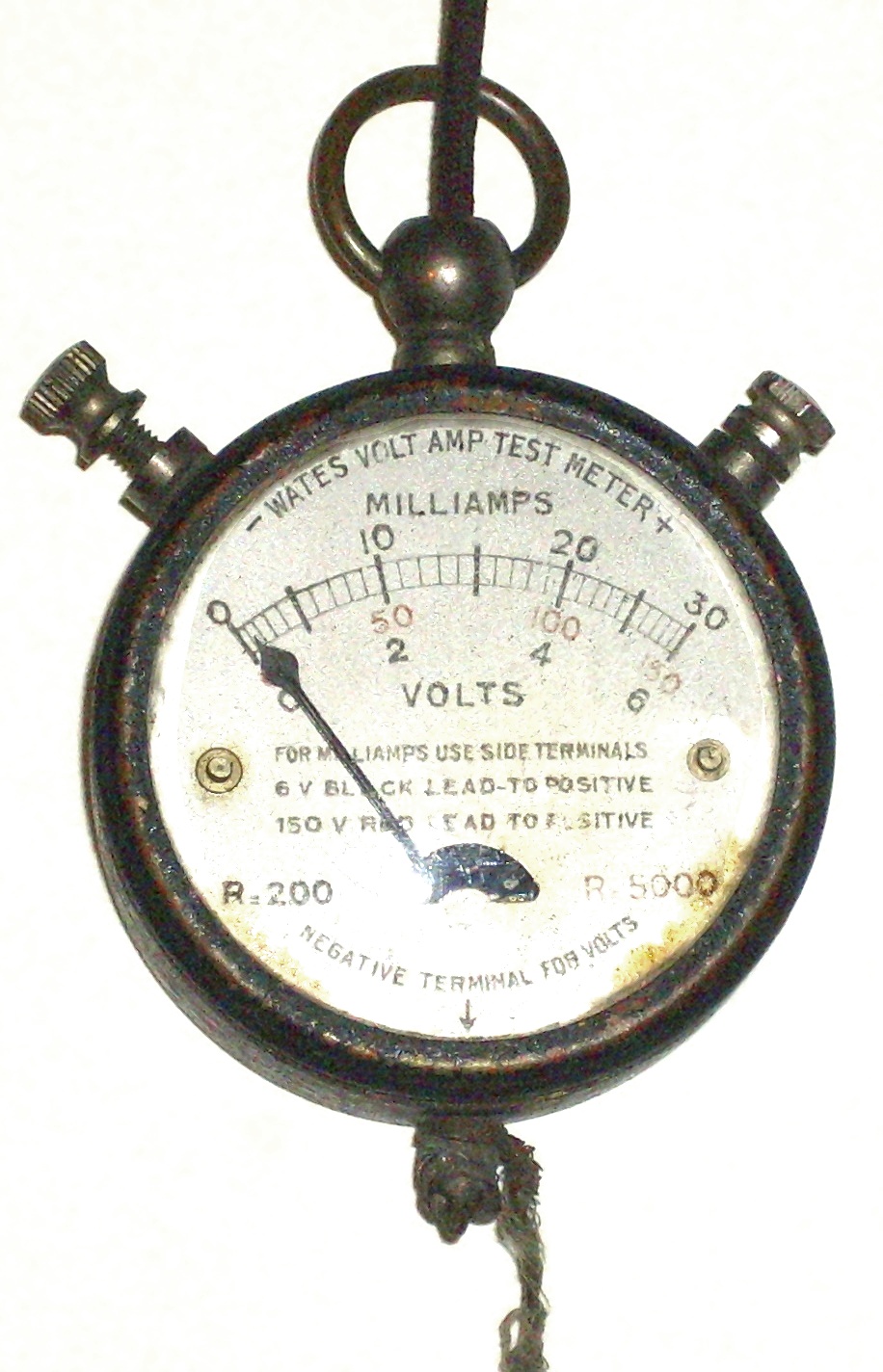
Multimeter
A multimeter (also known as a multi-tester, volt-ohm-milliammeter, volt-ohmmeter or VOM, avometer or ampere-volt-ohmmeter) is a measuring instrument that can measure multiple electrical properties. A typical multimeter can measure voltage, electrical resistance, resistance, and electric current, current, in which case can be used as a voltmeter, ohmmeter, and ammeter. Some feature the measurement of additional properties such as temperature and capacitance. Analog multimeters use a microammeter with a moving pointer to display readings. Digital multimeters (DMMs) have numeric displays and are more precise than analog multimeters as a result. Meters will typically include probes that temporarily connect the instrument to the device or circuit under test, and offer some intrinsic safety features to protect the operator if the instrument is connected to high voltages that exceed its measurement capabilities. Multimeters vary in size, features, and price. They can be portable handh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oscilloscope
An oscilloscope (formerly known as an oscillograph, informally scope or O-scope) is a type of electronic test instrument that graphically displays varying voltages of one or more signals as a function of time. Their main purpose is capturing information on electrical signals for debugging, analysis, or characterization. The displayed waveform can then be analyzed for properties such as amplitude, frequency, rise time, time interval, distortion, and others. Originally, calculation of these values required manually measuring the waveform against the scales built into the screen of the instrument. Modern digital instruments may calculate and display these properties directly. Oscilloscopes are used in the sciences, engineering, biomedical, automotive and the telecommunications industry. General-purpose instruments are used for maintenance of electronic equipment and laboratory work. Special-purpose oscilloscopes may be used to analyze an automotive ignition system or to display th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
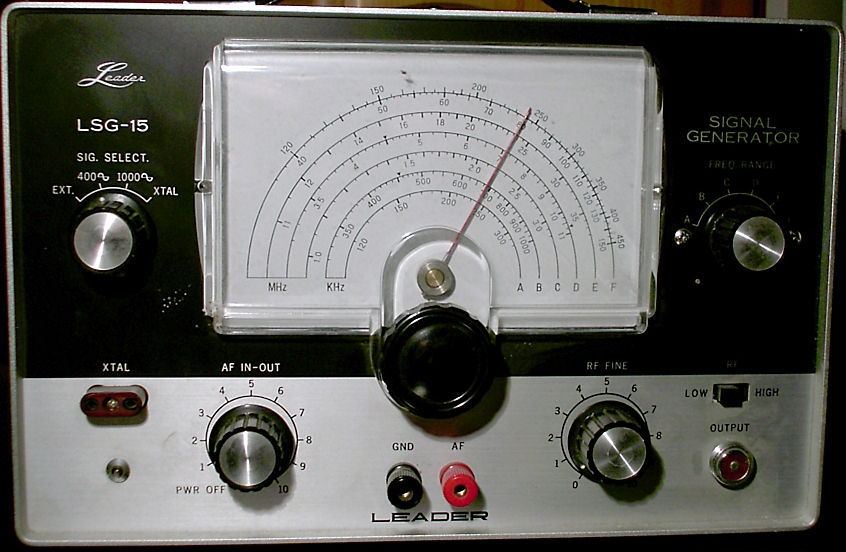
Frequency Generator
A signal generator is one of a class of electronic devices that generates electrical signals with set properties of amplitude, frequency, and wave shape. These generated signals are used as a stimulus for electronic measurements, typically used in designing, testing, troubleshooting, and repairing electronic or electroacoustic devices, though it often has artistic uses as well. There are many different types of signal generators with different purposes and applications and at varying levels of expense. These types include function generators, RF and microwave signal generators, pitch generators, arbitrary waveform generators, digital pattern generators, and frequency generators. In general, no device is suitable for all possible applications. A signal generator may be as simple as an oscillator with calibrated frequency and amplitude. More general-purpose signal generators allow control of all the characteristics of a signal. Modern general-purpose signal generators will have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Built-in Self-test
A built-in self-test (BIST) or built-in test (BIT) is a mechanism that permits a machine to test itself. Engineers design BISTs to meet requirements such as: *high reliability *lower repair cycle times or constraints such as: *limited technician accessibility *cost of testing during manufacture The main purpose of BIST is to reduce the complexity, and thereby decrease the cost and reduce reliance upon external (pattern-programmed) test equipment. BIST reduces cost in two ways: # reduces test-cycle duration # reduces the complexity of the test/probe setup, by reducing the number of I/O signals that must be driven/examined under tester control. Both lead to a reduction in hourly charges for automated test equipment (ATE) service. Applications BIST is commonly placed in weapons, avionics, medical devices, automotive electronics, complex machinery of all types, unattended machinery of all types, and integrated circuits. Automotive Automotive tests itself to enhance safety ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logic Built-in Self-test
Logic built-in self-test (or LBIST) is a form of built-in self-test (BIST) in which hardware and/or software is built into integrated circuits allowing them to test their own operation, as opposed to reliance on external automated test equipment. Advantages The main advantage of LBIST is the ability to test internal circuits having no direct connections to external pins, and thus unreachable by external automated test equipment. Another advantage is the ability to trigger the LBIST of an integrated circuit while running a built-in self test or power-on self test of the finished product. Disadvantages LBIST that requires additional circuitry (or read-only memory) increases the cost of the integrated circuit. LBIST that only requires temporary changes to programmable logic or rewritable memory avoids this extra cost, but requires more time to first program in the BIST and then to remove it and program in the final configuration. Another disadvantage of LBIST is the possibility tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Fault Tolerance
Software fault tolerance is the ability of computer software to continue its normal operation despite the presence of system or hardware faults. Fault-tolerant software has the ability to satisfy requirements despite failures. Following design patterns should be combined together to make the system more fault tolerant: retry, fallback, timeout, circuit breaker, and bulkhead pattern. To make your system more fault tolerant, you should measure 99th percentile latency and keep the remaining 1% (aka tail latencies) in check through self healing mechanisms. Introduction The only thing constant is change. This is certainly more true of software systems than almost any phenomenon, not all software change in the same way so software fault tolerance methods are designed to overcome execution errors by modifying variable values to create an acceptable program state.Ray Giguette and Johnette Hassell, “Toward A Resourceful Method of Software Fault Tolerance”, ACM Southeast regional co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Test Equipment
Test equipment is a general term describing equipment used in many fields. Types of test equipment include: Electrical and electronic test equipment Electrical test equipment * Battery tester, used to test the state of an electric battery * Continuity tester, used to determine if an electrical path can be established between two points ** Cable tester, used to verify the electrical connections in a signal cable or other wired assembly ** Receptacle tester, used to verify that an AC wall outlet is wired properly **Test light A test light, test lamp, voltage tester, or mains tester is a piece of electronic test equipment used to determine the presence of electricity in a piece of equipment under test. A test light is simpler and less costly than a measuring instrumen ..., used to determine the presence or absence of an electric voltage * Hipot tester, used to verify electrical insulation in finished products carrying high electrical potential Electronic test equipment {{see also, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |