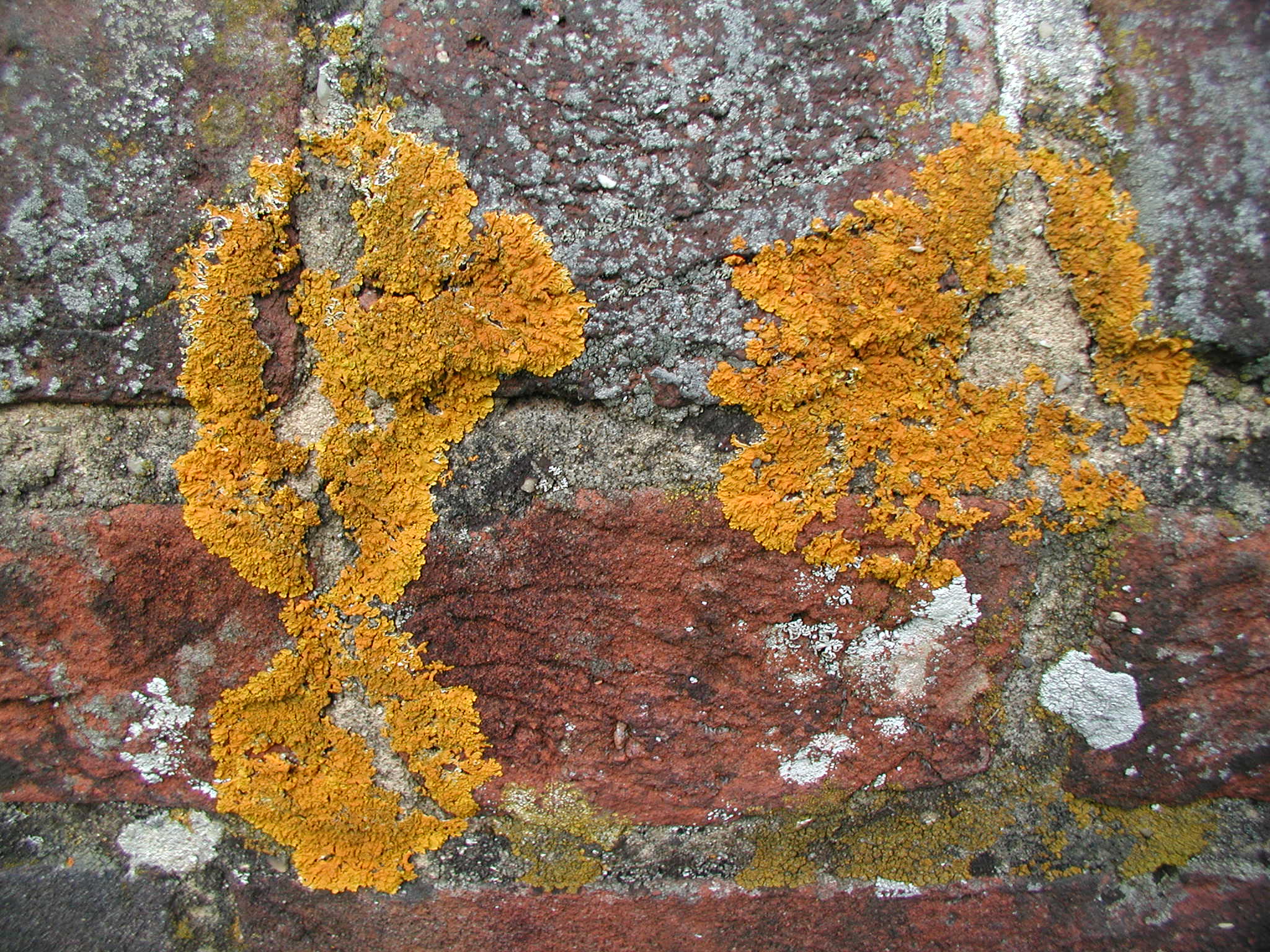|
Buellia Dispersa
''Buellia dispersa'' is a dull white to beige or dark brown crustose areolate lichen that grows on non-calcareous rock, such as basalt, granite and gneiss, in arid to semi-arid areas of northern Africa, Europe, and southwestern North America.Lichen Flora of the Greater Sonoran Desert Region; Nash, T.H., Ryan, B.D., Gries, C., Bugartz, F., (eds.), 2001, Vol 3/ref>Buellia dispersa in the Joshua Tree National Park (California, U.S.A.) Map collection; Kerry Knudsen, Kocourková Jana; Czech University of Life Sciences Prague, Faculty of Environmental Sciences, Department of Ecology, Czech Republic, 2012/ref> The areolas are distinct, becoming subsquamulose (lifting up at the edges) when separated and collecting in irregular patches, otherwise they form Rosette (botany), rosettes with lobed margins. There is no prothallus. It commonly occurs in the Mojave Desert, Channel Islands, and Santa Monica Mountains, also in the Cuyamaca Mountains, Santa Ana Mountains, and San Jacinto Mountains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustose Lichen
Crustose lichens are lichens that form a crust which strongly adheres to the Substrate (biology), substrate (soil, rock, tree bark, etc.), making separation from the substrate impossible without destruction. The basic structure of crustose lichens consists of a cortex (botany), cortex layer, an algal layer, and a medulla. The upper cortex layer is differentiated and is usually pigmented. The algal layer lies beneath the cortex. The medulla fastens the lichen to the substrate and is made up of Fungus, fungal hyphae. The surface of crustose lichens is characterized by branching cracks that periodically close in response to climatic variations such as alternate wetting and drying regimes. Subtypes * Powdery – considered as the simplest subtype due to the absence of an organized thallus. :The thallus appears powdery. :E.g. Genera ''Lepraria'', ''Vezdaea'' * Endolithic – grows inside the rock, usually in interstitial spaces between mineral grains. The :upper cortex is usually d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Monica Mountains
The Santa Monica Mountains is a coastal mountain range in Southern California, next to the Pacific Ocean. It is part of the Transverse Ranges. Because of its proximity to densely populated regions, it is one of the most visited natural areas in California. The Santa Monica Mountains National Recreation Area encompasses this mountain range. Geography The range extends approximately east-west from the Hollywood Hills in Los Angeles to Point Mugu in Ventura County. The western mountains, separating the Conejo Valley from Malibu, suddenly end at Mugu Peak as the rugged, nearly impassible shoreline gives way to tidal lagoons and coastal sand dunes of the alluvial Oxnard Plain. The mountain range contributed to the isolation of this vast coastal plain before regular transportation routes reached western Ventura County. The eastern mountains form a barrier between the San Fernando Valley and the Los Angeles Basin, separating "the Valley" on the north and west-central Los Angeles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lichens Of North America
Irwin M. Brodo (born 1935) is an emeritus scientist at the Canadian Museum of Nature, in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. He is an authority on the identification and biology of lichens. Irwin Brodo was honored in 1994 with an Acharius Medal presented to him by the International Association for Lichenology. Brodo did his undergraduate studies at Columbia University, and received a master's degree from Cornell University. He earned a Ph.D. in lichenology under the supervision of Henry Imshaug at Michigan State University. He later went on to teach at Université Laval and the University of Alaska, and he also supervised master's students at the University of Ottawa and Carleton University. Brodo's list of publications includes 75 research papers, 8 popular articles, 22 reviews and 6 editorials and obituaries. In 1993, Brodie was awarded the Mary E. Elliot Service Award for his meritorious service to the Canadian Botanical Association. One of Irwin Brodo's great achievements was the public ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lichens Of Europe
A lichen ( , ) is a composite organism that arises from algae or cyanobacteria living among filaments of multiple fungi species in a mutualistic relationship.Introduction to Lichens – An Alliance between Kingdoms . University of California Museum of Paleontology. Lichens have properties different from those of their component organisms. They come in many colors, sizes, and forms and are sometimes plant-like, but are not s. They may have tiny, leafless branches (); flat leaf-like structures ( |
Lichens Of Africa
A lichen ( , ) is a composite organism that arises from algae or cyanobacteria living among filaments of multiple fungi species in a mutualistic relationship.Introduction to Lichens – An Alliance between Kingdoms . University of California Museum of Paleontology. Lichens have properties different from those of their component organisms. They come in many colors, sizes, and forms and are sometimes plant-like, but are not s. They may have tiny, leafless branches (); flat leaf-like structures ( |
Lichen Species
A lichen ( , ) is a composite organism that arises from algae or cyanobacteria living among filaments of multiple fungi species in a mutualistic relationship.Introduction to Lichens – An Alliance between Kingdoms . University of California Museum of Paleontology. Lichens have properties different from those of their component organisms. They come in many colors, sizes, and forms and are sometimes plant-like, but are not s. They may have tiny, leafless branches (); flat leaf-like structures ( |
Buellia
''Buellia'' is a genus of mostly lichen-forming fungi in the family Caliciaceae. The fungi are usually part of a crustose lichen. In this case, the lichen species is given the same name as the fungus. But members may also grow as parasites on lichens (lichenicolous). The algae in the lichen (the photobiont partner) is always a member of the genus ''Trebouxia''. Lichens in the genus are commonly called disc lichens, or button lichens.Field Guide to California Lichens, Stephen Sharnoff, Yale University Press, 2014, The genus has a widespread distribution and contains about 450 species. Genetic studies indicate that the genus ''Amandinea'' and ''Buellia'' may be the same,Scheidegger, C. 2009. Amandinea Choisy ex Scheid. & H. Mayrhofer (1993). In: C. W. Smith, A. Aptroot, B. J. Coppins, A. Fletcher, O. L. Gilbert, P. W. James and P. A. Wosley (eds.) The Lichens of Great Britain and Ireland. The British Lichen Society, Natural History Museum Publications, United Kingdom, pp. 142– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Buellia Species
This is a list of species in the predominantly crustose lichen genus ''Buellia''. They are commonly known as "button lichens" due to the characteristic shape of their apothecia. A 2020 estimate placed about 300 species in the genus. , Species Fungorum accepts 201 species (including 9 varieties) in ''Buellia''. A *'' Buellia adjuncta'' *'' Buellia aequata'' *'' Buellia aeruginascens'' *'' Buellia aeruginosa'' – Australia *'' Buellia aethalea'' *'' Buellia akatorensis'' – New Zealand *'' Buellia albulella'' – Australia *'' Buellia alectorialica'' – New Zealand *''Buellia amandineiformis'' – Australia *'' Buellia amblyogona'' *'' Buellia arborea'' *'' Buellia arenaria'' *''Buellia arnoldii'' *''Buellia asterella'' *''Buellia atroflavella'' *''Buellia austera'' – Australia *''Buellia austroabstracta'' – Australia *''Buellia austroalpina'' – Australia B *''Buellia badia'' *''Buellia billewersii'' – New Zealand *''Buellia bogongensis'' – A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonoran Desert
The Sonoran Desert ( es, Desierto de Sonora) is a desert in North America and ecoregion that covers the northwestern Mexican states of Sonora, Baja California, and Baja California Sur, as well as part of the southwestern United States (in Arizona and California). It is the hottest desert in both Mexico and the United States. It has an area of . In phytogeography, the Sonoran Desert is within the Sonoran Floristic province of the Madrean Region of southwestern North America, part of the Holarctic realm of the northern Western Hemisphere. The desert contains a variety of unique endemic plants and animals, notably, the saguaro (''Carnegiea gigantea'') and organ pipe cactus (''Stenocereus thurberi''). The Sonoran Desert is clearly distinct from nearby deserts (e.g., the Great Basin, Mojave, and Chihuahuan deserts) because it provides subtropical warmth in winter and two seasons of rainfall (in contrast, for example, to the Mojave's dry summers and cold winters). This creates an ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Jacinto Mountains
The San Jacinto Mountains (''Avii Hanupach''Munro, P., et al. ''A Mojave Dictionary''. Los Angeles: UCLA. 1992. in Mojave) are a mountain range in Riverside County, located east of Los Angeles in southern California in the United States. The mountains are named for one of the first Black Friars, Saint Hyacinth (San Jacinto in Spanish), who is a popular patron in Latin America. Geography The range extends for approximately from the San Bernardino Mountains southeast to the Santa Rosa Mountains. The San Jacinto Mountains are the northernmost of the Peninsular Ranges, which run from Southern California to the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula. The highest peak in the range is San Jacinto Peak (3,302 m; 10,834 ft), and the range is also a Great Basin Divide landform for the Salton Watershed to the east. The Coachella Valley stretches along the eastern side of the range, including the cities of Palm Springs and Rancho Mirage. San Gorgonio Pass separates th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Ana Mountains
The Santa Ana Mountains are a short peninsular mountain range along the coast of Southern California in the United States. They extend for approximately southeast of the Los Angeles Basin largely along the border between Orange and Riverside counties. Geography and climate Peaks and boundaries The range starts in the north at the Whittier Fault and Santa Ana Canyon, through which the Santa Ana River flows. To the north of the canyon are the smaller Chino Hills in Los Angeles and San Bernardino counties. The northernmost summit of the Santa Anas, at , is Sierra Peak. From there, the major summits are Pleasants Peak, ; Bedford Peak, ; and Bald Peak, . The next two peaks, Modjeska, ; and Santiago, , the highest summit in the range; form Saddleback Ridge. Saddleback, located approximately 20 mi (32 km) east of Santa Ana, is visible from much of Southern California. South of Saddleback are Trabuco Peak, ; Los Pinos Peak, and Sitton Peak, . Elsinore Peak, is incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuyamaca Mountains
The Cuyamaca Mountains ( Kumeyaay: ''‘Ekwiiyemak''), locally the Cuyamacas, are a mountain range of the Peninsular Ranges System, in San Diego County, southern California. The mountain range runs roughly northwest to southeast. The Laguna Mountains are directly adjacent to the east, with Palomar Mountain and Hot Springs Mountain more distant to the north. Most of the range consists of extensive oak forest and chaparral, part of the California montane chaparral and woodlands ecoregion, interspersed with pine forests and lush riparian zones, featuring year round creeks and waterfalls. The San Diego River and Sweetwater River both have their headwaters in these mountains, which flow over 50 miles to the ocean. The pine forests were extensively burned by the 2003 Cedar Fire, along with many large areas of chaparral and oak woodland, which has since experienced slow and steady regrowth. The high elevation results in snowfall throughout the winter months. Cuyamaca Peak, at , is San ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |