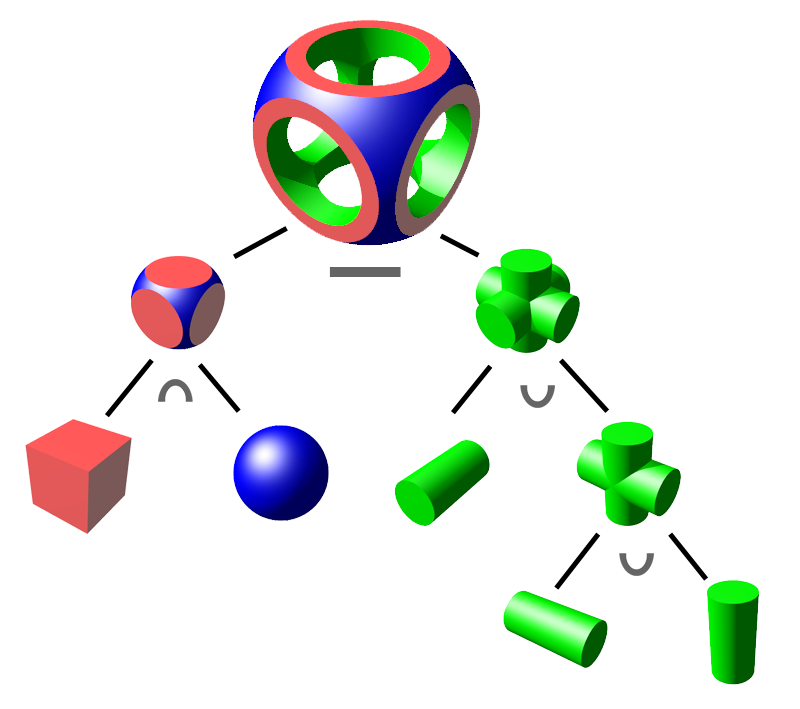|
Brush (video Game)
Brushes are templates used in some 3D video game engines, such as the Quake engine, its derivatives the GoldSrc and Source game engines, or the Unreal Engine, to construct levels. Brushes can be primitive shapes (such as cubes, spheres and cones), pre-defined shapes (such as staircases), or custom shapes (such as prisms and other polyhedra). During the map compilation process, brushes are turned into meshes that can be rendered by the game engine. Often brushes are restricted to convex shapes only, as this reduces the complexity of the binary space partitioning In computer science, binary space partitioning (BSP) is a method for space partitioning which recursively subdivides a Euclidean space into two convex sets by using hyperplanes as partitions. This process of subdividing gives rise to a represent ... process. However, using CSG operations, complex rooms and objects can be created by adding, subtracting and intersecting brushes to and from one another. Additionally, bru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3D Computer Graphics
3D computer graphics, or “3D graphics,” sometimes called CGI, 3D-CGI or three-dimensional computer graphics are graphics that use a three-dimensional representation of geometric data (often Cartesian) that is stored in the computer for the purposes of performing calculations and rendering digital images, usually 2D images but sometimes 3D images. The resulting images may be stored for viewing later (possibly as an animation) or displayed in real time. 3D computer graphics, contrary to what the name suggests, are most often displayed on two-dimensional displays. Unlike 3D film and similar techniques, the result is two-dimensional, without visual depth. More often, 3D graphics are being displayed on 3D displays, like in virtual reality systems. 3D graphics stand in contrast to 2D computer graphics which typically use completely different methods and formats for creation and rendering. 3D computer graphics rely on many of the same algorithms as 2D computer vector gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Game Engine
A game engine is a software framework primarily designed for the development of video games and generally includes relevant libraries and support programs. The "engine" terminology is similar to the term " software engine" used in the software industry. The game engine can also refer to the development software utilizing this framework, typically offering a suite of tools and features for developing games. Developers can use game engines to construct games for video game consoles and other types of computers. The core functionality typically provided by a game engine may include a rendering engine ("renderer") for 2D or 3D graphics, a physics engine or collision detection (and collision response), sound, scripting, animation, artificial intelligence, networking, streaming, memory management, threading, localization support, scene graph, and video support for cinematics. Game engine implementers often economize on the process of game development by reusing/ada ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quake Engine
The ''Quake'' engine is the game engine developed by id Software to power their 1996 video game '' Quake''. It featured true 3D real-time rendering and is now licensed under the terms of GNU General Public License v2.0 or later. After release, it immediately forked, as did the level design. Much of the engine remained in ''Quake II'' and ''Quake III Arena''. The ''Quake'' engine, like the ''Doom'' engine, used binary space partitioning (BSP) to optimise the world rendering. The ''Quake'' engine also used Gouraud shading for moving objects, and a static lightmap for nonmoving objects. Historically, the ''Quake'' engine has been treated as a separate engine from its successor, the ''Quake II'' engine. However, both engines are now considered variants of id Tech 2. Although, the codebases for ''Quake'' and ''Quake II'' were separate GPL releases. History The ''Quake'' engine was developed from 1995 for the video game ''Quake'', released on June 22, 1996. John Carmack did mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GoldSrc
GoldSrc ( ) is a proprietary game engine developed by Valve. At its core, GoldSrc is a heavily modified version of id Software's ''Quake'' engine. It originally made its debut in 1998 with ''Half-Life'', and would power future games developed by or with oversight from Valve, including ''Half-Life'' expansions, '' Day of Defeat'', and multiple games in the ''Counter-Strike'' series. GoldSrc was succeeded by the Source engine with the releases of '' Half-Life: Source'', ''Half-Life 2'', and '' Counter-Strike: Source'' in 2004. However, Valve continues to support the engine with periodic updates. Development The basis of GoldSrc is the engine used in the video game '' Quake'', albeit with heavy modification by Valve. While the engine served as the basis for GoldSrc, Gabe Newell has stated that a majority of the code used in the engine was created by Valve themselves. GoldSrc's artificial intelligence systems, for example, were essentially made from scratch. The engine also reuse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Source (game Engine)
Source is a 3D game engine developed by Valve Corporation, Valve. It debuted as the successor to GoldSrc in 2004 with the release of ''Counter-Strike: Source'' and ''Half-Life 2''. Updates to Source were released in incremental versions, with the engine being succeeded by Source 2 by the late 2010s. History Source distantly originates from the GoldSrc engine, itself a heavily modified version of John Carmack's Quake engine with some code from the Quake II engine. Carmack commented on his blog in 2004 that "there are still bits of early ''Quake'' code in ''Half-Life 2''". Valve employee Erik Johnson explained the engine's nomenclature on the Valve Developer Community: Source was developed part-by-part from this fork onwards, slowly replacing GoldSrc in Valve's internal projects and, in part, explaining the reasons behind its unusually modular nature. Valve's development of Source since has been a mixture of licensed middleware and in-house-developed code. Among others, Source us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unreal Engine
Unreal Engine (UE) is a 3D computer graphics game engine developed by Epic Games, first showcased in the 1998 first-person shooter game '' Unreal''. Initially developed for PC first-person shooters, it has since been used in a variety of genres of games and has seen adoption by other industries, most notably the film and television industry. Unreal Engine is written in C++ and features a high degree of portability, supporting a wide range of desktop, mobile, console, and virtual reality platforms. The latest generation, Unreal Engine 5, was launched in April 2022. Its source code is available on GitHub after registering an account, and commercial use is granted based on a royalty model. Epic waives their royalties margin for games until developers have earned in revenue and the fee is waived if developers publish on the Epic Games Store. Epic has included features from acquired companies like Quixel in the engine, which is seen as helped by '' Fortnite'''s revenue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Level (video Gaming)
In video games, a level (also referred to as a map, stage, or round in some older games) is any space available to the player during the course of completion of an objective. Video game levels generally have progressively-increasing difficulty to appeal to players with different skill levels. Each level may present new concepts and challenges to keep a player's interest high. In games with linear progression, levels are areas of a larger world, such as Green Hill Zone. Games may also feature interconnected levels, representing locations. Although the challenge in a game is often to defeat some sort of character, levels are sometimes designed with a movement challenge, such as a jumping puzzle, a form of obstacle course. Players must judge the distance between platforms or ledges and safely jump between them to reach the next area. These puzzles can slow the momentum down for players of fast action games; the first '' Half-Life'''s penultimate chapter, "Interloper", featured m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometric Primitive
In vector computer graphics, CAD systems, and geographic information systems, geometric primitive (or prim) is the simplest (i.e. 'atomic' or irreducible) geometric shape that the system can handle (draw, store). Sometimes the subroutines that draw the corresponding objects are called "geometric primitives" as well. The most "primitive" primitives are point and straight line segment, which were all that early vector graphics systems had. In constructive solid geometry, primitives are simple geometric shapes such as a cube, cylinder, sphere, cone, pyramid, torus. Modern 2D computer graphics systems may operate with primitives which are curves (segments of straight lines, circles and more complicated curves), as well as shapes (boxes, arbitrary polygons, circles). A common set of two-dimensional primitives includes lines, points, and polygons, although some people prefer to consider triangles primitives, because every polygon can be constructed from triangles. All other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyhedra
In geometry, a polyhedron (plural polyhedra or polyhedrons; ) is a three-dimensional shape with flat polygonal faces, straight edges and sharp corners or vertices. A convex polyhedron is the convex hull of finitely many points, not all on the same plane. Cubes and pyramids are examples of convex polyhedra. A polyhedron is a 3-dimensional example of a polytope, a more general concept in any number of dimensions. Definition Convex polyhedra are well-defined, with several equivalent standard definitions. However, the formal mathematical definition of polyhedra that are not required to be convex has been problematic. Many definitions of "polyhedron" have been given within particular contexts,. some more rigorous than others, and there is not universal agreement over which of these to choose. Some of these definitions exclude shapes that have often been counted as polyhedra (such as the self-crossing polyhedra) or include shapes that are often not considered as valid polyhe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bsp (Quake)
BSP may refer to: Business * Bell System Practices, technical documentation series published internally by the AT&T Bell System * Billing and Settlement Plan, an accounting system for airlines * Business service provider, a category of company providing business processes as services * Business system planning, a method of analysing, defining and designing the information architecture of organisations Science and technology * Bone sialoprotein, a component of mineralized tissues * British Standard Pipe, an international standard set of screw thread sizes used in pipes and pipe fittings outside the US * Bromsulphthalein, a dye used in liver function tests Computing * Binary space partitioning, a method for recursively subdividing a space * Bit-slice processor, a cascadable processor architecture * BSP (file format), used in games such as the Quake series and games that use the Source game engine * Blog service provider, a company offering blog services * Board support package ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Space Partitioning
In computer science, binary space partitioning (BSP) is a method for space partitioning which recursively subdivides a Euclidean space into two convex sets by using hyperplanes as partitions. This process of subdividing gives rise to a representation of objects within the space in the form of a tree data structure known as a BSP tree. Binary space partitioning was developed in the context of 3D computer graphics in 1969. The structure of a BSP tree is useful in rendering because it can efficiently give spatial information about the objects in a scene, such as objects being ordered from front-to-back with respect to a viewer at a given location. Other applications of BSP include: performing geometrical operations with shapes (constructive solid geometry) in CAD, collision detection in robotics and 3D video games, ray tracing, and other applications that involve the handling of complex spatial scenes. Overview Binary space partitioning is a generic process of recursively d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constructive Solid Geometry
Constructive solid geometry (CSG; formerly called computational binary solid geometry) is a technique used in solid modeling. Constructive solid geometry allows a modeler to create a complex surface or object by using Boolean operators to combine simpler objects,, potentially generating visually complex objects by combining a few primitive ones.. In 3D computer graphics and CAD, CSG is often used in procedural modeling. CSG can also be performed on polygonal meshes, and may or may not be procedural and/or parametric. Contrast CSG with polygon mesh modeling and box modeling. Workings The simplest solid objects used for the representation are called ''geometric primitives''. Typically they are the objects of simple shape: cuboids, cylinders, prisms, pyramids, spheres, cones. The set of allowable primitives is limited by each software package. Some software packages allow CSG on curved objects while other packages do not. An object is ''constructed'' from primitives by mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |