|
Broadly Neutralizing HIV-1 Antibodies
Broadly neutralizing HIV-1 antibodies (bNAbs) are neutralizing antibodies which neutralize multiple HIV-1 viral strains. bNAbs are unique in that they target conserved epitopes of the virus, meaning the virus may mutate, but the targeted epitopes will still exist. In contrast, non-bNAbs are specific for individual viral strains with unique epitopes. The discovery of bNAbs has led to an important area of research, namely, discovery of a vaccine, not only limited to HIV, but also other rapidly mutating viruses like influenza. Characteristics The following table shows the characteristics of various HIV-1 bNAbs In addition to targeting conserved epitopes, bNAbs are known to have long variable regions on their immunoglobulin (Ig) isotypes and subclasses. When compared to non-bNAbs, sequence variability from the germline immunoglobulin isotype is 7 fold. This implies that bNAbs develop from intense affinity maturation in the germinal centers hence the reason for high sequence variab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutralizing Antibodies
A neutralizing antibody (NAb) is an antibody that defends a cell from a pathogen or infectious particle by neutralizing any effect it has biologically. Neutralization renders the particle no longer infectious or pathogenic. Neutralizing antibodies are part of the humoral response of the adaptive immune system against viruses, intracellular bacteria and microbial toxin. By binding specifically to surface structures (antigen) on an infectious particle, neutralizing antibodies prevent the particle from interacting with its host cells it might infect and destroy. Mechanism In order to enter cells, pathogens, such as circulating viral particles or extracellular bacteria, use molecules on their surfaces to interact with the cell surface receptors of their target cell which allows them to enter the cell and start their replication cycle. Neutralizing antibodies can inhibit infectivity by binding to the pathogen and blocking the molecules needed for cell entry. This can be due to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
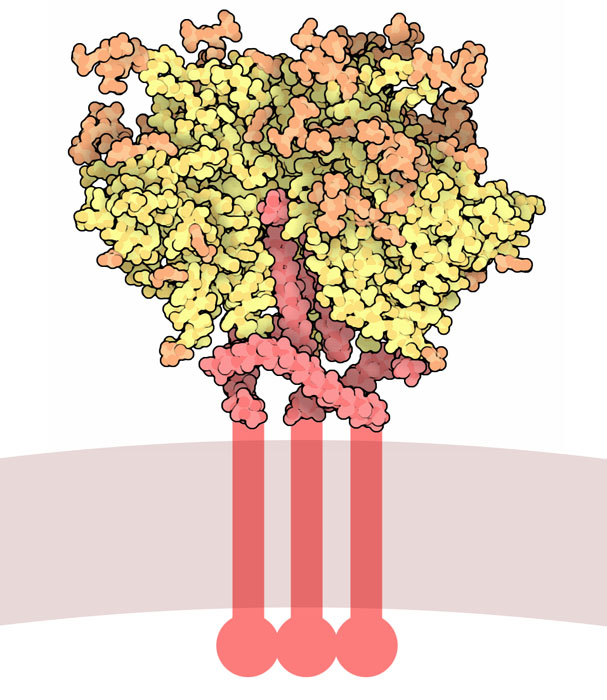
Gp41
Gp41 also known as glycoprotein 41 is a subunit of the envelope protein complex of retroviruses, including human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Gp41 is a transmembrane protein that contains several sites within its ectodomain that are required for infection of host cells. As a result of its importance in host cell infection, it has also received much attention as a potential target for HIV vaccines. Gene and post-translational modifications Gp41 is coded with gp120 as one gp160 by the ''env'' gene of HIV. Gp160 is then extensively glycosylated and proteolytically cleaved by furin, a host cellular protease. The high glycosylation of the env coded glycoproteins allows them to escape the human body's immune system. In contrast to gp120, however, gp41 is less glycosylated and more conserved (less prone to genetic variations). Once gp160 has been cleaved into its individual subunits, the subunits are then associated non-covalently on the surface of the viral envelope. Structur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Databases
Biological databases are libraries of biological sciences, collected from scientific experiments, published literature, high-throughput experiment technology, and computational analysis. They contain information from research areas including genomics, proteomics, metabolomics, microarray gene expression, and phylogenetics. Information contained in biological databases includes gene function, structure, localization (both cellular and chromosomal), clinical effects of mutations as well as similarities of biological sequences and structures. Biological databases can be classified by the kind of data they collect (see below). Broadly, there are molecular databases (for sequences, molecules, etc.), functional databases (for physiology, enzyme activities, phenotypes, ecology etc), taxonomic databases (for species and other taxonomic ranks), images and other media, or specimens (for museum collections etc.) Databases are important tools in assisting scientists to analyze and explain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells, including biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. The study of chemical and physical structure of biological macromolecules is known as molecular biology. Molecular biology was first described as an approach focused on the underpinnings of biological phenomena - uncovering the structures of biological molecules as well as their interactions, and how these interactions explain observations of classical biology. In 1945 the term molecular biology was used by physicist William Astbury. In 1953 Francis Crick, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and colleagues, working at Medical Research Council unit, Cavendish laboratory, Cambridge (now the MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology), made a double helix model of DNA which changed the entire research scenario. They proposed the DNA structure based on previous research done by Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UB-421
Semzuvolimab, formerly known as UB-421 is an experimental HIV antibody, under development by United Biomedical, Inc. (UBI), headquartered in Hauppauge, New York, U.S. for use in the treatment of HIV infection. By blocking the CDR2 domain of the CD4 receptor of the virus, it prevents initial viral attachment to the host T cell A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell r ... and entry into the host immune cell via a competitive inhibition mechanism. The antibody is unlikely to promote resistance to itself via generation of CD4-independent virus, and has performed well in phase 2 open-label trials. Additionally, it offers hope to HIV patients whose infection has become multi-drug resistant. Furthermore, the antibody has shown long term suppression, which requires the patient to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HIV Vaccine Development
An HIV vaccine is a potential vaccine that could be either a preventive vaccine or a therapeutic vaccine, which means it would either protect individuals from being infected with HIV or treat HIV-infected individuals. It is thought that an HIV vaccine could either induce an immune response against HIV (active vaccination approach) or consist of preformed antibodies against HIV (passive vaccination approach). Two active vaccine regimens, studied in the RV 144 and Imbokodo trials, showed they can prevent HIV in some individuals. However, the protection was in relatively few individuals, and was not long lasting. For these reasons, no HIV vaccines have been licensed for the market yet. Difficulties in development In 1984, after it was confirmed that HIV caused AIDS, the United States Health and Human Services Secretary Margaret Heckler declared that a vaccine would be available within two years. However, priming the adaptive immune system to recognize the viral envelope protein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broadly Neutralizing HIV-1 Antibodies
Broadly neutralizing HIV-1 antibodies (bNAbs) are neutralizing antibodies which neutralize multiple HIV-1 viral strains. bNAbs are unique in that they target conserved epitopes of the virus, meaning the virus may mutate, but the targeted epitopes will still exist. In contrast, non-bNAbs are specific for individual viral strains with unique epitopes. The discovery of bNAbs has led to an important area of research, namely, discovery of a vaccine, not only limited to HIV, but also other rapidly mutating viruses like influenza. Characteristics The following table shows the characteristics of various HIV-1 bNAbs In addition to targeting conserved epitopes, bNAbs are known to have long variable regions on their immunoglobulin (Ig) isotypes and subclasses. When compared to non-bNAbs, sequence variability from the germline immunoglobulin isotype is 7 fold. This implies that bNAbs develop from intense affinity maturation in the germinal centers hence the reason for high sequence variab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
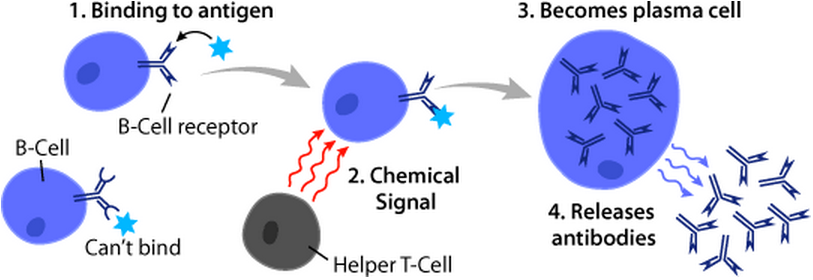
B Cells
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasma membrane where they serve as a part of B-cell receptors. When a naïve or memory B cell is activated by an antigen, it proliferates and differentiates into an antibody-secreting effector cell, known as a plasmablast or plasma cell. Additionally, B cells present antigens (they are also classified as professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs)) and secrete cytokines. In mammals, B cells mature in the bone marrow, which is at the core of most bones. In birds, B cells mature in the bursa of Fabricius, a lymphoid organ where they were first discovered by Chang and Glick, which is why the 'B' stands for bursa and not bone marrow as commonly believed. B cells, unlike the other two classes of lymphocytes, T cells and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English-speaking World
Speakers of English are also known as Anglophones, and the countries where English is natively spoken by the majority of the population are termed the '' Anglosphere''. Over two billion people speak English , making English the largest language by number of speakers, and the third largest language by number of native speakers. England and the Scottish Lowlands, countries of the United Kingdom, are the birthplace of the English language, and the modern form of the language has been being spread around the world since the 17th century, first by the worldwide influence of England and later the United Kingdom, and then by that of the United States. Through all types of printed and electronic media of these countries, English has become the leading language of international discourse and the lingua franca in many regions and professional contexts such as science, navigation and law. The United Kingdom remains the largest English-speaking country in Europe. The United States a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gp120
Envelope glycoprotein GP120 (or gp120) is a glycoprotein exposed on the surface of the HIV envelope. It was discovered by Professors Tun-Hou Lee and Myron "Max" Essex of the Harvard School of Public Health in 1988. The 120 in its name comes from its molecular weight of 120 kDa. Gp120 is essential for virus entry into cells as it plays a vital role in attachment to specific cell surface receptors. These receptors are DC-SIGN, Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycan and a specific interaction with the CD4 receptor, particularly on helper T-cells. Binding to CD4 induces the start of a cascade of conformational changes in gp120 and gp41 that lead to the fusion of the viral membrane with the host cell membrane. Binding to CD4 is mainly electrostatic although there are van der Waals interactions and hydrogen bonds. Gp120 is coded by the HIV ''env'' gene, which is around 2.5 kb long and codes for around 850 amino acids.Kuiken, C., Leitner, T., Foley, B., ''et al.'' (2008)"HIV Sequence Compe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HIV-1
The subtypes of HIV include two major types, HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). HIV-1 is related to viruses found in chimpanzees and gorillas living in western Africa, while HIV-2 viruses are related to viruses found in the sooty mangabey, a vulnerable West African primate. HIV-1 viruses can be further divided into groups M, N, O and P. The HIV-1 group M viruses predominate and are responsible for the AIDS pandemic. Group M can be further subdivided into subtypes based on genetic sequence data. Some of the subtypes are known to be more virulent or are resistant to different medications. Likewise, HIV-2 viruses are thought to be less virulent and transmissible than HIV-1 M group viruses, although HIV-2 is also known to cause AIDS. One of the obstacles to treatment of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is its high genetic variability. Major types HIV-1 HIV-1 is the most common and pathogenic strain of the virus. Over 2 million such infections occur annually. Scientists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)