|
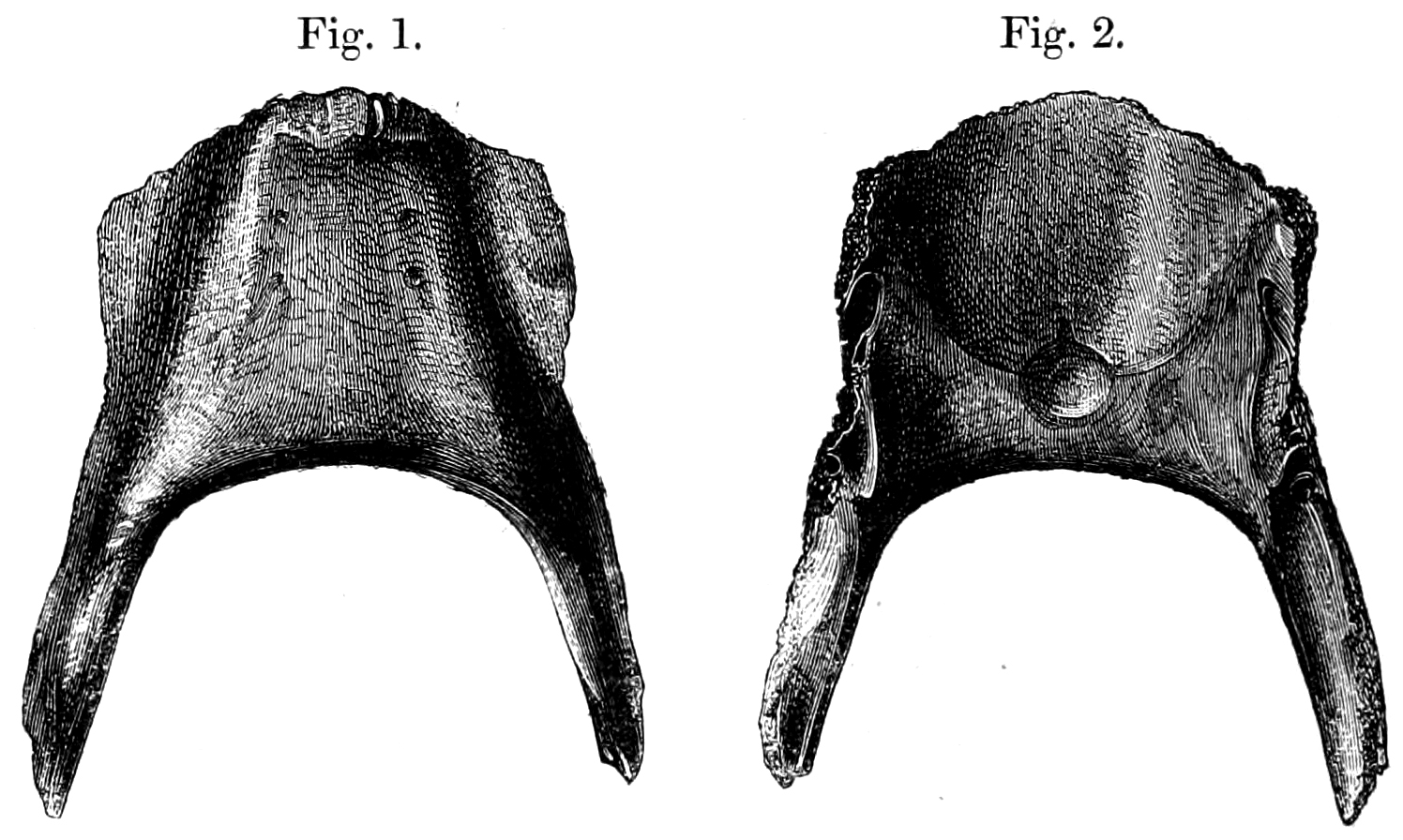
Broad-billed Parrot
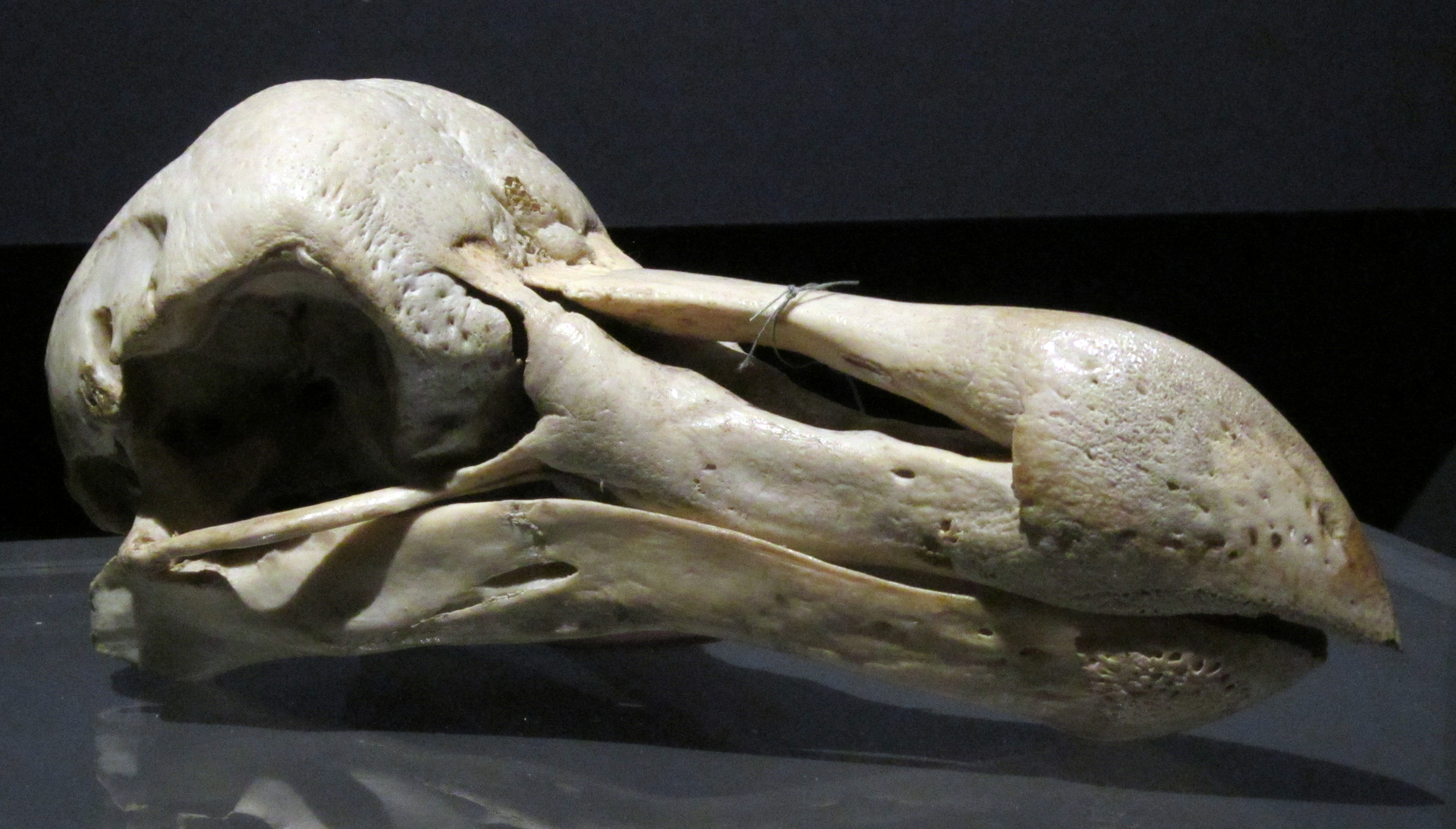
The broad-billed parrot or raven parrot (''Lophopsittacus mauritianus'') is a large extinct parrot in the family Psittaculidae. It was endemic to the Mascarene island of Mauritius in the Indian Ocean east of Madagascar. It is unclear what other species it is most closely related to, but it has been classified as a member of the tribe Psittaculini, along with other Mascarene parrots. It had similarities with the Rodrigues parrot (''Necropsittacus rodricanus''), and may have been closely related. The broad-billed parrot's head was large in proportion to its body, and there was a distinct crest of feathers on the front of the head. The bird had a very large beak, comparable in size to that of the hyacinth macaw, which would have enabled it to crack hard seeds. Subfossil bones indicate that the species exhibited greater sexual dimorphism in overall size and head size than any living parrot. The exact colouration is unknown, but a contemporary description indicates that it had mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Newton
Alfred Newton Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS HFRSE (11 June 18297 June 1907) was an England, English zoology, zoologist and ornithology, ornithologist. Newton was Professor of Comparative Anatomy at Cambridge University from 1866 to 1907. Among his numerous publications were a four-volume ''Dictionary of Birds'' (1893–6), entries on ornithology in the Encyclopædia Britannica (9th edition) while also an editor of the journal ''Ibis (journal), Ibis'' from 1865 to 1870. In 1900 he was awarded the Royal Medal of the Royal Society and the Linnean Medal, Gold Medal of the Linnaean Society. He founded the British Ornithologists Union. Life Alfred Newton was born near Geneva in Switzerland, the fifth son of William Newton (MP for Ipswich), William Newton of Elveden Hall in Suffolk, Member of Parliament (United Kingdom), Member of Parliament (MP) for ; his mother Elizabeth (1789–1843) was the daughter of Richard Slater Milnes, MP for . The family wealth was founded on sugar pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most animals and some plants. Differences may include secondary sex characteristics, size, weight, colour, markings, or behavioural or cognitive traits. These differences may be subtle or exaggerated and may be subjected to sexual selection and natural selection. The opposite of dimorphism is ''monomorphism'', which is when both biological sexes are phenotypically indistinguishable from each other. Overview Ornamentation and coloration Common and easily identified types of dimorphism consist of ornamentation and coloration, though not always apparent. A difference in coloration of sexes within a given species is called sexual dichromatism, which is commonly seen in many species of birds and reptiles. Sexual selection leads to the exaggerated dim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
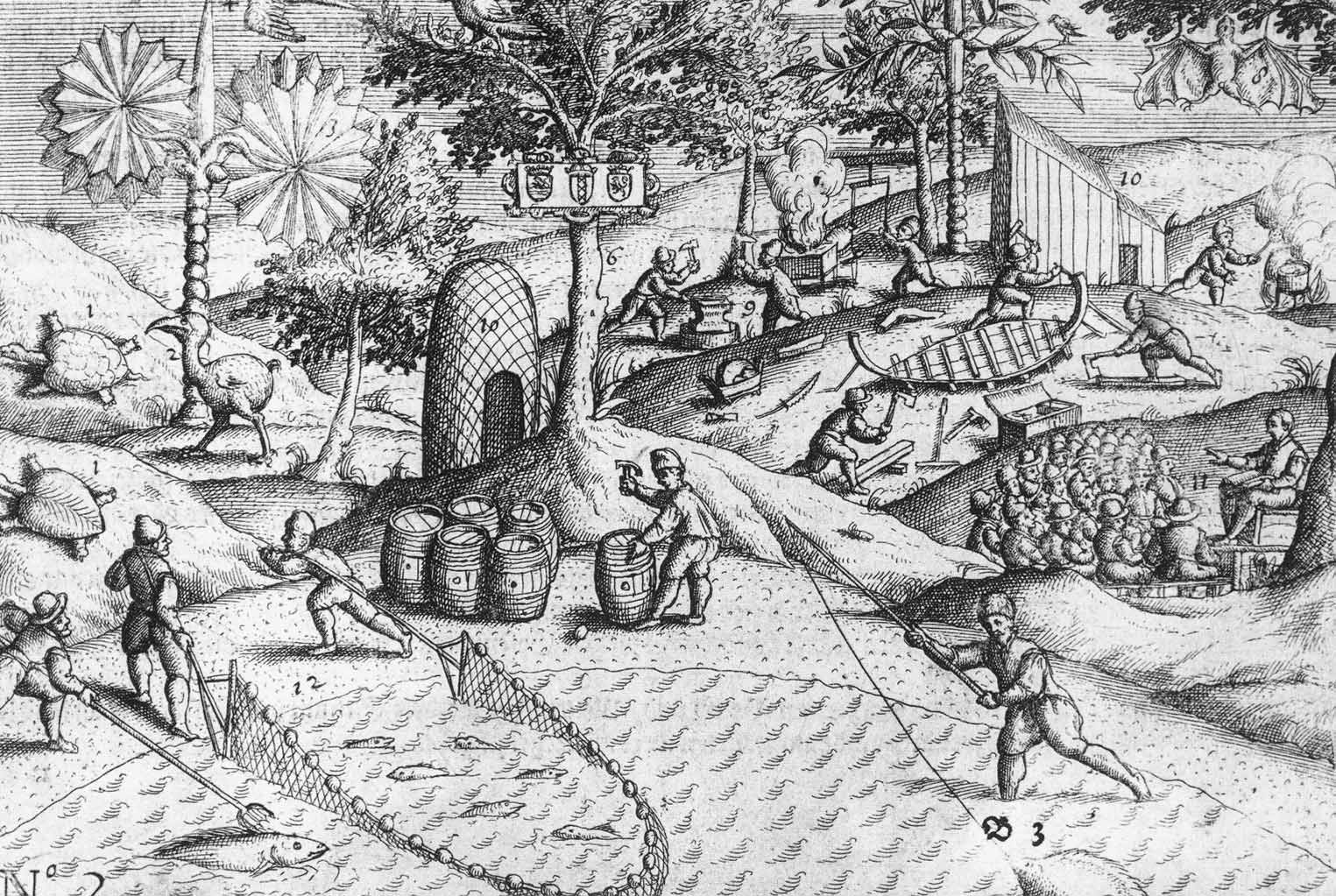
View Of The Mauritius Roadstead - Engraving
A view is a sight or prospect or the ability to see or be seen from a particular place. View, views or Views may also refer to: Common meanings * View (Buddhism), a charged interpretation of experience which intensely shapes and affects thought, sensation, and action * Graphical projection in a technical drawing or schematic ** Multiview orthographic projection, standardizing 2D images to represent a 3D object * Opinion, a belief about subjective matters * Page view, a visit to a World Wide Web page * Panorama, a wide-angle view * Scenic viewpoint, an elevated location where people can view scenery * World view, the fundamental cognitive orientation of an individual or society encompassing the entirety of the individual or society's knowledge and point-of-view Places * View, Kentucky, an unincorporated community in Crittenden County * View, Texas, an unincorporated community in Taylor County Arts, entertainment, and media Music * ''View'' (album), the 2003 debut album ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudolf II
Rudolf II (18 July 1552 – 20 January 1612) was Holy Roman Emperor (1576–1612), King of Hungary and Kingdom of Croatia (Habsburg), Croatia (as Rudolf I, 1572–1608), King of Bohemia (1575–1608/1611) and Archduke of Austria (1576–1608). He was a member of the House of Habsburg. Rudolf's legacy has traditionally been viewed in three ways:Hotson, 1999. an ineffectual ruler whose mistakes led directly to the Thirty Years' War; a great and influential patron of Northern Mannerism, Northern Mannerist art; and an intellectual devotee of occult arts and learning which helped seed what would be called the Scientific Revolution. Determined to unify Christendom, he initiated the Long Turkish War (1593–1606) with the Ottoman Empire. Exhausted by war, his citizens in Hungary revolted in the Bocskai uprising, Bocskai Uprising, which led to more authority given to his brother Matthias, Holy Roman Emperor, Matthias. Under his reign, there was a policy of toleration towards Judaism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roelant Savery
Roelant Savery (or ''Roeland(t) Maertensz Saverij'', or ''de Savery'', or many variants; 1576 – buried 25 February 1639) was a Flanders-born Dutch Golden Age painter. Life Savery was born in Kortrijk. Like so many other artists, he belonged to an Anabaptist family that fled north from the Spanish-occupied Southern Netherlands when Roelant was about 4 years old and settled in Haarlem around 1585. He was taught painting by his older brother Jacob Savery (c. 1565 – 1603) and Hans Bol. After his schooling, Savery traveled to Prague around 1604, where he became court painter of the Emperors Rudolf II (1552–1612) and Mathias (1557–1619), who had made their court a center of mannerist art. Between 1606 and 1608 he traveled to Tyrol to study plants. Gillis d'Hondecoeter became his pupil. Before 1616 Savery moved back to Amsterdam, and lived in the Sint Antoniesbreestraat. In 1618 he settled in Utrecht, where he joined the artist's guild a year later. His nephew Hans would ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signboards
Signage is the design or use of signs and symbols to communicate a message. A signage also means signs ''collectively'' or being considered as a group. The term ''signage'' is documented to have been popularized in 1975 to 1980. Signs are any kind of visual graphics created to display information to a particular audience. This is typically manifested in the form of wayfinding information in places such as streets or on the inside and outside buildings. Signs vary in form and size based on location and intent, from more expansive banners, billboards, and murals, to smaller street signs, street name signs, sandwich boards and lawn signs. Newer signs may also use digital or electronic displays. The main purpose of signs is to communicate, to convey information designed to assist the receiver with decision-making based on the information provided. Alternatively, promotional signage may be designed to persuade receivers of the merits of a given product or service. Signage is distin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacob Savery
Jacob Savery or Jacob Savery the ElderName variations: Jacob Maertensz. Saverij and Jacques Savery (1566 – buried 23 April 1603) was a Flemish painter, etcher and draughtsman. He was trained in Antwerp and later moved to the Dutch Republic after 1584. He specialised in still lifes, animals, landscapes en genre paintings. Life Jacob was born in Kortrijk into a family of painters. His father was Maerten Savery. Jacob probably apprenticed with the Flemish Mannerist painter Hans Bol as was reported by the early biographer Karel van Mander.Iaques Savry an in |
Crow
A crow is a bird of the genus ''Corvus'', or more broadly a synonym for all of ''Corvus''. Crows are generally black in colour. The word "crow" is used as part of the common name of many species. The related term "raven" is not pinned scientifically to any certain trait, but is rather a general grouping for larger ''Corvus spp.'' Species * ''Corvus albus'' – pied crow (Central African coasts to southern Africa) * ''Corvus bennetti'' – little crow (Australia) * ''Corvus brachyrhynchos'' – American crow (United States, southern Canada, northern Mexico) * ''Corvus capensis'' – Cape crow or Cape rook (Eastern and southern Africa) * ''Corvus cornix'' – hooded crow (Northern and Eastern Europe and Northern Africa and Middle East) * ''Corvus corone'' – carrion crow (Europe and eastern Asia) *''Corvus culminatus'' – Indian jungle crow (South Asia) * ''Corvus edithae'' – Somali crow or dwarf raven (eastern Africa) * ''Corvus enca'' – slender-billed crow (Malaysia, Born ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raven
A raven is any of several larger-bodied bird species of the genus ''Corvus''. These species do not form a single taxonomic group within the genus. There is no consistent distinction between "crows" and "ravens", common names which are assigned to different species chiefly on the basis of their size. The largest raven species are the common raven and the thick-billed raven. Etymology The term "raven" originally referred to the common raven (''Corvus corax''), the type species of the genus ''Corvus'', which has a larger distribution than any other species of ''Corvus'', ranging over much of the Northern Hemisphere. The modern English word ''raven'' has cognates in all other Germanic languages, including Old Norse (and subsequently modern Icelandic) and Old High German , all of which descend from Proto-Germanic . Collective nouns for a group of ravens (or at least the common raven) include "rave", "treachery", "unkindness" and "conspiracy". In practice, most people use the more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dodo
The dodo (''Raphus cucullatus'') is an extinct flightless bird that was endemic to the island of Mauritius, which is east of Madagascar in the Indian Ocean. The dodo's closest genetic relative was the also-extinct Rodrigues solitaire. The two formed the subfamily Raphinae, a clade of extinct flightless birds that were a part of the family which includes pigeons and doves. The closest living relative of the dodo is the Nicobar pigeon. A white dodo was once thought to have existed on the nearby island of Réunion, but it is now believed that this assumption was merely confusion based on the also-extinct Réunion ibis and paintings of white dodos. Subfossil remains show the dodo was about tall and may have weighed in the wild. The dodo's appearance in life is evidenced only by drawings, paintings, and written accounts from the 17th century. Since these portraits vary considerably, and since only some of the illustrations are known to have been drawn from live specimens, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacob Cornelis Van Neck
Jacob Corneliszoon van Neck (often anglicized to Jacob Cornelius van Neck) (1564–1638) was a Dutch naval officer and explorer who led the second Dutch expedition to Indonesia from 1598 to 1599. Early life Van Neck was from an Amsterdam family in good standing, and received a thorough education. Since he came from a commercial background and was not experienced in sailing, he took extra classes in navigation.Masselman, p. 111 Second Dutch Expedition Following the success of the first Dutch expedition to Indonesia in 1597, Van Neck was chosen to lead a second expedition in 1598, with the purpose of bringing back various spices. In May 1598, he left the port of Texel with eight vessels under his command. He was accompanied by Vice-Admiral Wybrand van Warwyck and noted polar explorer Jacob van Heemskerk. Following sailing directions written by Petrus Plancius, they made excellent progress, reaching the Cape of Good Hope in only three months. Soon after this, heavy storms s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Dutch Expedition To Indonesia
The Second Dutch Expedition to East Indies was an expedition that took place from 1598 to 1600, one of the Dutch forays into the East Indies spice trade that led to the establishment of the Dutch East India Company. It was led by Jacob Cornelius van Neck. Background During the 16th century, the Portuguese dominated the spice trade, but after the first Dutch expedition to Indonesia under Cornelis de Houtman, the backers of that expedition decided that the time was ripe for further forays into the Indonesian spice market. The company behind the first expedition, the Far-distance Company, and the recently established New Company for Voyages to East India joined forces and between them managed to raise nearly 800,000 guilders, the most money that had ever been raised in the Netherlands for a private venture. In 1592 the cartographer Petrus Plancius published a series of charts showing, in exact detail, the route to the Indies, which was the spark that instigated the first Dut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |