|
Brillouin Spectroscopy
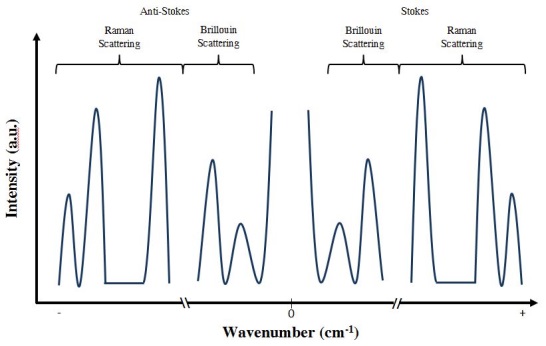
Brillouin spectroscopy is an empirical spectroscopy technique which allows the determination of elastic moduli of materials. The technique uses inelastic scattering of light when it encounters acoustic phonons in a crystal, a process known as Brillouin scattering, to determine phonon energies and therefore interatomic potentials of a material. The scattering occurs when an electromagnetic wave interacts with a density wave, photon-phonon scattering. This technique is commonly used to determine the elastic properties of materials in mineral physics and material science. Brillouin spectroscopy can be used to determine the complete elastic tensor of a given material which is required in order to understand the bulk elastic properties. Comparison with Raman spectroscopy Brillouin spectroscopy is similar to Raman spectroscopy in many ways; in fact the physical scattering processes involved are identical. However, the type of information gained is significantly different. The proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empirical
Empirical evidence for a proposition is evidence, i.e. what supports or counters this proposition, that is constituted by or accessible to sense experience or experimental procedure. Empirical evidence is of central importance to the sciences and plays a role in various other fields, like epistemology and law. There is no general agreement on how the terms ''evidence'' and ''empirical'' are to be defined. Often different fields work with quite different conceptions. In epistemology, evidence is what justifies beliefs or what determines whether holding a certain belief is rational. This is only possible if the evidence is possessed by the person, which has prompted various epistemologists to conceive evidence as private mental states like experiences or other beliefs. In philosophy of science, on the other hand, evidence is understood as that which '' confirms'' or ''disconfirms'' scientific hypotheses and arbitrates between competing theories. For this role, it is important that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raman Scattering
Raman scattering or the Raman effect () is the inelastic scattering of photons by matter, meaning that there is both an exchange of energy and a change in the light's direction. Typically this effect involves vibrational energy being gained by a molecule as incident photons from a visible laser are shifted to lower energy. This is called normal Stokes Raman scattering. The effect is exploited by chemists and physicists to gain information about materials for a variety of purposes by performing various forms of Raman spectroscopy. Many other variants of Raman spectroscopy allow rotational energy to be examined (if gas samples are used) and electronic energy levels may be examined if an X-ray source is used in addition to other possibilities. More complex techniques involving pulsed lasers, multiple laser beams and so on are known. Light has a certain probability of being scattered by a material. When photons are scattered, most of them are elastically scattered ( Rayleigh scatt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubic Elastic Constants
Cubic may refer to: Science and mathematics * Cube (algebra), "cubic" measurement * Cube, a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex ** Cubic crystal system, a crystal system where the unit cell is in the shape of a cube * Cubic function, a polynomial function of degree three * Cubic equation, a polynomial equation (reducible to ''ax''3 + ''bx''2 + ''cx'' + ''d'' = 0) * Cubic form, a homogeneous polynomial of degree 3 * Cubic graph (mathematics - graph theory), a graph where all vertices have degree 3 * Cubic plane curve (mathematics), a plane algebraic curve ''C'' defined by a cubic equation * Cubic reciprocity (mathematics - number theory), a theorem analogous to quadratic reciprocity * Cubic surface, an algebraic surface in three-dimensional space * Cubic zirconia, in geology, a mineral that is widely synthesized for use as a diamond simulacra * CUBIC, a histology method Computing * Cubic IDE, a modular deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
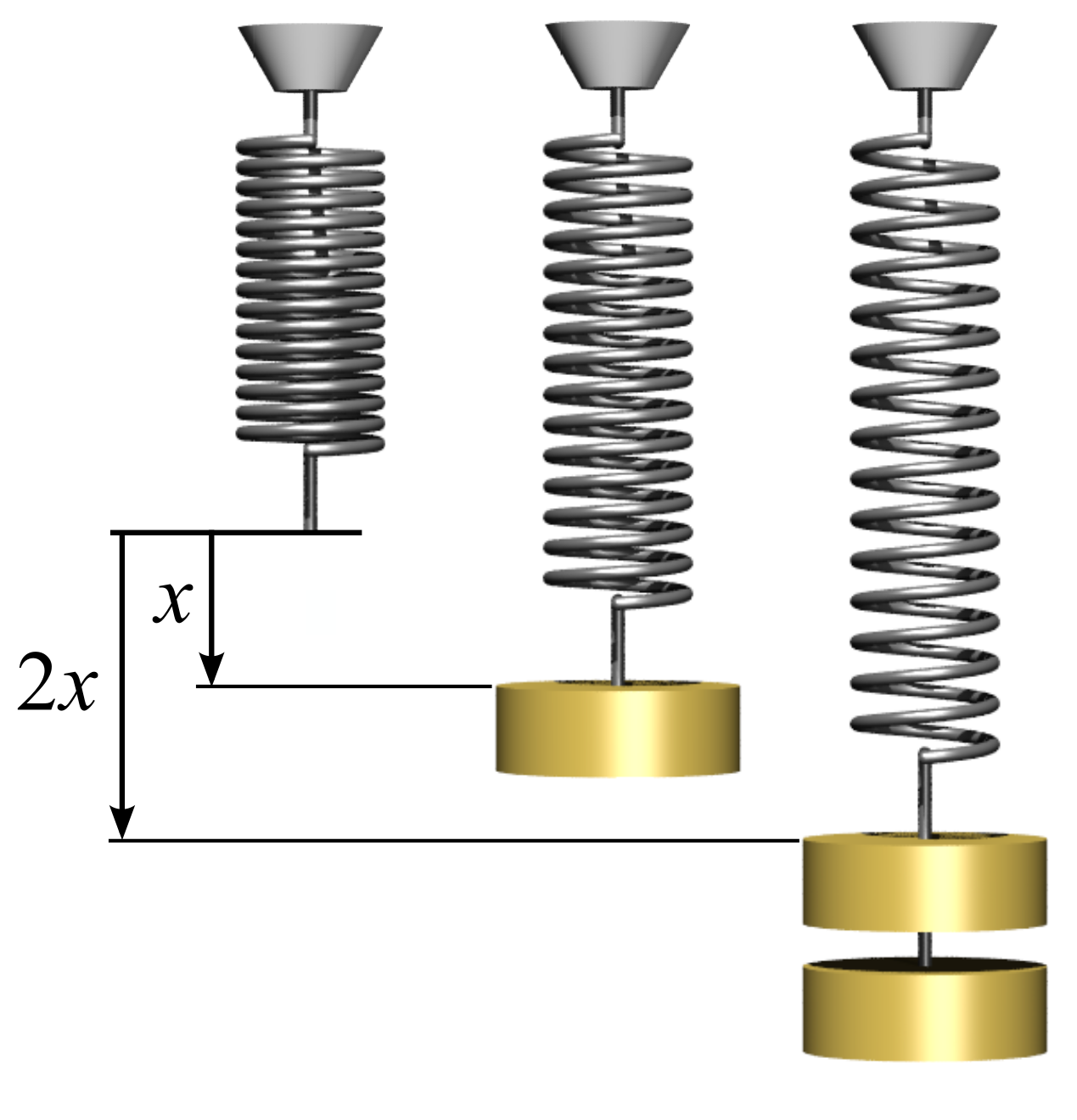
Hooke's Law
In physics, Hooke's law is an empirical law which states that the force () needed to extend or compress a spring by some distance () scales linearly with respect to that distance—that is, where is a constant factor characteristic of the spring (i.e., its stiffness), and is small compared to the total possible deformation of the spring. The law is named after 17th-century British physicist Robert Hooke. He first stated the law in 1676 as a Latin anagram. He published the solution of his anagram in 1678 as: ("as the extension, so the force" or "the extension is proportional to the force"). Hooke states in the 1678 work that he was aware of the law since 1660. Hooke's equation holds (to some extent) in many other situations where an elastic body is deformed, such as wind blowing on a tall building, and a musician plucking a string of a guitar. An elastic body or material for which this equation can be assumed is said to be linear-elastic or Hookean. Hooke's law i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubic Elastic Constants
Cubic may refer to: Science and mathematics * Cube (algebra), "cubic" measurement * Cube, a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex ** Cubic crystal system, a crystal system where the unit cell is in the shape of a cube * Cubic function, a polynomial function of degree three * Cubic equation, a polynomial equation (reducible to ''ax''3 + ''bx''2 + ''cx'' + ''d'' = 0) * Cubic form, a homogeneous polynomial of degree 3 * Cubic graph (mathematics - graph theory), a graph where all vertices have degree 3 * Cubic plane curve (mathematics), a plane algebraic curve ''C'' defined by a cubic equation * Cubic reciprocity (mathematics - number theory), a theorem analogous to quadratic reciprocity * Cubic surface, an algebraic surface in three-dimensional space * Cubic zirconia, in geology, a mineral that is widely synthesized for use as a diamond simulacra * CUBIC, a histology method Computing * Cubic IDE, a modular deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica ( silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical formula of SiO2. Quartz is the second most abundant mineral in Earth's continental crust, behind feldspar. Quartz exists in two forms, the normal α-quartz and the high-temperature β-quartz, both of which are chiral. The transformation from α-quartz to β-quartz takes place abruptly at . Since the transformation is accompanied by a significant change in volume, it can easily induce microfracturing of ceramics or rocks passing through this temperature threshold. There are many different varieties of quartz, several of which are classified as gemstones. Since antiquity, varieties of quartz have been the most commonly used minerals in the making of jewelry and hardstone carvings, especially in Eurasia. Quartz is the mineral definin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffraction Grating
In optics, a diffraction grating is an optical component with a periodic structure that diffracts light into several beams travelling in different directions (i.e., different diffraction angles). The emerging coloration is a form of structural coloration. The directions or diffraction angles of these beams depend on the wave (light) incident angle to the diffraction grating, the spacing or distance between adjacent diffracting elements (e.g., parallel slits for a transmission grating) on the grating, and the wavelength of the incident light. The grating acts as a dispersive element. Because of this, diffraction gratings are commonly used in monochromators and spectrometers, but other applications are also possible such as optical encoders for high precision motion control and wavefront measurement. For typical applications, a reflective grating has ridges or ''rulings'' on its surface while a transmissive grating has transmissive or hollow slits on its surface. Such a gratin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rayleigh Scattering
Rayleigh scattering ( ), named after the 19th-century British physicist Lord Rayleigh (John William Strutt), is the predominantly elastic scattering of light or other electromagnetic radiation by particles much smaller than the wavelength of the radiation. For light frequencies well below the resonance frequency of the scattering particle (normal dispersion regime), the amount of scattering is inversely proportional to the fourth power of the wavelength. Rayleigh scattering results from the electric polarizability of the particles. The oscillating electric field of a light wave acts on the charges within a particle, causing them to move at the same frequency. The particle, therefore, becomes a small radiating dipole whose radiation we see as scattered light. The particles may be individual atoms or molecules; it can occur when light travels through transparent solids and liquids, but is most prominently seen in gases. Rayleigh scattering of sunlight in Earth's atmosphere cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wave Polarization
In physics, mathematics, and related fields, a wave is a propagating dynamic disturbance (change from equilibrium) of one or more quantities. Waves can be periodic, in which case those quantities oscillate repeatedly about an equilibrium (resting) value at some frequency. When the entire waveform moves in one direction, it is said to be a ''traveling wave''; by contrast, a pair of superimposed periodic waves traveling in opposite directions makes a ''standing wave''. In a standing wave, the amplitude of vibration has nulls at some positions where the wave amplitude appears smaller or even zero. Waves are often described by a ''wave equation'' (standing wave field of two opposite waves) or a one-way wave equation for single wave propagation in a defined direction. Two types of waves are most commonly studied in classical physics. In a ''mechanical wave'', stress and strain fields oscillate about a mechanical equilibrium. A mechanical wave is a local deformation (strain) in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
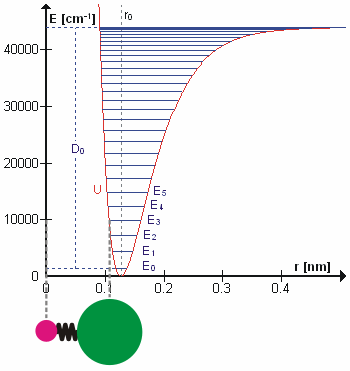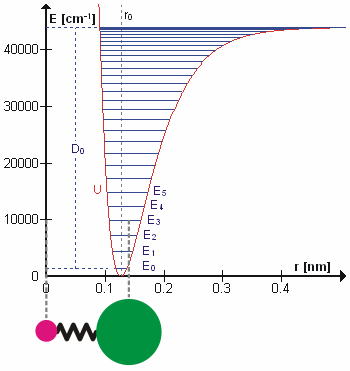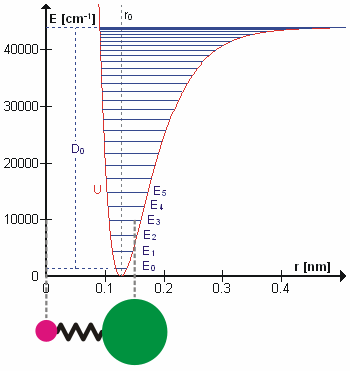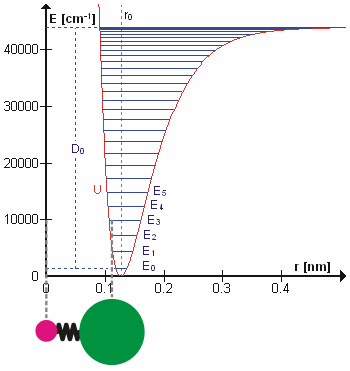
Molecular Vibration
A molecular vibration is a periodic motion of the atoms of a molecule relative to each other, such that the center of mass of the molecule remains unchanged. The typical vibrational frequencies range from less than 1013 Hz to approximately 1014 Hz, corresponding to wavenumbers of approximately 300 to 3000 cm−1 and wavelengths of approximately 30 to 3 µm. For a diatomic molecule A−B, the vibrational frequency in s−1 is given by \nu = \frac \sqrt , where k is the force constant in dyne/cm or erg/cm2 and μ is the reduced mass given by \frac = \frac+\frac. The vibrational wavenumber in cm−1 is \tilde \;= \frac \sqrt, where c is the speed of light in cm/s. Vibrations of polyatomic molecules are described in terms of normal modes, which are independent of each other, but each normal mode involves simultaneous vibrations of different parts of the molecule. In general, a non-linear molecule with ''N'' atoms has 3''N'' – 6 normal modes of vibration, but a ''lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raman Spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy () (named after Indian physicist C. V. Raman) is a spectroscopic technique typically used to determine vibrational modes of molecules, although rotational and other low-frequency modes of systems may also be observed. Raman spectroscopy is commonly used in chemistry to provide a structural fingerprint by which molecules can be identified. Raman spectroscopy relies upon inelastic scattering of photons, known as Raman scattering. A source of monochromatic light, usually from a laser in the visible, near infrared, or near ultraviolet range is used, although X-rays can also be used. The laser light interacts with molecular vibrations, phonons or other excitations in the system, resulting in the energy of the laser photons being shifted up or down. The shift in energy gives information about the vibrational modes in the system. Infrared spectroscopy typically yields similar yet complementary information. Typically, a sample is illuminated with a laser beam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

_(2019)_1662-1683_landscape.png)