|
Boundary Problem (in Spatial Analysis)
A boundary problem in analysis is a phenomenon in which geographical patterns are differentiated by the shape and arrangement of boundaries that are drawn for administrative or measurement purposes. The boundary problem occurs because of the loss of neighbors in analyses that depend on the values of the neighbors. While geographic phenomena are measured and analyzed within a specific unit, identical spatial data can appear either dispersed or clustered depending on the boundary placed around the data. In analysis with point data, dispersion is evaluated as dependent of the boundary. In analysis with areal data, statistics should be interpreted based upon the boundary. Definition In spatial analysis, four major problems interfere with an accurate estimation of the statistical parameter: the boundary problem, scale problem, pattern problem (or spatial autocorrelation), and modifiable areal unit problem. The boundary problem occurs because of the loss of neighbours in analyses that d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatial Analysis
Spatial analysis or spatial statistics includes any of the formal techniques Technique or techniques may refer to: Music * The Techniques, a Jamaican rocksteady vocal group of the 1960s *Technique (band), a British female synth pop band in the 1990s * ''Technique'' (album), by New Order, 1989 * ''Techniques'' (album), by M ... which studies entities using their topological, geometric, or geographic properties. Spatial analysis includes a variety of techniques, many still in their early development, using different analytic approaches and applied in fields as diverse as astronomy, with its studies of the placement of galaxies in the cosmos, to chip fabrication engineering, with its use of "place and route" algorithms to build complex wiring structures. In a more restricted sense, spatial analysis is the technique applied to structures at the human scale, most notably in the analysis of geographic data or Spatial transcriptomics, transcriptomics data. Complex issues arise in spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatial Autocorrelation
Spatial analysis or spatial statistics includes any of the formal techniques which studies entities using their topological, geometric, or geographic properties. Spatial analysis includes a variety of techniques, many still in their early development, using different analytic approaches and applied in fields as diverse as astronomy, with its studies of the placement of galaxies in the cosmos, to chip fabrication engineering, with its use of "place and route" algorithms to build complex wiring structures. In a more restricted sense, spatial analysis is the technique applied to structures at the human scale, most notably in the analysis of geographic data or transcriptomics data. Complex issues arise in spatial analysis, many of which are neither clearly defined nor completely resolved, but form the basis for current research. The most fundamental of these is the problem of defining the spatial location of the entities being studied. Classification of the techniques of spatial a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
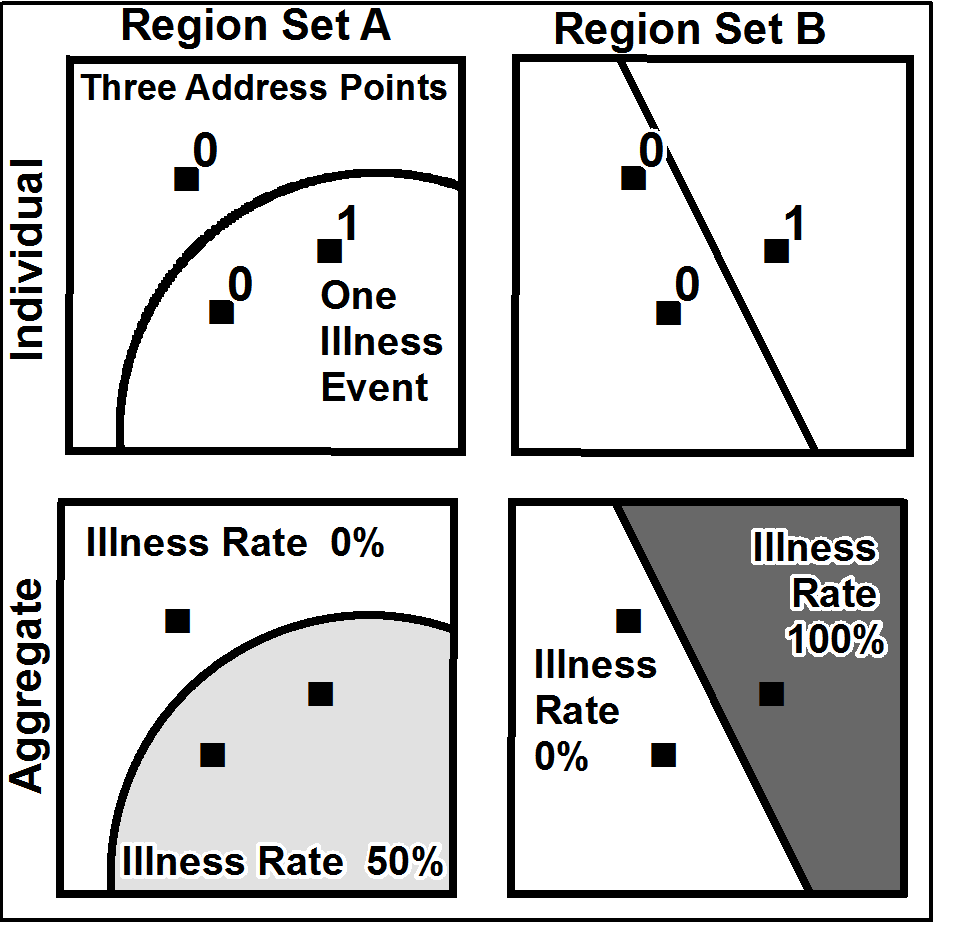
Modifiable Areal Unit Problem
__NOTOC__ The modifiable areal unit problem (MAUP) is a source of statistical bias that can significantly impact the results of statistical hypothesis tests. MAUP affects results when point-based measures of spatial phenomena are aggregated into districts, for example, population density or illness rates. The resulting summary values (e.g., totals, rates, proportions, densities) are influenced by both the shape and scale of the aggregation unit. For example, census data may be aggregated into county districts, census tracts, postcode areas, police precincts, or any other arbitrary spatial partition. Thus the results of data aggregation are dependent on the mapmaker's choice of which "modifiable areal unit" to use in their analysis. A census choropleth map calculating population density using state boundaries will yield radically different results than a map that calculates density based on county boundaries. Furthermore, census district boundaries are also subject to change ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Place Theory
Central place theory is an urban geographical theory that seeks to explain the number, size and range of market services in a commercial system or human settlements in a residential system.Goodall, B. (1987) The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography. London: Penguin. It was introduced in 1933 to explain the spatial distribution of cities across the landscape. The theory was first analyzed by German geographer Walter Christaller, who asserted that settlements simply functioned as 'central places' providing economic services to surrounding areas. Christaller explained that a large number of small settlements will be situated relatively close to one another for efficiency, and because people don’t want to travel far for everyday needs, like getting bread from a bakery. But people would travel further for more expensive and infrequent purchases or specialized goods and services which would be located in larger settlements that are farther apart. Building the theory To develop the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generalized Least Squares
In statistics, generalized least squares (GLS) is a technique for estimating the unknown parameters in a linear regression model when there is a certain degree of correlation between the residuals in a regression model. In these cases, ordinary least squares and weighted least squares can be statistically inefficient, or even give misleading inferences. GLS was first described by Alexander Aitken in 1936. Method outline In standard linear regression models we observe data \_ on ''n'' statistical units. The response values are placed in a vector \mathbf = \left( y_, \dots, y_ \right)^, and the predictor values are placed in the design matrix \mathbf = \left( \mathbf_^, \dots, \mathbf_^ \right)^, where \mathbf_ = \left( 1, x_, \dots, x_ \right) is a vector of the ''k'' predictor variables (including a constant) for the ''i''th unit. The model forces the conditional mean of \mathbf given \mathbf to be a linear function of \mathbf, and assumes the conditional variance of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity analysis is the study of how the uncertainty in the output of a mathematical model or system (numerical or otherwise) can be divided and allocated to different sources of uncertainty in its inputs. A related practice is uncertainty analysis, which has a greater focus on uncertainty quantification and propagation of uncertainty; ideally, uncertainty and sensitivity analysis should be run in tandem. The process of recalculating outcomes under alternative assumptions to determine the impact of a variable under sensitivity analysis can be useful for a range of purposes, including: * Testing the robustness of the results of a model or system in the presence of uncertainty. * Increased understanding of the relationships between input and output variables in a system or model. * Uncertainty reduction, through the identification of model input that cause significant uncertainty in the output and should therefore be the focus of attention in order to increase robustness (perh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concepts And Techniques In Modern Geography
''Concepts and Techniques in Modern Geography'', abbreviated CATMOG, is a series of 59 short publications, each focused on an individual method or theory in geography. Background and impact ''Concepts and Techniques in Modern Geography'' were produced by the Study Group in Quantitative Methods of the Institute of British Geographers. Each CATMOG publication was written on an individual topic in geography rather than a series of broad topics like traditional textbooks. This à la carte approach allowed only purchasing publications on topics of interest, keeping each CATMOG relatively cheap and accessible, lowering student costs. The first of these publications was published in 1975, and the last in 1996. Each was written by someone working professionally with its topic. As they focus on core concepts of the discipline and were written by experts in the field, they are still often cited today when discussing specific topics. The Quantitative Methods Research Group (QMRG) at the Roy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distance Decay
Distance decay is a geographical term which describes the effect of distance on cultural or spatial interactions. The distance decay effect states that the interaction between two locales declines as the distance between them increases. Once the distance is outside of the two locales' activity space, their interactions begin to decrease. It is thus an assertion that the mathematics of the inverse square law in physics can be applied to many geographic phenomena, and is one of the ways in which physics principles such as gravity are often applied metaphorically to geographic situations. Mathematical models Distance decay is graphically represented by a curving line that swoops concavely downward as distance along the x-axis increases. Distance decay can be mathematically represented as an inverse-square law by the expression I = const. \times d^ or I \propto 1/d^2, where is interaction and is distance. In practice, it is often parameterized to fit a specific situation, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Fallacy
An ecological fallacy (also ecological ''inference'' fallacy or population fallacy) is a formal fallacy in the interpretation of statistical data that occurs when inferences about the nature of individuals are deduced from inferences about the group to which those individuals belong. "Ecological fallacy" is a term that is sometimes used to describe the fallacy of division, which is not a statistical fallacy. The four common statistical ecological fallacies are: confusion between ecological correlations and individual correlations, confusion between group average and total average, Simpson's paradox, and confusion between higher average and higher likelihood. Examples Mean and median An example of ecological fallacy is the assumption that a population mean has a simple interpretation when considering likelihoods for an individual. For instance, if the mean score of a group is larger than zero, this does not imply that a random individual of that group is more likely to have a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuzzy Architectural Spatial Analysis
Fuzzy architectural spatial analysis (FASA) (also fuzzy inference system (FIS) based architectural space analysis or fuzzy spatial analysis) is a spatial analysis method of analysing the spatial formation and architectural space intensity within any architectural organization. Fuzzy architectural spatial analysis is used in architecture, interior design, urban planning and similar spatial design fields. Overview Fuzzy architectural spatial analysis was developed by Burcin Cem Arabacioglu (2010) from the architectural theories of space syntax and visibility graph analysis,Turner, Alasdair; Doxa, Maria; O'Sullivan, David and Penn, Alan (2001). "From isovists to visibility graphs: a methodology for the analysis of architectural space". Environment and Planning B 28 (1): 103–121. and is applied with the help of a fuzzy system with a Mamdami inference system based on fuzzy logic within any architectural space. Fuzzy architectural spatial analysis model analyses the space by con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographic Information System
A geographic information system (GIS) is a type of database containing geographic data (that is, descriptions of phenomena for which location is relevant), combined with software tools for managing, analyzing, and visualizing those data. In a broader sense, one may consider such a system to also include human users and support staff, procedures and workflows, body of knowledge of relevant concepts and methods, and institutional organizations. The uncounted plural, ''geographic information systems'', also abbreviated GIS, is the most common term for the industry and profession concerned with these systems. It is roughly synonymous with geoinformatics and part of the broader geospatial field, which also includes GPS, remote sensing, etc. Geographic information science, the academic discipline that studies these systems and their underlying geographic principles, may also be abbreviated as GIS, but the unambiguous GIScience is more common. GIScience is often considered a subdi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Level Of Analysis
The term "level of analysis" is used in the social sciences to point to the location, size, or scale of a research target. "Level of analysis" is distinct from the term "unit of observation" in that the former refers to a more or less integrated set of relationships while the latter refers to the distinct unit from which data have been or will be gathered. Together, the unit of observation and the level of analysis help define the population of a research enterprise. Level of analysis vs unit of analysis Level of analysis is closely related to the term unit of analysis, and some scholars have used them interchangingly, while others argue for a need for distinction. Ahmet Nuri Yurdusev wrote that "the level of analysis is more of an issue related to the framework/context of analysis and the level at which one conducts one's analysis, whereas the question of the unit of analysis is a matter of the 'actor' or the 'entity' to be studied". Manasseh Wepundi noted the difference between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |