|
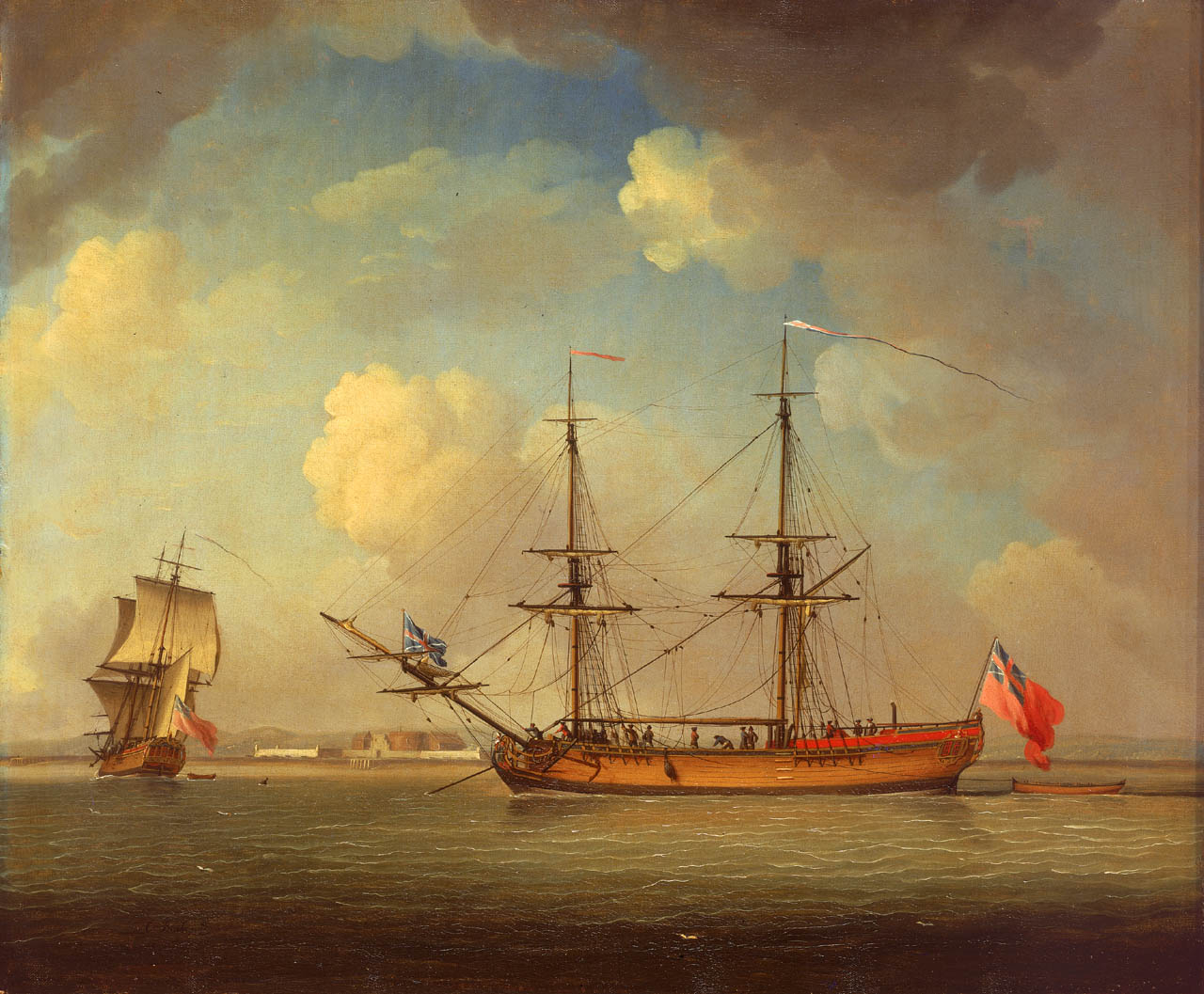
Bonetta-class Sloop
The ''Bonetta'' class was a class of three sloops of wooden construction built for the Royal Navy between 1755 and 1756. All three were built by contract with commercial builders to a common design prepared by Thomas Slade, the Surveyor of the Navy. All three were ordered on 9 July 1755, assigned names on 29 July 1755, and were built as two-masted snow-rigged vessels. Vessels References * *McLaughlan, Ian. ''The Sloop of War 1650-1763''. Seaforth Publishing, 2014. . *Winfield, Rif. ''British Warships in the Age of Sail 1714-1792: Design, Construction, Careers and Fates''. Seaforth Publishing, 2007. . {{DEFAULTSORT:Bonetta class sloop Sloop classes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sloop-of-war
In the 18th century and most of the 19th, a sloop-of-war in the Royal Navy was a warship with a single gun deck that carried up to eighteen guns. The rating system covered all vessels with 20 guns and above; thus, the term ''sloop-of-war'' encompassed all the unrated combat vessels, including the very small gun-brigs and cutters. In technical terms, even the more specialised bomb vessels and fireships were classed as sloops-of-war, and in practice these were employed in the sloop role when not carrying out their specialised functions. In World War I and World War II, the Royal Navy reused the term "sloop" for specialised convoy-defence vessels, including the of World War I and the highly successful of World War II, with anti-aircraft and anti-submarine capability. They performed similar duties to the American destroyer escort class ships, and also performed similar duties to the smaller corvettes of the Royal Navy. Rigging A sloop-of-war was quite different from a civilian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Builder's Old Measurement
Builder's Old Measurement (BOM, bm, OM, and o.m.) is the method used in England from approximately 1650 to 1849 for calculating the cargo capacity of a ship. It is a volumetric measurement of cubic capacity. It estimated the tonnage of a ship based on length and maximum beam (nautical), beam. It is expressed in "tons burden" ( en-em , burthen , enm , byrthen ), and abbreviated "tons bm". The formula is: : \text = \frac where: * ''Length'' is the length, in foot (length), feet, from the stem (ship), stem to the sternpost; * ''Beam (nautical), Beam'' is the maximum beam, in feet. The Builder's Old Measurement formula remained in effect until the advent of steam propulsion. Steamships required a different method of estimating tonnage, because the ratio of length to beam was larger and a significant volume of internal space was used for boilers and machinery. In 1849, the Moorsom System was created in the United Kingdom. The Moorsom system calculates the cargo-carrying capaci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snow (ship)
In sailing, a snow, snaw or snauw is a square-rigged vessel with two masts, complemented by a snow- or trysail-mast stepped immediately abaft (behind) the main mast.Hans Haalmeijer (2009). Pinassen, fluiten en galjassen, the Netherlands: Uitgeverij De Alk B.V. History The word 'snow' comes from 'snauw', which is an old Dutch word for beak, a reference to the characteristic sharp bow of the vessel. The snow evolved from the (three-masted) ship: the mizzen mast of a ship was gradually moved closer towards the mainmast, until the mizzen mast was no longer a separate mast, but was instead made fast at the main mast top. As such, in the 17th century the snow used to be sometimes classified as a three-masted vessel. The snow dates back to the late 17th century and originally had a loose-footed gaff sail; the boom was introduced somewhere in the 18th century. It was a popular type of vessel in the Baltic Sea and was employed by a large number of nations during its time. The snow was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sloop-of-war
In the 18th century and most of the 19th, a sloop-of-war in the Royal Navy was a warship with a single gun deck that carried up to eighteen guns. The rating system covered all vessels with 20 guns and above; thus, the term ''sloop-of-war'' encompassed all the unrated combat vessels, including the very small gun-brigs and cutters. In technical terms, even the more specialised bomb vessels and fireships were classed as sloops-of-war, and in practice these were employed in the sloop role when not carrying out their specialised functions. In World War I and World War II, the Royal Navy reused the term "sloop" for specialised convoy-defence vessels, including the of World War I and the highly successful of World War II, with anti-aircraft and anti-submarine capability. They performed similar duties to the American destroyer escort class ships, and also performed similar duties to the smaller corvettes of the Royal Navy. Rigging A sloop-of-war was quite different from a civilian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the middle decades of the 17th century, and through the 18th century, the Royal Navy vied with the Dutch Navy and later with the French Navy for maritime supremacy. From the mid 18th century, it was the world's most powerful navy until the Second World War. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superiority globally. Owing to this historical prominence, it is common, even among non-Britons, to ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Slade
Sir Thomas Slade (1703/4–1771) was an English naval architect, most famous for designing HMS ''Victory'', Lord Nelson's flagship at the Battle of Trafalgar in 1805. Early life He was the son of Arthur Slade (1682–1746) and his wife Hannah Moore. His paternal uncle was Benjamin Slade, Master Shipwright at Deptford Dockyard. Career outline Like many who rose to the pinnacle of the design of British sailing warships, Thomas Slade began as a shipwright in the Royal Dockyards. His uncle Benjamin Slade was Master Shipwright at Plymouth Dockyard (a master shipwright was responsible for all ship construction and repair at the dockyard in which he served). In 1744 Thomas became Deputy Master Shipwright at Woolwich Dockyard. On 22 November 1750 he replaced his uncle, who had died that year, as Master Shipwright at Plymouth. On 27 May 1752 he was transferred temporarily back to Woolwich Dockyard as Master Shipwright, and from there to Chatham Dockyard on 17 June 1752 and subsequently ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surveyor Of The Navy
The Surveyor of the Navy also known as Department of the Surveyor of the Navy and originally known as Surveyor and Rigger of the Navy was a former principal commissioner and member of both the Navy Board from the inauguration of that body in 1546 until its abolition in 1832 and then a member Board of Admiralty from 1848-1859. In 1860 the office was renamed ''Controller of The Navy'' until 1869 when the office was merged with that of the Third Naval Lord's the post holder held overall responsibility for the design of British warships. History The office was established in 1546 under Henry VIII of England when the post holder was styled as ''Surveyor and Rigger of the Navy'' until 1611. Although until 1745 the actual design work for warships built at each Royal Dockyard was primarily the responsibility of the individual Master Shipwright at that Royal Dockyard. For vessels built by commercial contract (limited to wartime periods, when the Royal Dockyards could not cope with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snow (ship)
In sailing, a snow, snaw or snauw is a square-rigged vessel with two masts, complemented by a snow- or trysail-mast stepped immediately abaft (behind) the main mast.Hans Haalmeijer (2009). Pinassen, fluiten en galjassen, the Netherlands: Uitgeverij De Alk B.V. History The word 'snow' comes from 'snauw', which is an old Dutch word for beak, a reference to the characteristic sharp bow of the vessel. The snow evolved from the (three-masted) ship: the mizzen mast of a ship was gradually moved closer towards the mainmast, until the mizzen mast was no longer a separate mast, but was instead made fast at the main mast top. As such, in the 17th century the snow used to be sometimes classified as a three-masted vessel. The snow dates back to the late 17th century and originally had a loose-footed gaff sail; the boom was introduced somewhere in the 18th century. It was a popular type of vessel in the Baltic Sea and was employed by a large number of nations during its time. The snow was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Bonetta (1756)
Thirteen ships of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS ''Bonetta'': * was a 4-gun sloop launched in 1673 and sold in 1687. * was a 4-gun sloop launched in 1699 and sold in 1712. * was a sloop in service in 1718 and sold in 1719. * was a 3-gun sloop launched in 1721 and sold in 1731. * was a 14-gun sloop launched in 1732. She foundered in 1744. * was a 10-gun sloop launched in 1756 and sold in 1776. ''Lloyd's Register'' (1778) shows the ''Hawke'', of 220 tons (bm), Thames-built, as the former sloop-of-war ''Bonetta''. It gives ''Hawke''s master as S. Gribble, her owner as Calvert & Co., her armament as two 12-pounder and twelve 9-pounder guns, and her trade as privateer. * was a 14-gun sloop launched in 1779. She was at Yorktown, but rather than scuttling her, the British handed her over to French on 19 October 1781 under the terms of capitulation. The French sent her as a cartel to New York, after which she returned to their control. On 3 January 1782 recaptured her. ''B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotherhithe
Rotherhithe () is a district of south-east London, England, and part of the London Borough of Southwark. It is on a peninsula on the south bank of the Thames, facing Wapping, Shadwell and Limehouse on the north bank, as well as the Isle of Dogs to the east of the Thames and is a part of the London Docklands, Docklands area. It borders Bermondsey to the west and Deptford to the south east. Rotherhithe has a long history as a port, with Elizabethan era, Elizabethan shipyards and working docks until the 1970s. In the 1980s, the area along the river was redeveloped as housing through a mix of warehouse conversions and new-build developments. Following the arrival of the Jubilee line in 1999 (giving quick connections to the West End of London, West End and to Canary Wharf) and the London Overground in 2010 (providing a quick route to the City of London), the rest of Rotherhithe is now a gentrification, gentrifying residential and commuter area, with urban regeneration progressing arou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woolwich
Woolwich () is a district in southeast London, England, within the Royal Borough of Greenwich. The district's location on the River Thames led to its status as an important naval, military and industrial area; a role that was maintained throughout the 16th to 20th centuries. After several decades of economic hardship and social deprivation, the area now has several large-scale urban renewal projects. Geography Woolwich is situated from Charing Cross. It has a long frontage to the south bank of the Thames river. From the riverside it rises up quickly along the northern slopes of Shooter's Hill towards the common, at and the ancient London–Dover Road, at . The ancient parish of Woolwich, more or less the present-day wards Woolwich Riverside and Woolwich Common, comprises . This included North Woolwich, which is now part of the London Borough of Newham. The ancient parishes of Plumstead and Eltham became part of the civil parish of Woolwich in 1930. Parts of the wards ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Merlin (1756)
Fourteen ships and one shore establishment of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS ''Merlin'', after Merlin, the wizard in Arthurian legend (the shore establishment RNAS Donibristle, like the other Naval Air Stations in Scotland, was named after the sea bird): * was a 10-gun pinnance built in 1579 and listed until 1601. * was a 14-gun yacht launched in 1652 and captured by a Dutch squadron off Cadiz in 1665 while she was convoying victualing ships to Tangier; her resistance restricted the Dutch to capturing only four of her charges. * was an 8-gun yacht launched in 1666 and sold in 1698. * was a 2-gun sloop launched in 1699 and sold in 1712. * was a 10-gun sloop launched in 1744 and sold in 1750. * was a 10-gun sloop in service in 1753. * was a 10-gun sloop launched in 1756. She was captured by a French privateer in 1757, but recaptured later that year and renamed HMS ''Zephyr''. The French frigate ''Gracieuse'' recaptured her in August 1778;Hepper (1994), p.53. she was disarme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |