|
Boko Language
Boko, or Boo, is a Mande language of Benin and Nigeria. Names Boko language can be better known as Boko, but it is also known as Boo or with the Hausa name Busanci (also spelled Busanchi, Bussanci Or Bussanchi). One person or speaker is called a Bokoni and more persons/speakers are called Bokona and the language of the Bokona/Bussawa people is called Bokonya. The Boko people are one of two subgroups of the Bissa people, the other being the Busa people, who speak the Busa language. They are not a clan but a subgroup. They are related to the Bariba people, who speak the Bariba language, which is a Gur language. The Bissa people proper speak the Bissa language, which is closely related to Boko. Geographic distribution Nigeria In Nigeria, Boko is spoken in Borgu LGA of Niger State, in Bagudo LGA of Kebbi State, and in Baruten LGA of Kwara state. A number of Boko have migrated to other parts of Nigeria, including Abuja. The Boko people are referred to as Bussawa in Hausa. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benin
Benin ( , ; french: Bénin , ff, Benen), officially the Republic of Benin (french: République du Bénin), and formerly Dahomey, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso to the north-west, and Niger to the north-east. The majority of its population lives on the southern coastline of the Bight of Benin, part of the Gulf of Guinea in the northernmost tropical portion of the Atlantic Ocean. The capital is Porto-Novo, and the seat of government is in Cotonou, the most populous city and economic capital. Benin covers an area of and its population in was estimated to be approximately million. It is a tropical nation, dependent on agriculture, and is an exporter of palm oil and cotton. Some employment and income arise from subsistence farming. The official language of Benin is French, with indigenous languages such as Fon, Bariba, Yoruba and Dendi also spoken. The largest religious group in Benin is Sunni Islam (27 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
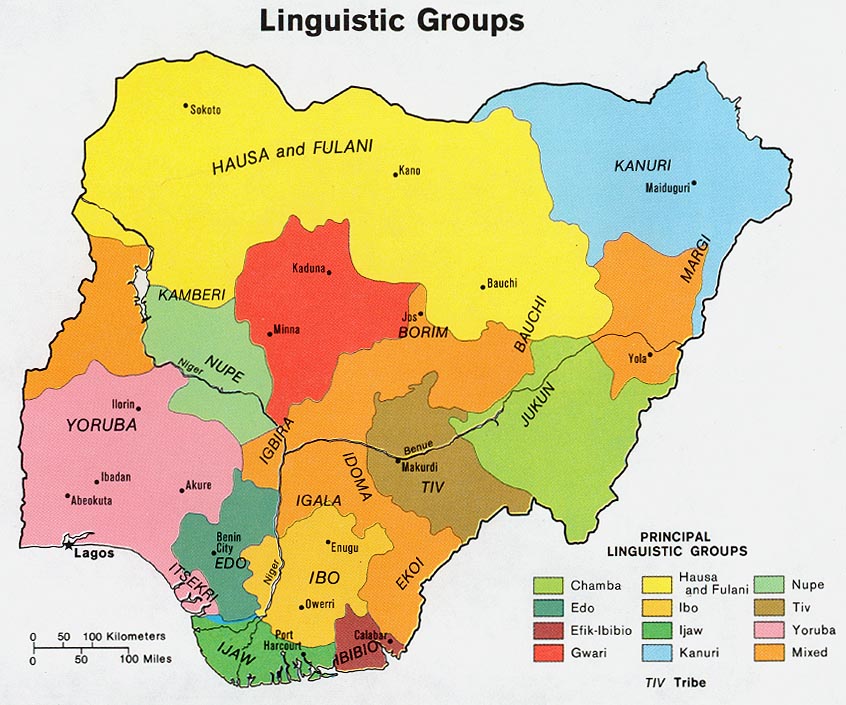
Kwara State
Kwara State ( yo, Ìpínlẹ̀ Kwárà), is a state in Western Nigeria, bordered to the east by Kogi State, to the north by Niger state, and to the south by Ekiti, Osun, and Oyo states, while its western border makes up part of the international border with Benin Republic. Its capital is the city of Ilorin and the state has 16 local government areas. Of the 36 states of Nigeria, Kwara is the ninth largest in area, but the sixth least populous, with an estimated population of about 3.2 million as at 2016. Geographically, Kwara state is split between the West Sudanian savanna in the west, and the Guinean forest–savanna mosaic ecoregion in the rest of the state. Important geographic features of the state include rivers, with the Niger flowing along the northern border into Lake Jeba, before continuing as the border, while the Awun, Asa, Aluko, and Oyun rivers flow through the interior. In the far northwest of the state is the Borgu section of the Kainji National Park, a lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fulfulde
Fula ,Laurie Bauer, 2007, ''The Linguistics Student’s Handbook'', Edinburgh also known as Fulani or Fulah (, , ; Adlam: , , ), is a Senegambian language spoken by around 30 million people as a set of various dialects in a continuum that stretches across some 18 countries in West and Central Africa. Along with other related languages such as Serer and Wolof, it belongs to the Atlantic geographic group within Niger–Congo, and more specifically to the Senegambian branch. Unlike most Niger-Congo languages, Fula does not have tones. It is spoken as a first language by the Fula people ("Fulani", ff, Fulɓe, link=no) from the Senegambia region and Guinea to Cameroon, Nigeria, and Sudan and by related groups such as the Toucouleur people in the Senegal River Valley. It is also spoken as a second language by various peoples in the region, such as the Kirdi of northern Cameroon and northeastern Nigeria. Nomenclature Several names are applied to the language, just as to the Fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoruba Language
Yoruba (, ; Yor. '; Ajami script, Ajami: ) is a language spoken in West Africa, primarily in South West (Nigeria), Southwestern Middle Belt, and Central Nigeria. It is spoken by the Ethnic group, ethnic Yoruba people. The number of Yoruba speakers is roughly 50 million, plus about 2 million second-language speakers. As a pluricentric language, it is primarily spoken in a dialectal area spanning Nigeria and Benin with smaller migrated communities in Côte d'Ivoire, Sierra Leone and The Gambia. Yoruba vocabulary is also used in the Afro-Brazilian religion known as Candomblé, in the Caribbean religion of Santería in the form of the liturgical Lucumí language and various Afro-American religions of North America. Practitioners of these religions in the Americas no longer speak or understand the Yorùbá language, rather they use remnants of Yorùbá language for singing songs that for them are shrouded in mystery. Usage of a lexicon of Yorùbá words and short phrases during ritua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hausa Language
Hausa (; /; Ajami: ) is a Chadic language spoken by the Hausa people in the northern half of Nigeria, Ghana, Cameroon, Benin and Togo, and the southern half of Niger, Chad and Sudan, with significant minorities in Ivory Coast. Hausa is a member of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family and is the most widely spoken language within the Chadic languages, Chadic branch of that family. Ethnologue estimated that it was spoken as a first language by some 47 million people and as a second language by another 25 million, bringing the total number of Hausa speakers to an estimated 72 million. In Nigeria, the Hausa-speaking film industry is known as Hausa-language cinema, Kannywood. Classification Hausa belongs to the West Chadic languages subgroup of the Chadic languages group, which in turn is part of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. Geographic distribution Native speakers of Hausa, the Hausa people, are mostly found in southern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendi Language
Dendi is a Songhay language used as a trade language across northern Benin (along the Niger River. It forms a dialect cluster with Zarma and Koyraboro Senni but it is heavily influenced by Bariba. Dendi has been described as a four- tone language.Joe Salmons, ''Accentual change and language contact: Comparative survey and a case study of early Northern Europe'' Distribution Dendi is mainly spoken in Northern Benin, but also in other parts of Benin, and neighbouring countries. The Dendi people are the main group in the Departments of Alibori, Borgou, Donga, and Atakora. In Nigeria, the Dendi people are found in Bordering States (Kebbi, Kwara, Niger, and Sokoto), and in other parts of Nigeria. They are usually referred by the Hausa name Dendawa (which is also used for the Songhai people The Songhai people (also Ayneha, Songhay or Sonrai)'' are an ethnolinguistic group in West Africa who speak the various Songhai languages. Their history and ''lingua franca'' is linked to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bokobaru Language
Busa, or Bisã, is the Mande language of the former Borgu Emirate in northwestern Nigeria and northern Benin. It is called ''Busanci'' in Hausa, and has also been called ''Zugweya''. Names Busa language can be better known as Busa, but it is also known with the native name Bisã or with the Hausa name Busanci (also spelled Busanchi, Bussanci Or Bussanchi); This should not be confused with the Busa language of Papua New Guinea or the related Bissa language of Burkina Faso, Ghana, Togo and Ivory Coast. One person or speaker is called a Busa and more persons/speakers are called Busano and the language of the Busano/Bussawa people is called Bisã. The Busa people are one of two subgroups of the Bissa people, the other being the Boko people, who speak the Boko language. They are not a clan but a subgroup. They are related to the Bariba people, who speak the Bariba language, which is a Gur language. The Bissa people proper speak the Bissa language, which is closely related to Bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samo Languages
Samo (Sane, San, Sa), also known as Mande Samo, is a dialect cluster of Niger-Congo languages spoken in Burkina Faso and Mali. Varieties Intelligibility between Samo varieties is low. The following have been coded as separate languages: *Matya Samo, spoken in Kossi Province, Sourou Province (Nouna and Solenzo areas) and Mali *Maya Samo, spoken in Sourou Province, Yatenga Province, and Zondoma Province *Southern/Maka Samo, spoken in Nayala Province (Nouna and Solenzo areas); Sourou Province; Sanguie Province; Passore ProvinceThe Seenku language, Seenku Sembla language is also called 'Southern Samo'. Demographics Samo dialect populations and locations: List of Samo villages organised by department and dialect:Berthelette, John (2002). Survey report on the San (Samo) language'. SIL Electronic Survey Reports 2002-005.PDF Sample vocabulary Sample basic vocabulary of Samo dialects: Writing System Notes and references {{Authority control Mande languages Langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volta River
The Volta River is the main river system in the West African country of Ghana. It flows south into Ghana from the Bobo-Dioulasso highlands of Burkina Faso. The main parts of the river are the Black Volta, the White Volta, and the Red Volta. In the northwest, the Black Volta forms the international borders between the Ivory Coast, Ghana, and Burkina Faso. The Volta flows southward along the Akwapim-Togoland highlands, and it empties into the Atlantic Ocean at the Gulf of Guinea at Ada Foah. It has a smaller tributary river, the Oti, which enters Ghana from Togo in the east. The Volta River has been dammed at Akosombo for the purpose of generating hydroelectricity. The reservoir named Lake Volta stretches from Akosombo Dam in the south to the northern part of the country, and is the largest man-made reservoir by area in the world. Volta was named by the Portuguese, meaning twist or turn. The country of Burkina Faso was formerly called Upper Volta, after the river. The reserv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Mande Languages
The Eastern Mande languages (called Eastern Eastern Mande by Kastenholz, and Niger–Volta by SchreiberSchreiber, Henning. 2008. ''Eine historische Phonologie der Niger-Volta-Sprachen: Ein Beitrag zur Erforschung der Sprachgeschichte der östlichen Ost-Mandesprachen'' (Mande Languages and Linguistics 7). Cologne: Rüdiger Köppe. and also known as the Bisa–Busa languages) are a branch of the Mande languages spoken in seven areas: northwest Burkina Faso, the border region of northern Benin and Nigeria, and one language, Bissa, also spoken in Ghana, Togo, and Ivory Coast and the Samo languages also spoken in Mali. Member languages * Bissa, spoken in Burkina Faso, Ghana, Togo, and Ivory Coast * Boko of Benin and Nigeria * Busa of Nigeria and Benin * Bokobaru of Nigeria *Samo languages Samo (Sane, San, Sa), also known as Mande Samo, is a dialect cluster of Niger-Congo languages spoken in Burkina Faso and Mali. Varieties Intelligibility between Samo varieties is low. The follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |