|
BlackPast
BlackPast.org is a web-based reference center that is dedicated primarily to the understanding of African-American history and Afro-Caribbean history and the history of people of Sub-Saharan African ancestry. In 2011 the American Library Association's Reference and User Services Association included it in its list of the 25 Best Free Reference Websites of the Year. According to BlackPast.org, the website has a global audience of about two million visitors per year from over 100 nations. In 2009, Canada, Australia, Great Britain, Brazil, and Germany ranked as the top five countries in visitors to the site after the United States."History of BlackPast.org (2004– )" ''BlackPast.org''. A 2008 website review described it as easily navigable and well organized but also as containing omissions among some features ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quintard Taylor
__FORCETOC__ Quintard Taylor is a historian, founder of BlackPast.org, an online encyclopedia dedicated to provide public with information concerning African American history, and former professor of University of Washington. Personal life Taylor was born in December 11, 1948 to Quintard Taylor Sr. and Grace Taylor in Brownsville, Tennessee. He finished his high school in Brownsville, Tennessee. Taylor completed his B.A. from St. Augustine's College in 1969 in American History, and finished his M.A. degree and his Ph.D. from the University of Minnesota in 1971 and 1977, respectively in History. While he was a teacher at the Washington State University, he married Carolyn and he had three children, Quintard III, and twins, William and Jamila. He taught in several universities including, Washington State University, California Polytechnic State University, and University of Oregon, and University of Washington, until his retirement in June 2018. He was also responsible for variou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African-American History
African-American history began with the arrival of Africans to North America in the 16th and 17th centuries. Former Spanish slaves who had been freed by Francis Drake arrived aboard the Golden Hind at New Albion in California in 1579. The European colonization of the Americas, and the resulting transatlantic slave trade, led to a large-scale transportation of enslaved Africans across the Atlantic; of the roughly 10–12 million Africans who were sold by the Barbary slave trade, either to European slavery or to servitude in the Americas, approximately 388,000 landed in North America. After arriving in various European colonies in North America, the enslaved Africans were sold to white colonists, primarily to work on cash crop plantations. A group of enslaved Africans arrived in the English colony of Virginia in 1619, marking the beginning of slavery in the colonial history of the United States; by 1776, roughly 20% of the British North American population was of African d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Digital Information Infrastructure And Preservation Program
The National Digital Information Infrastructure and Preservation Program (NDIIPP) of the United States was an archival program led by the Library of Congress to archive and provide access to digital resources. The program convened several working groups, administered grant projects, and disseminated information about digital preservation issues. The U.S. Congress established the program in 2000, and official activity specific to NDIIPP itself wound down between 2016 and 2018. The Library was chosen because of its role as one of the leading providers of high-quality content on the Internet. The Library of Congress has formed a national network of partners dedicated to preserving specific types of digital content that is at risk of loss. In July 2010, the Library launched a National Digital Stewardship Alliance (NDSA) to extend the work of NDIIPP to more institutions. The organization, which has been hosted by the Digital Library Federation since January 2016, focuses on several g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bibliographic Databases And Indexes
Bibliography (from and ), as a discipline, is traditionally the academic study of books as physical, cultural objects; in this sense, it is also known as bibliology (from ). English author and bibliographer John Carter describes ''bibliography'' as a word having two senses: one, a list of books for further study or of works consulted by an author (or enumerative bibliography); the other one, applicable for collectors, is "the study of books as physical objects" and "the systematic description of books as objects" (or descriptive bibliography). Etymology The word was used by Greek writers in the first three centuries CE to mean the copying of books by hand. In the 12th century, the word started being used for "the intellectual activity of composing books." The 17th century then saw the emergence of the modern meaning, that of description of books. Currently, the field of bibliography has expanded to include studies that consider the book as a material object. Bibliography, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Studies Organizations
Black is a color which results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without hue, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness. Black and white have often been used to describe opposites such as good and evil, the Dark Ages versus Age of Enlightenment, and night versus day. Since the Middle Ages, black has been the symbolic color of solemnity and authority, and for this reason it is still commonly worn by judges and magistrates. Black was one of the first colors used by artists in Neolithic cave paintings. It was used in ancient Egypt and Greece as the color of the underworld. In the Roman Empire, it became the color of mourning, and over the centuries it was frequently associated with death, evil, witches, and magic. In the 14th century, it was worn by royalty, clergy, judges, and government officials in much of Europe. It became the color worn by English romantic poets, businessmen a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timeline Of The Civil Rights Movement
This is a timeline of the civil rights movement in the United States, a nonviolent mid-20th century freedom movement to gain legal equality and the enforcement of constitutional rights for people of color. The goals of the movement included securing equal protection under the law, ending legally institutionalized racial discrimination, and gaining equal access to public facilities, education reform, fair housing, and the ability to vote. 1947–1953 1947 * April 14In '' Mendez v. Westminster'', the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit rules that the forced segregation of Mexican-American students into separate "Mexican schools" was unconstitutional and unlawful. 1948 * In ''Delgado v Bastrop I.S.D.'', the Texas Attorney General decided that segregation of Mexican-American children was illegal. * In '' Shelley v. Kraemer'', the U.S. Supreme Court ruled that racially restrictive covenants violate the Fourteenth Amendment's equal protection clause and thus cannot be enf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schomburg Center For Research In Black Culture
The Schomburg Center for Research in Black Culture is a research library of the New York Public Library (NYPL) and an archive repository for information on people of African descent worldwide. Located at 515 Malcolm X Boulevard (Lenox Avenue) between West 135th and 136th Streets in the Harlem neighborhood of Manhattan, New York City, it has, almost from its inception, been an integral part of the Harlem community. It is named for Afro-Puerto Rican scholar Arturo Alfonso Schomburg. The resources of the center are broken up into five divisions, the Art and Artifacts Division, the Jean Blackwell Hutson General Research and Reference Division, the Manuscripts, Archives and Rare Books Division, the Moving Image and Recorded Sound Division, and the Photographs and Prints Division. In addition to research services, the center hosts readings, discussions, art exhibitions, and theatrical events. It is open to the general public. Early history 135th Street branch In 1901, Andrew Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Museums Focused On African Americans
This is a list of museums in the United States whose primary focus is on African American culture and history. Such museums are commonly known as African American museums. According to scholar Raymond Doswell, an African American museum is "an institution established for the preservation of African-derived culture." Museums have a mission of "collecting and preserving material on history and cultural heritage." African American museums share these goals with archives, genealogy groups, historical societies, and research libraries. Museums differ from archives, genealogy groups, historical societies, memorials, and research libraries because they have as a basic educational or aesthetic purpose the collection and display of objects, and regular exhibitions for the public. Being open to the public (not just researchers or by appointment) and having regular hours sets museums apart from historical sites or other facilities that may call themselves museums. History of African Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Slavery In The United States
The legal institution of human chattel slavery, comprising the enslavement primarily of Africans and African Americans, was prevalent in the United States of America from its founding in 1776 until 1865, predominantly in the South. Slavery was established throughout European colonization in the Americas. From 1526, during early colonial days, it was practiced in what became Britain's colonies, including the Thirteen Colonies that formed the United States. Under the law, an enslaved person was treated as property that could be bought, sold, or given away. Slavery lasted in about half of U.S. states until abolition. In the decades after the end of Reconstruction, many of slavery's economic and social functions were continued through segregation, sharecropping, and convict leasing. By the time of the American Revolution (1775–1783), the status of enslaved people had been institutionalized as a racial caste associated with African ancestry. During and immediately follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black History Month
Black History Month is an annual observance originating in the United States, where it is also known as African-American History Month. It has received official recognition from governments in the United States and Canada, and more recently has been observed in Ireland, and the United Kingdom. It began as a way of remembering important people and events in the history of the African diaspora. It is celebrated in February in the United States and Canada, while in Ireland, and the United Kingdom it is observed in October. History Negro History Week (1926) The precursor to Black History Month was created in 1926 in the United States, when historian Carter G. Woodson and the Association for the Study of Negro Life and History (ASNLH) announced the second week of February to be "Negro History Week".Scott, Daryl Michael"The Origins of Black History Month" Association for the Study of African American Life and History, 2011, www.asalh.org/. This week was chosen because it coi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Association For The Study Of African American Life And History
The Association for the Study of African American Life and History (ASALH) is an organization dedicated to the study and appreciation of African-American History. It is a non-profit organization founded in Chicago, Illinois, on September 9, 1915, during the National Half Century Exposition and Lincoln Jubilee, and incorporated in Washington, D.C., on October 2, 1915, as the Association for the Study of Negro Life and History (ASNLH) by Carter G. Woodson, William B. Hartgrove, George Cleveland Hall, Alexander L. Jackson, and James E. Stamps. The association is based in Washington, D.C. In 1973, ASNLH was renamed the Association for the Study of Afro-American Life and History. ASALH's official mission is "to promote, research, preserve, interpret, and disseminate information about Black life, history, and culture to the global community." Its official vision is "to be the premier Black Heritage and learned society with a diverse and inclusive membership supported by a strong net ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
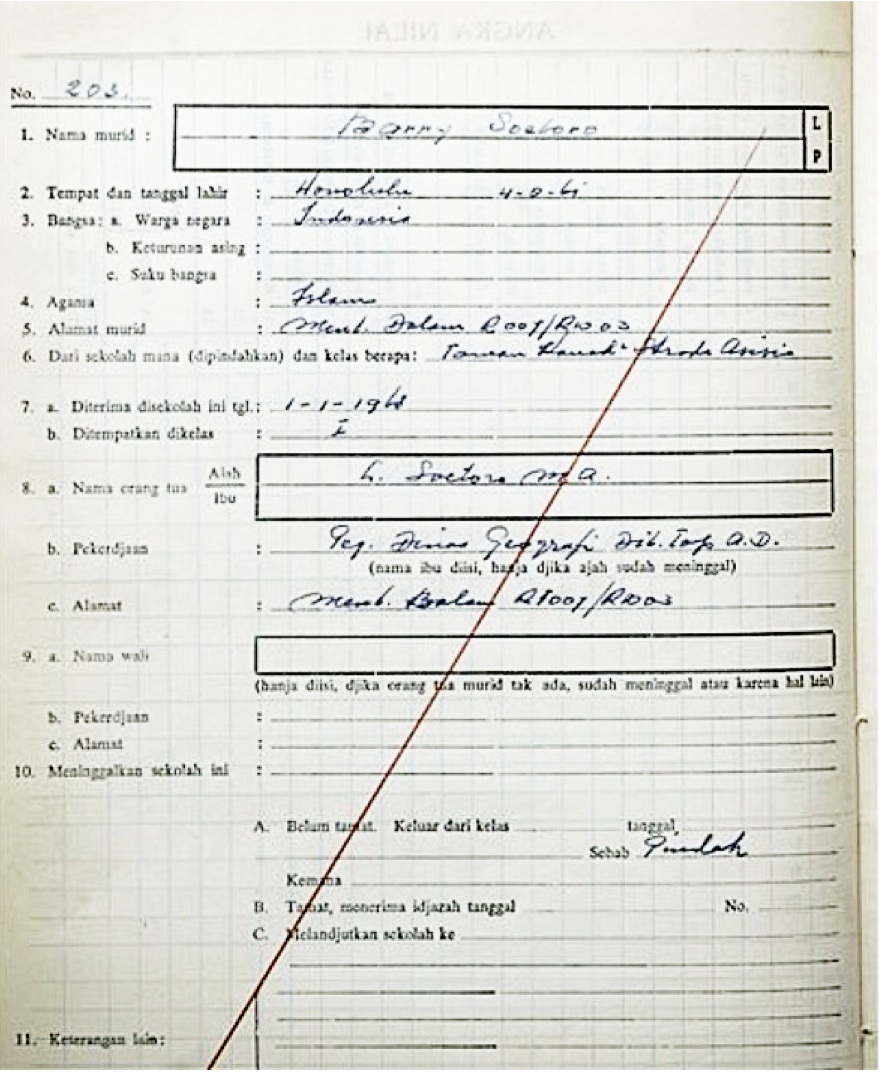
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the United States. He previously served as a U.S. senator from Illinois from 2005 to 2008 and as an Illinois state senator from 1997 to 2004, and previously worked as a civil rights lawyer before entering politics. Obama was born in Honolulu, Hawaii. After graduating from Columbia University in 1983, he worked as a community organizer in Chicago. In 1988, he enrolled in Harvard Law School, where he was the first black president of the '' Harvard Law Review''. After graduating, he became a civil rights attorney and an academic, teaching constitutional law at the University of Chicago Law School from 1992 to 2004. Turning to elective politics, he represented the 13th district in the Illinois Senate from 1997 until 2004, when he ran for the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |