|
Black Student Movement
The Black Student Movement (BSM) is an organization at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. It is the second largest student-run organization and one of the largest cultural organizations on the school's campus. The organization was created on November 7, 1967 to combat problems of black recruit, admissions, and integration on UNC-CH campus. History The Black Student Movement was established on November 7, 1967 as a result Black student dissatisfaction with the NAACP chapter on the campus and because of the slow enrollment of the black population on campus. In 1961 the NAACP chapter had been formed and had actively protested against segregation and discrimination, but by 1967 more militant students led by Preston Dobbins and Reggie Hawkins felt that the NAACP was overly conservative. They voted to disband the chapter and instead form the Black Student Movement. The NAACP's magazine, ''The Crisis'', reported that the chapter president, Kelly Alexander Jr., opposed demand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of North Carolina At Chapel Hill
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, the designation is reserved for colleges that have a graduate school. The word ''university'' is derived from the Latin ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". The first universities were created in Europe by Catholic Church monks. The University of Bologna (''Università di Bologna''), founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *Being a high degree-awarding institute. *Having independence from the ecclesiastic schools, although conducted by both clergy and non-clergy. *Using the word ''universitas'' (which was coined at its foundation). *Issuing secular and non-secular degrees: grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law, notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The unive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
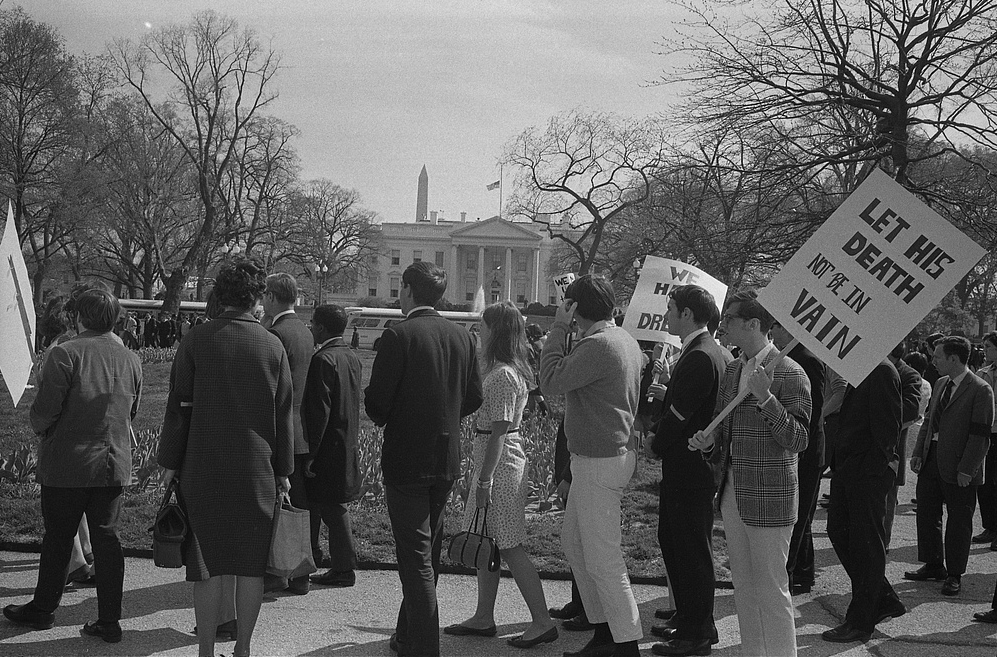
Assassination Of Martin Luther King
Martin Luther King Jr., an African-American clergyman and civil rights leader, was fatally shot at the Lorraine Motel in Memphis, Tennessee, on April 4, 1968, at 6:01 p.m. CST. He was rushed to St. Joseph's Hospital, where he died at 7:05 p.m. He was a prominent leader of the civil rights movement and a Nobel Peace Prize laureate who was known for his use of nonviolence and civil disobedience. James Earl Ray, a fugitive from the Missouri State Penitentiary, was arrested on June 8, 1968, at London's Heathrow Airport, extradited to the United States and charged with the crime. On March 10, 1969, he pleaded guilty and was sentenced to 99 years in the Tennessee State Penitentiary. He later made many attempts to withdraw his guilty plea and to be tried by a jury, but was unsuccessful. Ray died in prison in 1998. The King family and others believe that the assassination was the result of a conspiracy involving the U.S. government, the mafia, and Memphis police, as all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of North Carolina At Chapel Hill Student Organizations
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. The first universities in Europe were established by Catholic Church monks. The University of Bologna (), Italy, which was founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *being a high degree-awarding institute. *using the word ''universitas'' (which was coined at its foundation). *having independence from the ecclesiastic schools and issuing secular as well as non-secular degrees (with teaching conducted by both clergy and non-clergy): grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law, notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university in medieval life, 1179–1499", McFarland, 2008, , p. 55f.de Ridder-Symoens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Action Movement
The Black Action Movement was a series of protests by African American students against the policies and actions of the University of Michigan. The protests themselves took place on three occasions in 1970, 1975, and 1987 (BAM I, BAM II, BAM III). Many student organizations participated in the movement, which has been called one of the most challenging for administrators in the school's history. Alan Glenn of the '' Ann Arbor Chronicle'' said of the 1970 protests that "the BAM strike became one of the few protests of that era in which the students could make a valid claim of victory." First protest After the Assassination of Martin Luther King Jr. in 1968, students protested against the University of Michigan administration for lack of support for minorities on campus. The university agreed to certain concessions and to increase integration on campus. The 1970 Black Action Movement protests first began in late 1969, when black student organizations began to chafe at the slow progress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereotype
In social psychology, a stereotype is a generalized belief about a particular category of people. It is an expectation that people might have about every person of a particular group. The type of expectation can vary; it can be, for example, an expectation about the group's personality, preferences, appearance or ability. Stereotypes are sometimes overgeneralized, inaccurate, and resistant to new information, but can sometimes be accurate. While such generalizations about groups of people may be useful when making quick decisions, they may be erroneous when applied to particular individuals and are among the reasons for prejudicial attitudes. Explicit stereotypes An explicit stereotype refers to stereotypes that one is aware that one holds, and is aware that one is using to judge people. If person ''A ''is making judgments about a ''particular'' person ''B'' from a group ''G'', and person ''A'' has an explicit stereotype for group ''G'', their decision bias can be partiall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
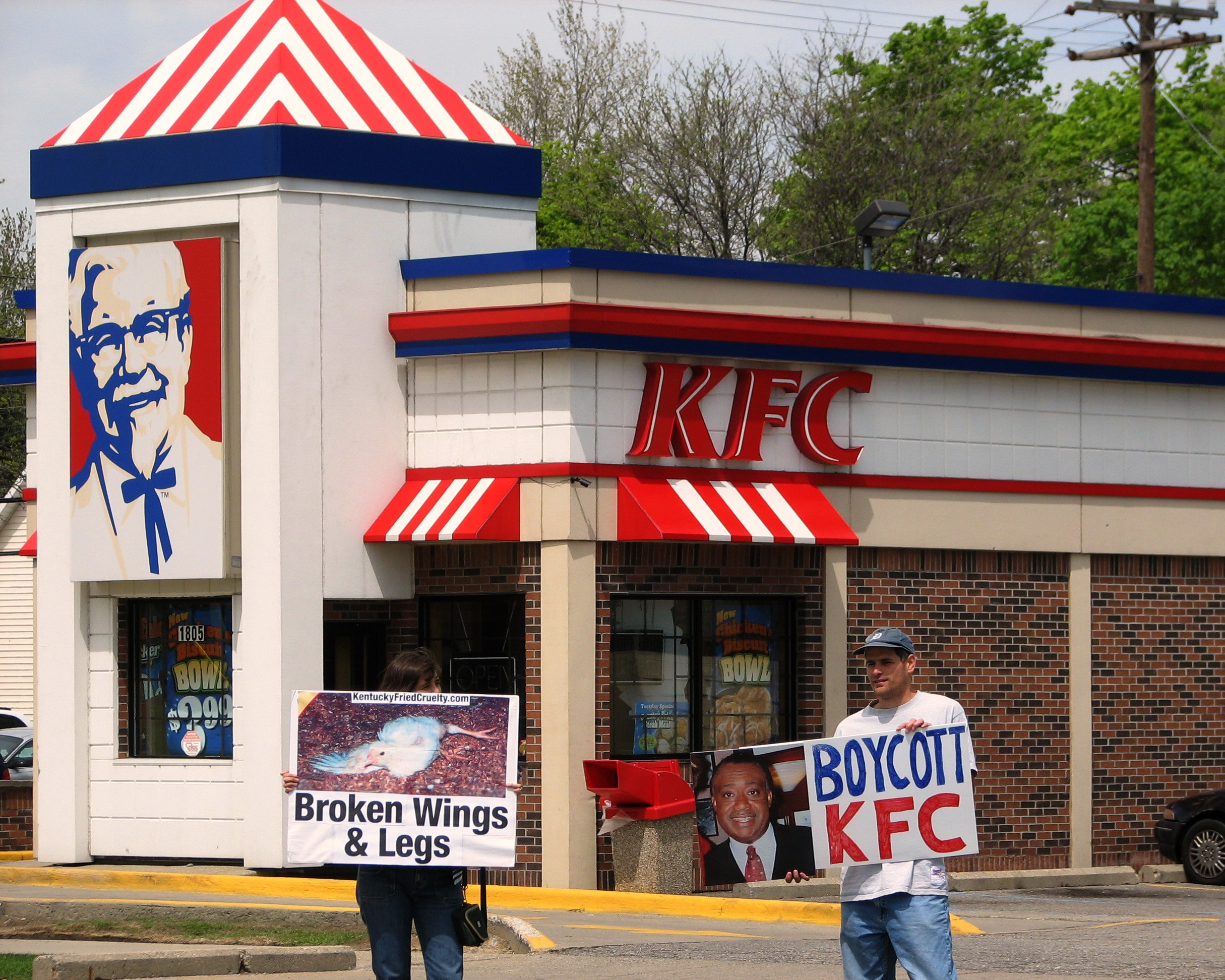
Boycott
A boycott is an act of nonviolent, voluntary abstention from a product, person, organization, or country as an expression of protest. It is usually for moral, social, political, or environmental reasons. The purpose of a boycott is to inflict some economic loss on the target, or to indicate a moral outrage, to try to compel the target to alter an objectionable behavior. The word is named after Captain Charles Boycott, agent of an absentee landlord in Ireland, against whom the tactic was successfully employed after a suggestion by Irish nationalist leader Charles Stewart Parnell and his Irish Land League in 1880. Sometimes, a boycott can be a form of consumer activism, sometimes called moral purchasing. When a similar practice is legislated by a national government, it is known as a sanction. Frequently, however, the threat of boycotting a business is an empty threat, with no significant effect on sales. Etymology The word ''boycott'' entered the English language during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picketing (protest)
Picketing is a form of protest in which people (called pickets or picketers) congregate outside a place of work or location where an event is taking place. Often, this is done in an attempt to dissuade others from going in (" crossing the picket line"), but it can also be done to draw public attention to a cause. Picketers normally endeavor to be non-violent. It can have a number of aims, but is generally to put pressure on the party targeted to meet particular demands or cease operations. This pressure is achieved by harming the business through loss of customers and negative publicity, or by discouraging or preventing workers or customers from entering the site and thereby preventing the business from operating normally. Picketing is a common tactic used by trade unions during strikes, who will try to prevent dissident members of the union, members of other unions and non-unionised workers from working. Those who cross the picket line and work despite the strike are known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confederate Flag
The flags of the Confederate States of America have a history of three successive designs during the American Civil War. The flags were known as the "Stars and Bars", used from 1861 to 1863; the "Stainless Banner", used from 1863 to 1865; and the "Blood-Stained Banner", used in 1865 shortly before the Confederacy's dissolution. A rejected national flag design was also used as a battle flag by the Confederate Army and featured in the "Stainless Banner" and "Blood-Stained Banner" designs. Although this design was never a national flag, it is the most commonly recognized symbol of the Confederacy. Since the end of the Civil War, private and official use of the Confederate flags, particularly the battle flag, has continued amid philosophical, political, cultural, and racial controversy in the United States. These include flags displayed in states; cities, towns and counties; schools, colleges and universities; private organizations and associations; and individuals. The battle fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Evander McNair
Robert Evander McNair Sr. (December 14, 1923November 17, 2007) was the 108th governor of South Carolina, a Democrat, who served from 1965 to 1971. Early life and education McNair was born in Cades, a town in Williamsburg County, South Carolina. In 1944, he married Josephine Robinson of Allendale, South Carolina. He served in the U.S. Navy during World War II, having been awarded a Bronze Star. After the war, he completed his bachelor's degree in 1947 at the University of South Carolina, where he was a member of the Euphradian Society. He received a law degree at the same school in 1948. While attending USC, McNair served as the first governor of the South Carolina Student Legislature, was initiated into the Kappa Sigma fraternity. Early career He went on to practice law in Moncks Corner and Allendale, South Carolina. from which he was elected in 1950 to the South Carolina House of Representatives. He was elected lieutenant governor in 1962, then succeeded Donald S. Russell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orangeburg Massacre
The Orangeburg massacre refers to the shooting of protesters by South Carolina Highway Patrol officers in Orangeburg, South Carolina, on the South Carolina State University campus on the evening of February 8, 1968. About 200 protesters had previously demonstrated against racial segregation at a local bowling alley. Three of the protesters, African-American males, were killed and 28 other protesters were injured. Background There were several incidents centering on the segregation of the local bowling alley, All-Star Bowling Lane, that led up to the Orangeburg Massacre on February 8, 1968. In the fall of 1967, some of the black leaders within the community tried to convince Harry K. Floyd, the owner of the bowling alley, to allow African Americans. Floyd was unwilling to desegregate and as a result, protests began in early February 1968. On February 5, 1968, a group of around 40 students from South Carolina State University entered the bowling alley and left peacefully after t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campus
A campus is traditionally the land on which a college or university and related institutional buildings are situated. Usually a college campus includes libraries, lecture halls, residence halls, student centers or dining halls, and park-like settings. A modern campus is a collection of buildings and grounds that belong to a given institution, either academic or non-academic. Examples include the Googleplex and the Apple Campus. Etymology The word derives from a Latin word for "field" and was first used to describe the large field adjacent Nassau Hall of the College of New Jersey (now Princeton University) in 1774. The field separated Princeton from the small nearby town. Some other American colleges later adopted the word to describe individual fields at their own institutions, but "campus" did not yet describe the whole university property. A school might have one space called a campus, another called a field, and still another called a yard. History The tradition of a camp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time-and-a-half
Time-and-a-half is payment to a worker (or workers) at 1.5 times their usual hourly rate. It is usually paid as an incentive to work on a particular day (such as Saturday) or as government-mandated compensation for having workers work on particular days (such as public holidays). New Zealand In New Zealand, if an employee works on a public holiday, the employee gets time-and-a-half for the hours worked and, if the day was an otherwise working day for the employee, an alternative holiday to take at another time. United States In the United States, this provision, as well as the minimum wage, was first instituted by the Fair Labor Standards Act. The act was passed in 1938, during the Great Depression. Overtime pay was intended as a penalty or fine upon the employer, not as a bonus to the employee. Hoping to increase employment opportunities, Congress encouraged employers to hire more workers for the same amount of time: it was believed to be better for three workers to work forty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)

