|
Black-capped Paradise Kingfisher
The black-capped paradise kingfisher (''Tanysiptera nigriceps'') or black-headed paradise kingfisher, is a bird in the tree kingfisher subfamily, Halcyoninae. It is native to several islands in the Bismarck Archipelago to the east of New Guinea. Like all paradise kingfishers, this bird has colourful plumage with a red bill and long distinctive tail streamers. Taxonomy The first formal description of the black-capped paradise kingfisher was by the English lawyer and zoologist Philip Sclater in 1877. He coined the current binomial name ''Tanysiptera nigriceps''. The genus ''Tanysiptera'' had been introduced by the Irish zoologist Nicholas Aylward Vigors in 1825. The name ''Tanysiptera'' is from classical Greek ''tanusipteros'' meaning "long-feathered". The specific epithet ''nigriceps'' is from the Latin ''niger'' for "black" and ''-ceps'' for "head". The black-capped paradise kingfisher has sometimes been considered as a subspecies as the buff-breasted paradise kingfisher (''Tan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip Sclater
Philip Lutley Sclater (4 November 1829 – 27 June 1913) was an England, English lawyer and zoologist. In zoology, he was an expert ornithologist, and identified the main zoogeographic regions of the world. He was Secretary of the Zoological Society of London for 42 years, from 1860–1902. Early life Sclater was born at Tangier Park, in Wootton St Lawrence, Hampshire, where his father William Lutley Sclater had a country house. George Sclater-Booth, 1st Baron Basing was Philip's elder brother. Philip grew up at Hoddington House where he took an early interest in birds. He was educated in school at Twyford and at thirteen went to Winchester College and later Corpus Christi College, Oxford where he studied scientific ornithology under Hugh Edwin Strickland. In 1851 he began to study law and was admitted a Fellow of Corpus Christi College. In 1856 he travelled to America and visited Lake Superior and the upper St. Croix River (Wisconsin–Minnesota), St. Croix River, cano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oscar Neumann
Oscar Rudolph Neumann (3 September 1867 in Berlin – 17 May 1946 in Chicago) was a German ornithologist and naturalist who explored and collected specimens in Africa. He fled via Cuba and settled in the United States to escape Nazi persecution of Jews. Neumann's starling (''Onychognathus neumanni'') and several other species are named after him. Neumann was born in wealthy Jewish family, the son of Maximilian and Anna née Meyer. A younger sister of his was Elsa Neumann (1872-1902) who became one of the first physics doctorates from Berlin University. Another sister Alice was a sculptor. He travelled to German East Africa across Tanganyika, Uganda and Kenya in 1892 and collected for the Berlin Museum publishing descriptions. In 1899 he accompanied Baron Carlo von Erlanger through Somaliland and southern Ethiopia, collecting birds that went to Lord Walter Rothschild's bird collection in Tring. In 1915 he went to New Guinea and also made an expedition to Sulawesi in 1938 sponso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birds Of New Britain
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the ostrich. There are about ten thousand living species, more than half of which are passerine, or "perching" birds. Birds have whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further evolved for swimming. Birds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanysiptera
The paradise kingfishers (genus ''Tanysiptera'') are a group of tree kingfishers endemic to New Guinea — with the exception of two species also present in the Moluccas and Queensland. The genus was erected by the Irish zoologist Nicholas Aylward Vigors in 1825. The type species is the common paradise kingfisher. The name ''Tanysiptera'' is from classical Greek ''tanusipteros'' meaning "long-feathered". The birds in the genus have distinctive long tail streamers. Habitat and distribution The centre of paradise kingfishers is New Guinea: Several species occur on this 786,000 km2 large island. In addition, there are several island endemisms that occur on islands of the Moluccas and the Louisiade Archipelago. Most paradise kingfishers are resident birds. The buff-breasted paradise kingfisher, which also occurs in the extreme northeast of Australia, moves to New Guinea in the winter half-year. The common paradise kingfisher has the biggest spread among the paradisiacis birds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossary Of Bird Terms
The following is a glossary of common English language terms used in the description of birds—warm-blooded vertebrates of the class Aves and the only living dinosaurs, characterized by , the ability to in all but the approximately 60 extant species of flightless birds, toothless, , the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Among other details such as size, proportions and shape, terms defining bird features developed and are used to describe features unique to the class—especially evolutionary adaptations that developed to aid flight. There are, for example, numerous terms describing the complex structural makeup of feathers (e.g., , and ); types of feathers (e.g., , and feathers); and their growth and loss (e.g., , and ). There are thousands of terms that are unique to the study of birds. This glossary makes no attempt to cover them all, concentrating on terms that might be found across ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nominate Race
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species have subspecies, but for those that do there must be at least two. Subspecies is abbreviated subsp. or ssp. and the singular and plural forms are the same ("the subspecies is" or "the subspecies are"). In zoology, under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, the subspecies is the only taxonomic rank below that of species that can receive a name. In botany and mycology, under the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants, other infraspecific ranks, such as variety, may be named. In bacteriology and virology, under standard bacterial nomenclature and virus nomenclature, there are recommendations but not strict requirements for recognizing other important infraspecific ranks. A taxonomist decides whether ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Of York Island, Papua New Guinea
Duke of York Island is the largest island of Duke of York Islands, Papua New Guinea, at . The island is named after Prince Edward, the brother of King George III of Great Britain. There is also a Duke of York Island at in North Victoria Land in East-Antarctica Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest contine ..., at the southern end of Robertson Bay, not far from Cape Adare. Islands of Papua New Guinea {{PapuaNewGuinea-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
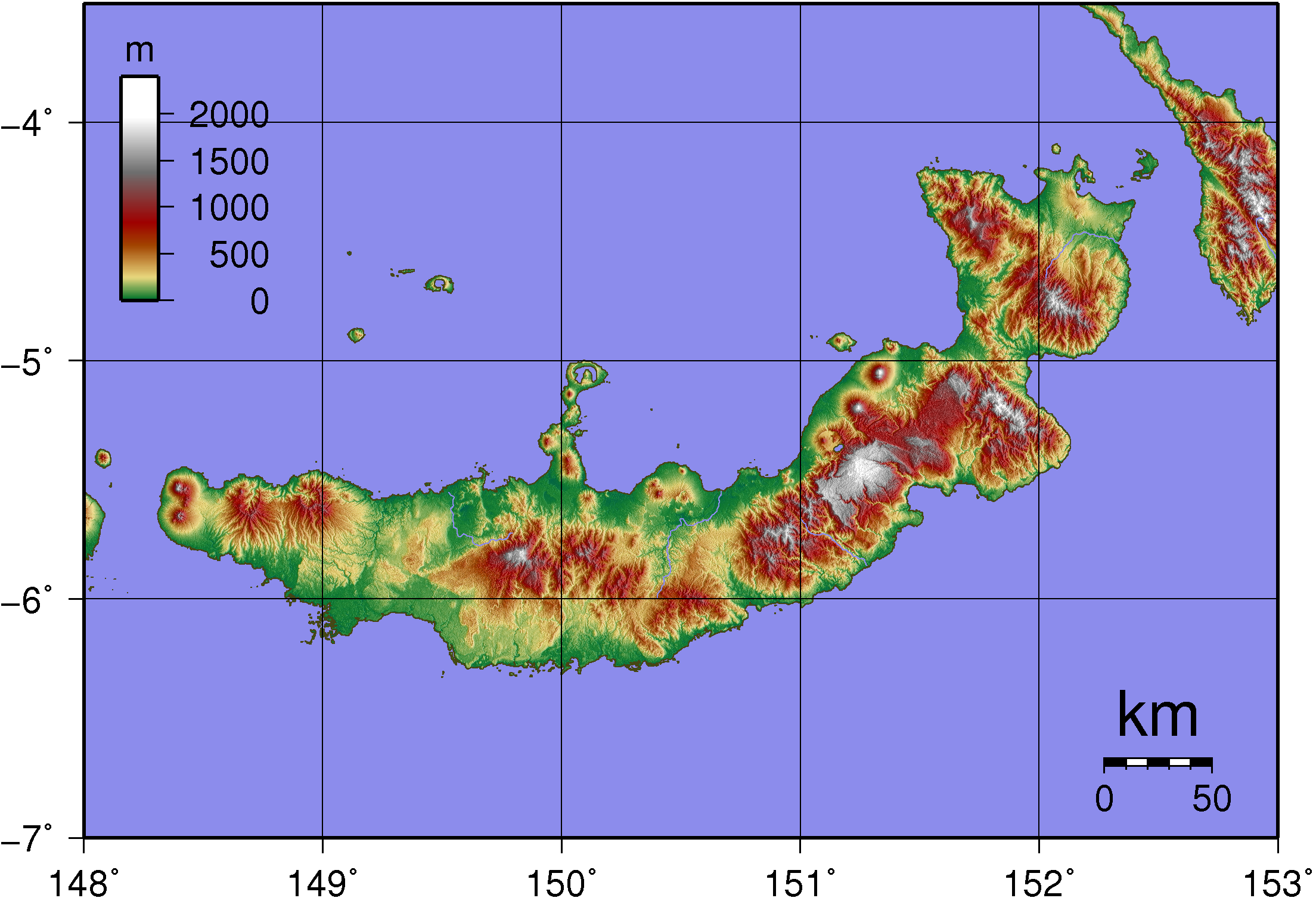
New Britain
New Britain ( tpi, Niu Briten) is the largest island in the Bismarck Archipelago, part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea. It is separated from New Guinea by a northwest corner of the Solomon Sea (or with an island hop of Umboi the Dampier and Vitiaz Straits) and from New Ireland by St. George's Channel. The main towns of New Britain are Rabaul/Kokopo and Kimbe. The island is roughly the size of Taiwan. While the island was part of German New Guinea, it was named Neupommern ("New Pomerania"). In common with most of the Bismarcks it was largely formed by volcanic processes, and has active volcanoes including Ulawun (highest volcano nationally), Langila, the Garbuna Group, the Sulu Range, and the volcanoes Tavurvur and Vulcan of the Rabaul caldera. A major eruption of Tavurvur in 1994 destroyed the East New Britain provincial capital of Rabaul. Most of the town still lies under metres of ash, and the capital has been moved to nearby Kokopo. Geography New Britain e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umboi Island
Umboi (also named Rooke or Siassi) is a volcanic island between the mainland of Papua New Guinea and the island of New Britain. It is separated from New Britain by the Dampier Strait and Huon Peninsula, and New Guinea by the Vitiaz Strait. It has an elevation of . Languages are Papuan Kobai; and Austronesian: Mbula, Karanai, and Saveng languages. The Siassi Archipelago lies off the southeast coast of Umboi Island (a total of 18 islands, only seven are inhabited). During the mid-1920s, the population of the Siassi Islands was a little over 700 people. It had more than doubled (to almost 1700 people) by the early 1960s, and then decreased to a little more than 1600 people by the early 1980s. The Siassi support themselves through traditional trade based on a barter system; they are important middlemen who deliver pigs, pots and wooden bowls by sea in their canoes. See also * List of volcanoes in Papua New Guinea * Siassi Rural LLG Siassi Rural LLG is a local-level govern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buff-breasted Paradise Kingfisher
The buff-breasted paradise kingfisher (''Tanysiptera sylvia'') is a bird in the tree kingfisher subfamily, Halcyoninae. It is native to Australia and New Guinea. It migrates in November from New Guinea to its breeding grounds in the rainforest of North Queensland, Australia. Like all paradise kingfishers, this bird has colourful plumage with a red bill, buff breast and distinctive long tail streamers. Taxonomy The buff-breasted paradise kingfisher was first described by the English ornithologist and bird artist John Gould in 1850 as ''Tanysiptera sylvia'' from specimens supplied by the naturalist John MacGillivray, which had been collected on the Cape York Peninsula in Australia. The genus name is derived from the Greek meaning 'long' and meaning 'wing', whilst ''sylvia'' is from the Latin ''silva'', meaning 'forest'.Lederer, R & Burr, C (2014). ''Latin for birdwatchers''. Crows Nest, NSW: Allen & Unwin. . Until recently the species was known as the white-tailed kingfisher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tree Kingfisher
The tree kingfishers, also called wood kingfishers or Halcyoninae, are the most numerous of the three subfamilies of birds in the kingfisher family, with around 70 species divided into 12 genera, including several species of kookaburras. The subfamily appears to have arisen in Indochina and Maritime Southeast Asia and then spread to many areas around the world. Tree kingfishers are widespread through Asia and Australasia, but also appear in Africa and the islands of the Pacific and Indian Oceans, using a range of habitats from tropical rainforest to open woodlands. The tree kingfishers are short-tailed, large-headed, compact birds with long, pointed bills. Like other Coraciiformes, they are brightly coloured. Most are monogamous and territorial, nesting in holes in trees or termite nests. Both parents incubate the eggs and feed the chicks. Although some tree kingfishers frequent wetlands, none are specialist fish-eaters. Most species dive onto prey from a perch, mainly taking s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas Aylward Vigors
Nicholas Aylward Vigors (1785 – 26 October 1840) was an Ireland, Irish zoologist and politician. He popularized the classification of birds on the basis of the quinarian system. Early life Vigors was born at Old Leighlin, County Carlow on 1785 as first son from Capt. Nicholas Aylward Vigors which served in 29th (Worcestershire) Regiment of Foot, 29th (Worcestershire) Regiment and, his first wife, Catherine Vigors, daughter of Solomon Richards of Solsborough. He matriculated at Trinity College, Oxford on November 1803 before he was admitted at Lincoln's Inn on November 1806. Without completing his studies, he served in the army during the Peninsular War from 1809 to 1811 and wounded in Battle of Barrosa, Battle of Barossa on 5 March 1811. Though, he haven't completed his studies yet, he still published "An inquiry into the nature and extent of poetick licence" in London at 1810. He then returned to Oxford to continued his studies and achieved his Bachelor of Arts on 1817 an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)