|
Birth Tourism In Hong Kong
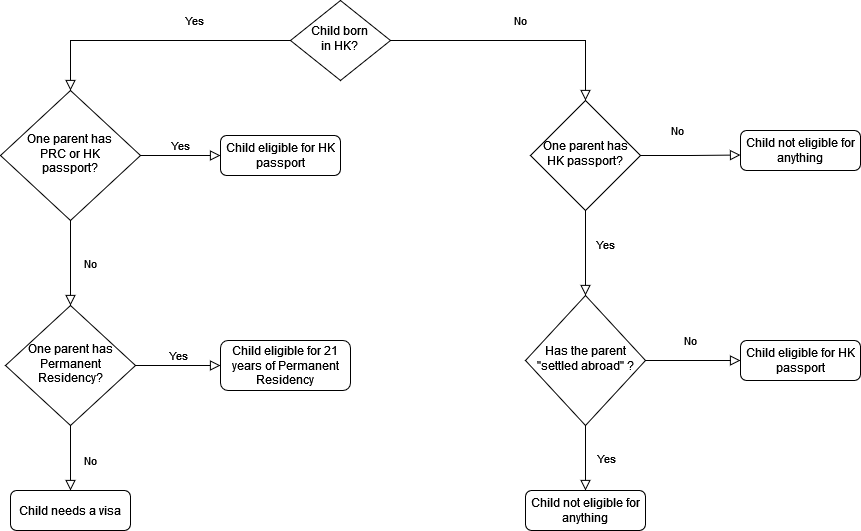
The term "anchor babies in Hong Kong" ( zh, c=雙非嬰兒, links=no) refers to children born in Hong Kong whose parents (usually from Mainland China) are not Hong Kong permanent residents. Since 2003, an Individual Visit Scheme targeted to boost the economy of Hong Kong has begun. It provides an opportunity for pregnant women visiting from Mainland China to give birth to their infants in Hong Kong. This entitles their children to the right of abode in Hong Kong as well as the opportunity to benefit from Hong Kong's education system. These pregnant women use local obstetric services through legal (e.g. births through reservation) or illegal (e.g. A&E births) ways. The large influx of visiting Mainland pregnant women causes a shortage of hospital resources, resulting in much criticism of visiting pregnant women and their anchor children, including labelling them as "locusts". Over 170,000 new births were anchor babies between 2001 and 2011 in which 32,653 were born in 2010. CY Leu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mainland China
"Mainland China" is a geopolitical term defined as the territory governed by the People's Republic of China (including islands like Hainan or Chongming), excluding dependent territories of the PRC, and other territories within Greater China. By convention, the territories that fall outside of the Chinese mainland include: * Hong Kong, a quasi-dependent territory under PRC rule that is officially designated a " Special Administrative Region of the PRC" (formerly a British colony) * Macau, a quasi-dependent territory under PRC rule that is officially designated a "Special Administrative Region of the PRC" (formerly a Portuguese colony) * Territories ruled by the Republic of China (ROC, commonly referred to as Taiwan), including the island of Taiwan, the Penghu (Pescadores) islands in the Taiwan Strait, and the islands Kinmen, Matsu, and Wuqiu (Kinmen) offshore of Fujian. Overseas Chinese, especially Malaysian Chinese and Chinese Singaporeans, use this term to describe p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permanent Residents Of Hong Kong
The Hong Kong Basic Law classifies residents of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region () as either permanent residents or non-permanent residents. Hong Kong residents have rights under the Basic Law including freedom of speech, freedom of movement and freedom of religious belief. Permanent residents Hong Kong permanent residents have the right of abode in Hong Kong and the right to vote in elections for the Legislative Council and the District Council. It is also the ''de facto'' citizenship status in Hong Kong because most of citizen rights are associated with the right of abode. However, Hong Kong permanent residents are not entitled to a Hong Kong passport or stand for office in some Legislative Council constituencies, unless they are also naturalised Chinese citizens. Under the Hong Kong Basic Law, permanent residents are: # Chinese citizens born in Hong Kong before or after the establishment of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region; # Chinese citizens wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Individual Visit Scheme
The Individual Visit Scheme begun on 28 July 2003 allowing travelers from Mainland China to visit Hong Kong and Macau on an individual basis; prior to the Scheme, Mainland residents could only visit on business visas or on group tours. The outbreak of SARS in Hong Kong from March to June 2003 resulted in a sharp drop in Mainland and foreign visitors to an unprecedented low, adversely affecting the tourist industry. The main reason for launching the Individual Visit Scheme was to boost the economy of Hong Kong and Macau. In the initial stage of the scheme, residents of Beijing, Shanghai, and 8 Guangdong provincial cities (Dongguan, Foshan, Guangzhou, Huizhou, Jiangmen, Shenzhen, Zhongshan and Zhuhai) could apply for visas to visit the two 'Special Administrative Regions' individually. The scheme was extended to all 21 cities of Guangdong province in July 2004, and to 9 other cities in Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Fujian provinces in July 2004. The visas, issued by the Public Securit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Of Abode In Hong Kong
Right of abode in Hong Kong entitles a person to live and work in the territory without any restrictions or conditions of stay. Someone who has that right is a Hong Kong permanent resident. Foreign nationals may acquire the right of abode after meeting a seven-year residency requirement and are given most rights usually associated with citizenship, including the right to vote in regional elections. However, they are not entitled to hold territorial passports or stand for office in some Legislative Council constituencies, unless they also naturalise as Chinese citizens. As a special administrative region of China, Hong Kong does not have its own nationality law and natural-born residents are generally Chinese citizens. Prior to 1997, the territory was a colony of the United Kingdom and right of abode was tied to British nationality law. Although Hong Kong, mainland China, and Macau constitute a single country, local residents with Chinese citizenship do not have automatic re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CY Leung
Leung Chun-ying (; born 12 August 1954), also known as CY Leung, is a Hong Kong politician and chartered surveyor, who has served as vice-chairman of the National Committee of the Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference since March 2017. He was previously the third Chief Executive of Hong Kong between 2012 and 2017. A surveyor by profession, Leung entered politics when he joined the Hong Kong Basic Law Consultative Committee (HKBLCC) in 1985 and became its secretary-general in 1988. In 1999, he was appointed the convenor of the Executive Council of Hong Kong, a position he held until 2011, when he resigned to run in the 2012 Chief Executive election. Initially regarded as the underdog, Leung ran a successful campaign against front-runner Henry Tang, receiving 689 votes from the Election Committee and with the support of the Liaison Office. At the beginning of his administration, Leung faced the anti-Moral and National Education protests and the Hong Kong Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birth Tourism
Birth tourism is the practice of traveling to another country for the purpose of giving birth in that country. The main reason for birth tourism is to obtain citizenship for the child in a country with birthright citizenship (''jus soli''). Such a child is sometimes called an "anchor baby" if their citizenship is intended to help their parents obtain permanent residency in the country. Other reasons for birth tourism include access to public schooling, healthcare, sponsorship for the parents in the future, or even circumvention of China's two-child policy. Popular destinations include the United States and Canada. Another target for birth tourism is Hong Kong, where some mainland Chinese citizens travel to give birth to gain right of abode for their children. In an effort to discourage birth tourism, Australia, France, Pakistan, Germany, Ireland, New Zealand, South Africa, and the United Kingdom have modified their citizenship laws at different times, mostly by granting citizens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hong Kong–Mainland China Conflict
Relations between people in Hong Kong and mainland China have been relatively tense since the early 2000s. Various factors have contributed, including different interpretations of the "one country, two systems" principle; policies of the Hong Kong and central governments to encourage mainland visitors to Hong Kong; and the changing economic environment. More broadly, there exists resentment toward mainland-Hong Kong convergence and assimilation, as well as the increasing interference from the government of China and its ruling Chinese Communist Party (CCP) in Hong Kong's internal affairs. Background Hong Kong was originally ruled by China up to the Qing dynasty in 1842 when the Treaty of Nanking ceded the island to the British Empire and later expanded to include the Kowloon Peninsula in 1860 after the Second Opium War and later by the Convention for the Extension of Hong Kong Territory in 1898 to lease the New Territories. From 1941 to 1945, it was occupied by the Japanese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Of Abode In Hong Kong
Right of abode in Hong Kong entitles a person to live and work in the territory without any restrictions or conditions of stay. Someone who has that right is a Hong Kong permanent resident. Foreign nationals may acquire the right of abode after meeting a seven-year residency requirement and are given most rights usually associated with citizenship, including the right to vote in regional elections. However, they are not entitled to hold territorial passports or stand for office in some Legislative Council constituencies, unless they also naturalise as Chinese citizens. As a special administrative region of China, Hong Kong does not have its own nationality law and natural-born residents are generally Chinese citizens. Prior to 1997, the territory was a colony of the United Kingdom and right of abode was tied to British nationality law. Although Hong Kong, mainland China, and Macau constitute a single country, local residents with Chinese citizenship do not have automatic re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law Of Hong Kong
The law of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region has its foundation in the English common law system, inherited from being a former British colony and dependent territory. There are several sources of law, the primary ones being statutes enacted by the Legislative Council of Hong Kong and case law made by decisions of the courts of Hong Kong. Since the handover in 1997, the constitutional framework is provided by the Hong Kong Basic Law, which is a piece of National Law of the People's Republic of China and has, practically, constitutional status in Hong Kong. The principle of ‘one country, two systems’ was enshrined in Article 5 of the Basic Law until at least 2047, which contrasts the ‘socialist system and policies’ and ‘the previous capitalist system and way of life’. The Basic Law provides that the common law system shall be maintained. Some commentators described the theoretically hybrid system of civil law and common law as unique, although there are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hong Kong Society
Hong may refer to: Places *Høng, a town in Denmark *Hong Kong, a city and a special administrative region in China *Hong, Nigeria *Hong River in China and Vietnam *Lake Hong in China Surnames *Hong (Chinese name) *Hong (Korean name) Organizations *Hong (business), general term for a 19th–20th century trading company based in Hong Kong, Macau or Canton *Hongmen (洪門), a Chinese fraternal organization Creatures *Hamsa (bird), a mythical bird also known was hong *Hong (rainbow-dragon) ''Hong'' or ''jiang'' () is a two-headed dragon in Chinese mythology, comparable with rainbow serpent legends in various cultures and mythologies. Chinese "rainbow" names Chinese has three "rainbow" words, regular ''hong'' , literary ''didong'' , ..., a two-headed dragon in Chinese mythology * ''Hong'' (genus), a genus of ladybird {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immigration Law
Immigration law refers to the national statutes, regulations Regulation is the management of complex systems according to a set of rules and trends. In systems theory, these types of rules exist in various fields of biology and society, but the term has slightly different meanings according to context. For ..., and legal precedents governing immigration into and deportation from a country. Strictly speaking, it is distinct from other matters such as naturalization and citizenship, although they are sometimes conflated. Countries frequently maintain laws that regulate both the rights of entry and exit as well as internal rights, such as the duration of stay, freedom of movement, and the right to participate in commerce or government. Immigration laws vary around the world and throughout history, according to the Society, social and political climate of the place and time, as the acceptance of immigrants sways from the widely Inclusiveness, inclusive to the deeply Nationalism, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |