|
Birmingham Museum Of Science And Industry
Thinktank, Birmingham (formerly known as simply Thinktank) is a science museum in Birmingham, England. Opened in 2001, it is part of Birmingham Museums Trust and is located within the Millennium Point complex on Curzon Street, Digbeth. History The Birmingham Collection of Science & Industry was started in the mid-19th century, initially consisting of collections of weapons from the gun trade and the Birmingham Proof House. The Birmingham Museum & Art Gallery opened in 1885, including science collections. In 1951 the Museum of Science and Industry opened at Elkington Silver Electroplating Works, Newhall Street. Over the following years, the museum acquired individual artefacts, as well as entire collections, that were related to local industry and the history of science and technology. Birmingham City Council decided in 1995 to relocate the museum when it was given an opportunity by the Millennium Commission to construct a new building. The former museum closed in 1997, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millennium Point (Birmingham)
Millennium Point is a multi-use meeting and conference venue, public building and charitable trust in Birmingham, England, situated in the developing Eastside, Birmingham, Eastside of the city centre. The complex contains multiple event spaces, including a 354-seat auditorium, formerly Giant Screen IMAX cinema; Birmingham Thinktank, Birmingham Science Museum, Royal Birmingham Conservatoire's Birmingham School of Acting, School of Acting and Birmingham City University's Birmingham City University Faculty of Computing, Engineering and The Built Environment, Faculty of Computing, Engineering and The Built Environment, part of Birmingham Metropolitan College. The building is owned by the Millennium Point Charitable Trust with a percentage of profits from the organisation's commercial activity being invested into projects, events and initiatives which support Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics, science, technology, engineering and maths (STEM) and education in the West ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the locomotive's boiler to the point where it becomes gaseous and its volume increases 1,700 times. Functionally, it is a steam engine on wheels. In most locomotives, the steam is admitted alternately to each end of its cylinders, in which pistons are mechanically connected to the locomotive's main wheels. Fuel and water supplies are usually carried with the locomotive, either on the locomotive itself or in a tender coupled to it. Variations in this general design include electrically-powered boilers, turbines in place of pistons, and using steam generated externally. Steam locomotives were first developed in the United Kingdom during the early 19th century and used for railway transport until the middle of the 20th century. Richard Trevithick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LMS Princess Coronation Class
The London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS) Coronation Class is a class of express passenger steam locomotives designed by William Stanier. They were an enlarged and improved version of his previous design, the LMS Princess Royal Class, and on test were the most powerful steam locomotives ever used in Britain at 2,511 dbhp. The locomotives were specifically designed for power as it was intended to use them on express services between London Euston and Glasgow Central; their duties were to include the hauling of a proposed non-stop express, subsequently named the '' Coronation Scot''. The first ten locomotives of the Coronation class were built in a streamlined form in 1937 by the addition of a steel streamlined casing. Five of these ten were specifically set aside to pull the ''Coronation Scot''. Although a later batch of five unstreamlined locomotives was produced in 1938, most of the ensuing Coronation class were outshopped as streamliners. From 1944 until production en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
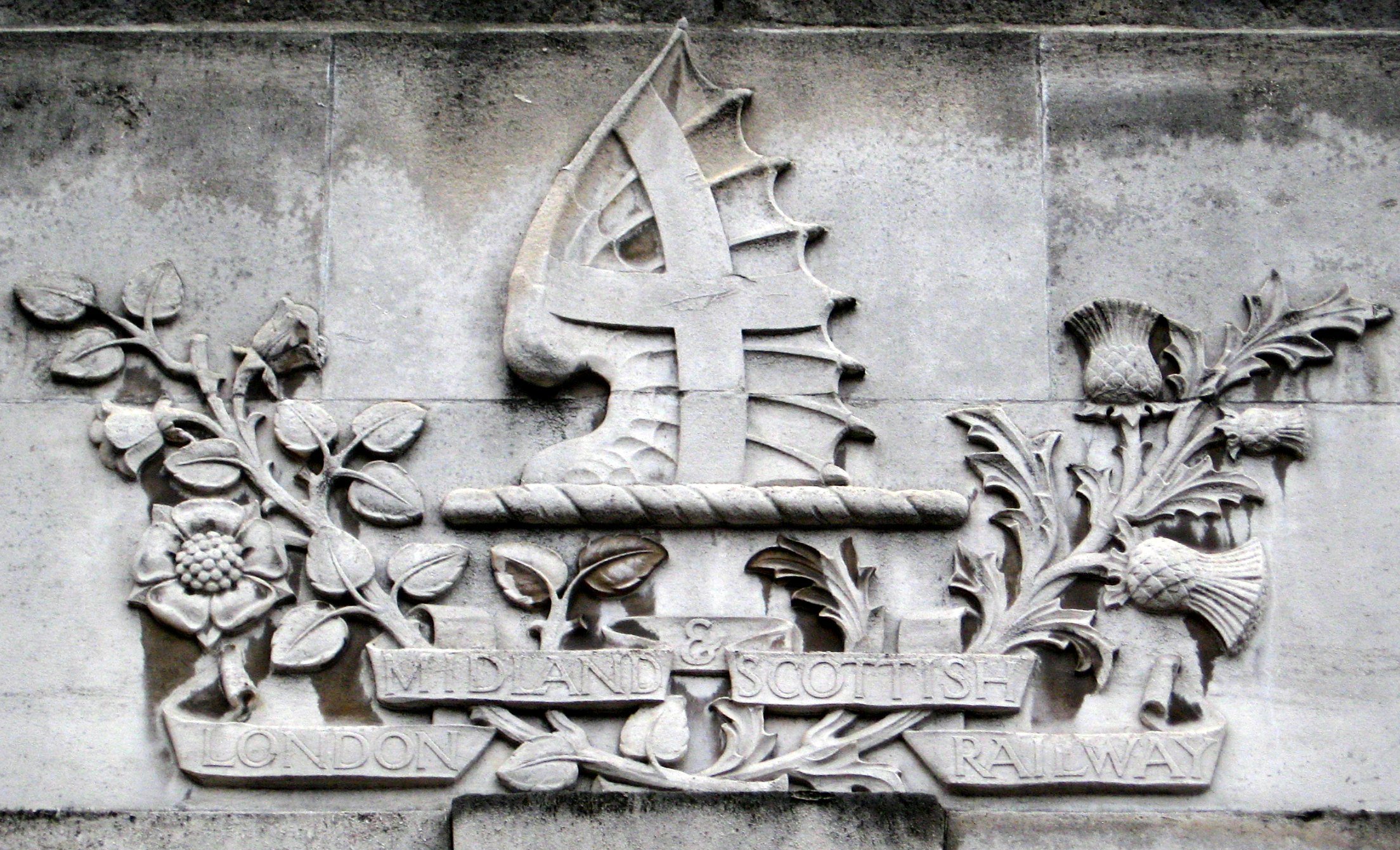
London, Midland And Scottish Railway
The London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMSIt has been argued that the initials LMSR should be used to be consistent with LNER, GWR and SR. The London, Midland and Scottish Railway's corporate image used LMS, and this is what is generally used in historical circles. The LMS occasionally also used the initials LM&SR. For consistency, this article uses the initials LMS.) was a British railway company. It was formed on 1 January 1923 under the Railways Act of 1921, which required the grouping of over 120 separate railways into four. The companies merged into the LMS included the London and North Western Railway, Midland Railway, the Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway (which had previously merged with the London and North Western Railway on 1 January 1922), several Scottish railway companies (including the Caledonian Railway), and numerous other, smaller ventures. Besides being the world's largest transport organisation, the company was also the largest commercial enterprise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
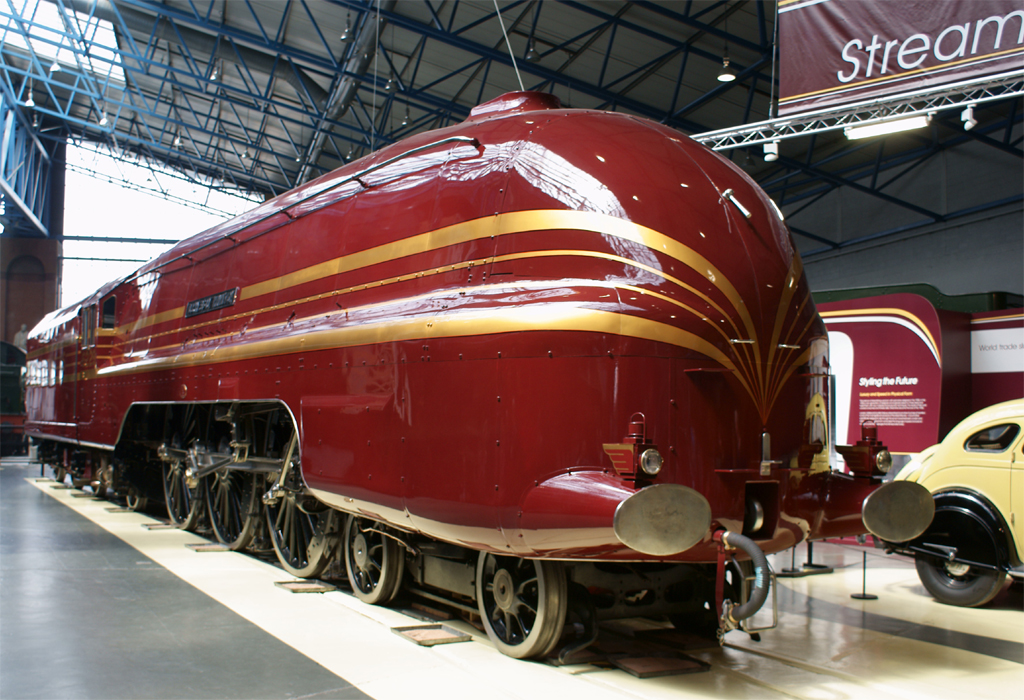
LMS Princess Coronation Class 6235 City Of Birmingham
London Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS), Coronation Class, LMS No. 6235, British Railways No. 46235 ''City of Birmingham'' is a preserved British steam locomotive. 6235 was originally built in 1939 at Crewe, and entered LMS stock in July 1939, one of the third batch (Lot No. 150). As built it was streamlined and was the first to be fitted with a double chimney (previous locomotives being built with single chimneys and later modified). Its livery was LMS crimson lake with cheat lines, but during the Second World War it acquired austere unlined black livery. Though it carried the name ''City of Birmingham'' from new, 6235 was officially named at a ceremony at Birmingham New Street on 20 March 1945, and a special coat of arms plate was then fitted above the nameplate. The streamlining was removed for maintenance reasons in April 1946, making 6235 the first streamliner to be destreamlined, and at the same time it was fitted with smoke deflectors, and livery continued to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Move It - Thinktank Birmingham Science Museum - City Of Birmingham Locomotive 46235 (8619609341)
Move may refer to: People *Daniil Move (born 1985), a Russian auto racing driver Brands and enterprises * Move (company), an online real estate company * Move (electronics store), a defunct Australian electronics retailer * Daihatsu Move Government, law and politics * Emigration * Immigration Organizations * MOVE (Hungary), an early Hungarian fascist group * MOVE (Philadelphia organization), a Philadelphia-based activist organization * The Move (Sam Fife), a nondenominational Christian group Science and technology Computing * Move (command), a shell command * Move, a state transition of a finite state machine * mv (short for ''move''), a Unix command *Move, an upcoming programming language for the Diem (digital currency) blockchain Other uses in science and technology * Motion (physics) * Move α, in linguistics, a feature of the Revised Extended Standard Theory (REST) of transformational grammar developed by Noam Chomsky Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Move'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loughborough College Of Technology
Loughborough ( ) is a market town in the Charnwood borough of Leicestershire, England, the seat of Charnwood Borough Council and Loughborough University. At the 2011 census the town's built-up area had a population of 59,932 , the second largest in the county after Leicester. It is close to the Nottinghamshire border and short distances from Leicester, Nottingham, East Midlands Airport and Derby. It has the world's largest bell foundry, John Taylor Bellfounders, which made bells for the Carillon War Memorial, a landmark in the Queens Park in the town, of Great Paul for St Paul's Cathedral, and for York Minster. History Medieval The earliest reference to Loughborough occurs in the Domesday Book of 1086, which calls it ''Lucteburne''. It appears as ''Lucteburga'' in a charter from the reign of Henry II, and as ''Luchteburc'' in the Pipe Rolls of 1186. The name is of Old English origin and means "Luhhede's ''burh'' or fortified place". Industrialisation The first sign of indu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
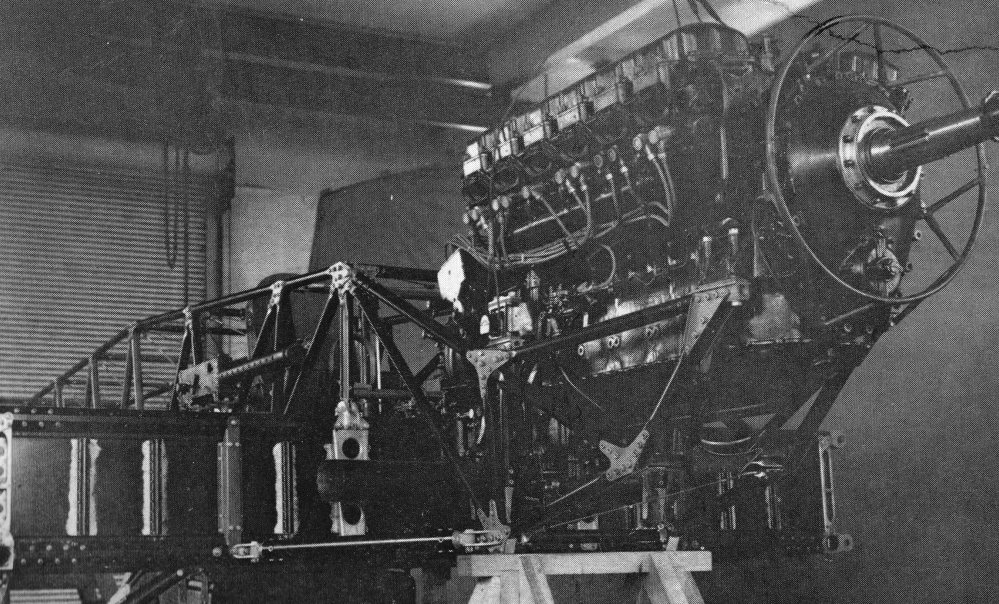
Hawker Aircraft Ltd
Hawker Aircraft Limited was a British aircraft manufacturer that was responsible for some of the most famous products in British aviation history. History Hawker had its roots in the aftermath of the First World War, which resulted in the bankruptcy of the Sopwith Aviation Company. Sopwith test pilot Harry Hawker and three others, including Thomas Sopwith, bought the assets of Sopwith and formed H.G. Hawker Engineering in 1920. In 1933, the company was renamed Hawker Aircraft Limited, and it took advantage of the Great Depression and a strong financial position to purchase the Gloster Aircraft Company in 1934. The next year, it merged with the engine and automotive company Armstrong Siddeley and its subsidiary, Armstrong Whitworth Aircraft, to form Hawker Siddeley Aircraft. This group also encompassed A. V. Roe and Company (Avro). The company continued to produce designs under the "Hawker" name as part of Hawker Siddeley Aircraft, which from 1955 was a division of Hawker Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawker Hurricane
The Hawker Hurricane is a British single-seat fighter aircraft of the 1930s–40s which was designed and predominantly built by Hawker Aircraft Ltd. for service with the Royal Air Force (RAF). It was overshadowed in the public consciousness by the Supermarine Spitfire during the Battle of Britain in 1940, but the Hurricane inflicted 60 percent of the losses sustained by the Luftwaffe in the campaign, and fought in all the major theatres of the Second World War. The Hurricane originated from discussions between RAF officials and aircraft designer Sir Sydney Camm about a proposed monoplane derivative of the Hawker Fury biplane in the early 1930s. Despite an institutional preference for biplanes and lack of interest by the Air Ministry, Hawker refined their monoplane proposal, incorporating several innovations which became critical to wartime fighter aircraft, including retractable landing gear and the more powerful Rolls-Royce Merlin engine. The Air Ministry ordered Hawker's ''Int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Move It - Thinktank Birmingham Science Museum - Hawker Hurricane Mark IV (8620462206)
Move may refer to: People *Daniil Move (born 1985), a Russian auto racing driver Brands and enterprises * Move (company), an online real estate company * Move (electronics store), a defunct Australian electronics retailer * Daihatsu Move Government, law and politics * Emigration * Immigration Organizations * MOVE (Hungary), an early Hungarian fascist group * MOVE (Philadelphia organization), a Philadelphia-based activist organization * The Move (Sam Fife), a nondenominational Christian group Science and technology Computing * Move (command), a shell command * Move, a state transition of a finite state machine * mv (short for ''move''), a Unix command *Move, an upcoming programming language for the Diem (digital currency) blockchain Other uses in science and technology * Motion (physics) * Move α, in linguistics, a feature of the Revised Extended Standard Theory (REST) of transformational grammar developed by Noam Chomsky Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Move'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castle Bromwich
Castle Bromwich () is a large suburban village situated within the Metropolitan Borough of Solihull in the English county of the West Midlands. It is bordered by the rest of the borough to the south east; also Sutton Coldfield to the east and north east, Shard End to the south west, Castle Vale, Erdington and Minworth to the north and Hodge Hill to the west – all areas of the City of Birmingham. It constitutes a civil parish, which had a population of 11,857 according to the 2001 census, falling to 11,217 at the 2011 census. The population has remained quite stable since then; the 2017 population estimate was 12,309. It was a civil parish within the Meriden Rural District of Warwickshire until the Local Government Act 1972 came into force in 1974, when it became part of the Metropolitan Borough of Solihull. In 1861, the population was 613. This rose to just over 1,000 in the 1920s, when half of the original parish was ceded to the City of Birmingham for the construction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)