|
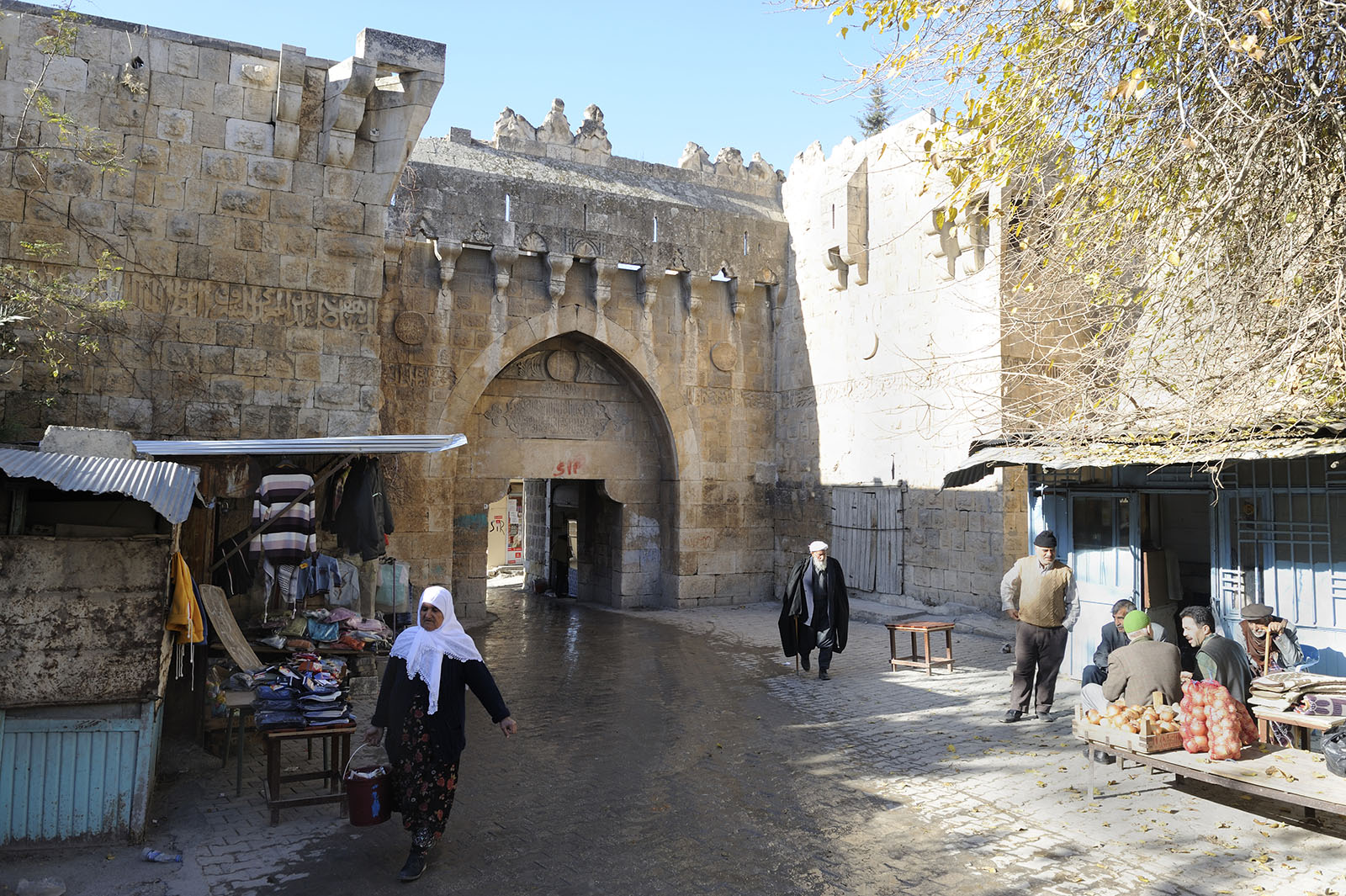
Birecik
Birecik; ku, Bêrecûk is a town and district of Şanlıurfa Province of Turkey, on the Euphrates. Built on a limestone cliff 400 ft. high on the left/east bank of the Euphrates, "at the upper part of a reach of that river, which runs nearly north-south, and just below a sharp bend in the stream, where it follows that course after coming from a long reach flowing more from the west". Etymology The historical name of the town, ''al-Bīra'' in Arabic and ''Bīreh'' in Syriac, derives from the Aramaic ''Bīrthā'', meaning fortress. It later evolved to ''Birecik'' with the addition of the Turkish diminutive suffix, ''cik''. It is called ''Belejik'' amongst the local population. Archaeology Birecik Dam Cemetery is an Early Bronze Age cemetery near Birecik. It was used extensively for about 500 years at the beginning of the third millennium BC. More than 300 graves were excavated here in 1997 and 1998. The site was discovered during the building of the Birecik Dam as part of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birecik Urfa Kap%C4%B1 7265
Birecik; ku, Bêrecûk is a town and district of Şanlıurfa Province of Turkey, on the Euphrates. Built on a limestone cliff 400 ft. high on the left/east bank of the Euphrates, "at the upper part of a reach of that river, which runs nearly north-south, and just below a sharp bend in the stream, where it follows that course after coming from a long reach flowing more from the west". Etymology The historical name of the town, ''al-Bīra'' in Arabic and ''Bīreh'' in Syriac, derives from the Aramaic ''Bīrthā'', meaning fortress. It later evolved to ''Birecik'' with the addition of the Turkish diminutive suffix, ''cik''. It is called ''Belejik'' amongst the local population. Archaeology Birecik Dam Cemetery is an Early Bronze Age cemetery near Birecik. It was used extensively for about 500 years at the beginning of the third millennium BC. More than 300 graves were excavated here in 1997 and 1998. The site was discovered during the building of the Birecik Dam as part of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birecik Ulu Camii 7287
Birecik; ku, Bêrecûk is a town and district of Şanlıurfa Province of Turkey, on the Euphrates. Built on a limestone cliff 400 ft. high on the left/east bank of the Euphrates, "at the upper part of a reach of that river, which runs nearly north-south, and just below a sharp bend in the stream, where it follows that course after coming from a long reach flowing more from the west". Etymology The historical name of the town, ''al-Bīra'' in Arabic and ''Bīreh'' in Syriac, derives from the Aramaic ''Bīrthā'', meaning fortress. It later evolved to ''Birecik'' with the addition of the Turkish diminutive suffix, ''cik''. It is called ''Belejik'' amongst the local population. Archaeology Birecik Dam Cemetery is an Early Bronze Age cemetery near Birecik. It was used extensively for about 500 years at the beginning of the third millennium BC. More than 300 graves were excavated here in 1997 and 1998. The site was discovered during the building of the Birecik Dam as part of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birecik Beyaz Kale 4261
Birecik; ku, Bêrecûk is a town and district of Şanlıurfa Province of Turkey, on the Euphrates. Built on a limestone cliff 400 ft. high on the left/east bank of the Euphrates, "at the upper part of a reach of that river, which runs nearly north-south, and just below a sharp bend in the stream, where it follows that course after coming from a long reach flowing more from the west". Etymology The historical name of the town, ''al-Bīra'' in Arabic and ''Bīreh'' in Syriac, derives from the Aramaic ''Bīrthā'', meaning fortress. It later evolved to ''Birecik'' with the addition of the Turkish diminutive suffix, ''cik''. It is called ''Belejik'' amongst the local population. Archaeology Birecik Dam Cemetery is an Early Bronze Age cemetery near Birecik. It was used extensively for about 500 years at the beginning of the third millennium BC. More than 300 graves were excavated here in 1997 and 1998. The site was discovered during the building of the Birecik Dam as part of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birecik Dam Cemetery
The Birecik Dam Cemetery is an Early Bronze Age cemetery in the Gaziantep region in southeastern Turkey. This cemetery was used extensively for a very short period of time at the beginning of the third millennium BC. Location and site description This three hectare cemetery is located several hundred meters from the Birecik Dam on the Euphrates River and is approximately 25 kilometers north of the ancient site of Carchemish. More than 300 graves were dug into the subsurface clay bed between 3100-2600 BC (Early Bronze IB-II), and despite the large size of this cemetery no attached settlement has been found.Sertok, K. and Ergeç, R. 1999. A New Early Bronze Age Cemetery: Excavation near the Birecik Dam, Southeastern Turkey. Preliminary Report (1997-98) ''Anatolica'' 25: 87-107 Summary of Excavation The Birecik Dam Cemetery was discovered during the building of the Birecik Dam as part of the GAP project, and it was subsequently excavated during two field seasons in 1997 and 1998 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birecik Dam
The Birecik Dam, one of the 21 dams of the Southeastern Anatolia Project of Turkey, is located on the Euphrates River downstream of Atatürk Dam and upstream of Birecik town west of Province of Şanlıurfa in the southeastern region of Turkey. It was purposed for irrigation and energy production. There is a run-of-the-river hydroelectric power plant, established in 2001, at the dam, with a power output of 672MW (six facilities at 112 MW each) can generate an average of 2.5 billion kWh per year. The Birecik dam is a structure consisting of a concrete gravity and clay core sandgravel fill with a height of from the foundation. It was designed by Coyne et Bellier. The total catchment area is . The Birecik project will be realized under the status of Build-Operate-Transfer ( BOT) model. The dam was built on top of the ruins of the ancient city of Zeugma. According to Bogumil Terminski (2015), the construction of the dam resulted in resettlement of approximately 6,000 people. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers''). Originating in Turkey, the Euphrates flows through Syria and Iraq to join the Tigris in the Shatt al-Arab, which empties into the Persian Gulf. Etymology The Ancient Greek form ''Euphrátēs'' ( grc, Εὐφράτης, as if from Greek εὖ "good" and φράζω "I announce or declare") was adapted from Old Persian 𐎢𐎳𐎼𐎠𐎬𐎢 ''Ufrātu'', itself from Elamite language, Elamite 𒌑𒅁𒊏𒌅𒅖 ''ú-ip-ra-tu-iš''. The Elamite name is ultimately derived from a name spelt in cuneiform as 𒌓𒄒𒉣 , which read as Sumerian language, Sumerian is "Buranuna" and read as Akkadian language, Akkadian is "Purattu"; many cuneiform signs have a Sumerian pronunciation and an Akkadian pronunciation, taken from a Sumerian word a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GAP Project
The Southeastern Anatolia Project ( tr, Güneydoğu Anadolu Projesi, GAP) is a multi-sector integrated regional development project based on the concept of sustainable development for the 9 million people (2005) living in the Southeastern Anatolia region of Turkey. GAP's basic aim is to eliminate regional development disparities by raising incomes and living standards and to contribute to the national development targets of social stability and economic growth by enhancing the productive and employment generating capacity of the rural sector. The total cost of the project is over 100 billion Turkish lira (TL) (2017 adjusted price), of which 30.6 billion TL of this investment was realized at the end of 2010. The real investment (corrected value) was 72.6% for the end of 2010. (in Turkish) The project area covers nine provinces (Adıyaman, Batman, Diyarbakır, Gaziantep, Kilis, Siirt, Şanlıurfa, Mardin, and Şırnak) which are located in the basins of the Euphrates and Tigris and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeugma, Commagene
Zeugma ( grc-gre, Ζεῦγμα; syr, ܙܘܓܡܐ) was an ancient Hellenistic era Greek and then Roman city of Commagene; located in modern Gaziantep Province, Turkey. It was named for the bridge of boats, or , that crossed the Euphrates at that location. Zeugma Mosaic Museum contains mosaics from the site, and is one of the largest mosaic museums in the world. History Zeugma was founded in the early 3rd century BC as the city of Seleucia by Seleucus I Nicator, a Diadochus (successor) to Alexander the Great and Hellenistic Greek founder of the Seleucid Kingdom, on the site where he had the first bridge over the Euphrates built. In 64 BC, the Roman Republic gained control of the city. Zeugma was of great importance to the Roman Empire as it was located at a strategically important place. Up to 70,000 people lived in the city, and it became a center for the military and commerce for the ancient Romans. In 253 AD, it was destroyed by the Sassanids, but was later rebuilt. In late a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apamea (Euphrates)
Apamea or Apameia ( gr, Απάμεια, syr, ܐܦܡܝܐ) was a Hellenistic city on the left (viz., the eastern) bank of the Euphrates, opposite the famous city of Zeugma, at the end of a bridge of boats (Greek: ''zeugma'') connecting the two, founded by Seleucus I Nicator (Pliny, v. 21). The city was rebuilt by Seleucus I. The site, once partially covered by the village of (formerly Rumkale), Şanlıurfa Province, Turkey, is now flooded by the lake formed by the Birecik Dam (Birejik Dam). The ancient term Zeugma actually referred to the twin cities on the opposing banks of the river. Today the name Zeugma is usually understood to refer to the settlement on the west bank, called Seleucia ( el, Σελεύκεια) after the founder, while the one on the East bank was called Apamea after his Persian wife Apama. See also * List of ancient Greek cities A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkish Dialects
There is considerable dialectal variation in Turkish. Turkish is a southern Oghuz language belonging to the Turkic languages. Turkish is natively and historically spoken by the Turkish people in Turkey, Cyprus, Bulgaria, Greece (primarily in Western Thrace), Kosovo, Meskhetia, North Macedonia, Romania, Iraq, Syria and other areas of traditional settlement which formerly, in whole or part, belonged to the Ottoman Empire. Turkish is the official language of Turkey, the de facto country of North Cyprus and is one of the official languages of Cyprus. It also has official (but not primary) status in the Prizren District of Kosovo and several municipalities of North Macedonia, depending on the concentration of Turkish-speaking local population. Modern standard Turkish is based on the dialect of Istanbul.. Nonetheless, dialectal variation persists, in spite of the levelling influence of the standard used in mass media and the Turkish education system since the 1930s.. The terms ''a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
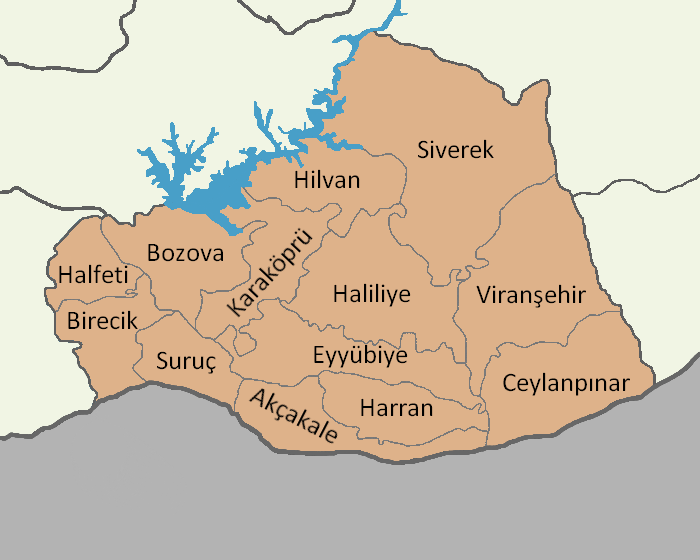
Şanlıurfa Province
Şanlıurfa Province ( tr, Şanlıurfa ili; ku, Parêzgeha Rihayê) or simply Urfa Province is a province in southeastern Turkey. The city of Şanlıurfa is the capital of the province which bears its name. The population is 1,845,667 (2014). The province is considered part of Turkish Kurdistan and has a Kurds, Kurdish majority with a significant Arabs, Arab and Turkish people, Turkish minority. Districts Şanlıurfa province is divided into 13 Districts of Turkey, districts (capital district in bold): * Urfa (Central district. In 2014 it was split into three districts: Eyyübiye, Haliliye and Karaköprü.) * Akçakale * Birecik * Bozova * Ceylanpınar * Halfeti * Harran * Hilvan * Siverek * Suruç * Viranşehir Geography Area 18,584 km2 (7,173 sq. miles), the largest province of Southeast Anatolia with: * Adıyaman to the north; * Syria to the south; * Mardin and Diyarbakır to the east; * Gaziantep to the west; Şanlıurfa includes several major components of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syriac Language
The Syriac language (; syc, / '), also known as Syriac Aramaic (''Syrian Aramaic'', ''Syro-Aramaic'') and Classical Syriac ܠܫܢܐ ܥܬܝܩܐ (in its literary and liturgical form), is an Aramaic language, Aramaic dialect that emerged during the first century AD from a local Aramaic dialect that was spoken by Arameans in the ancient Aramean kingdom of Osroene, centered in the city of Edessa. During the Early Christian period, it became the main literary language of various Aramaic-speaking Christian communities in the historical region of Syria (region), Ancient Syria and throughout the Near East. As a liturgical language of Syriac Christianity, it gained a prominent role among Eastern Christian communities that used both Eastern Syriac Rite, Eastern Syriac and Western Syriac Rite, Western Syriac rites. Following the spread of Syriac Christianity, it also became a liturgical language of eastern Christian communities as far as India (East Syriac ecclesiastical province), India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_en.jpg)