|
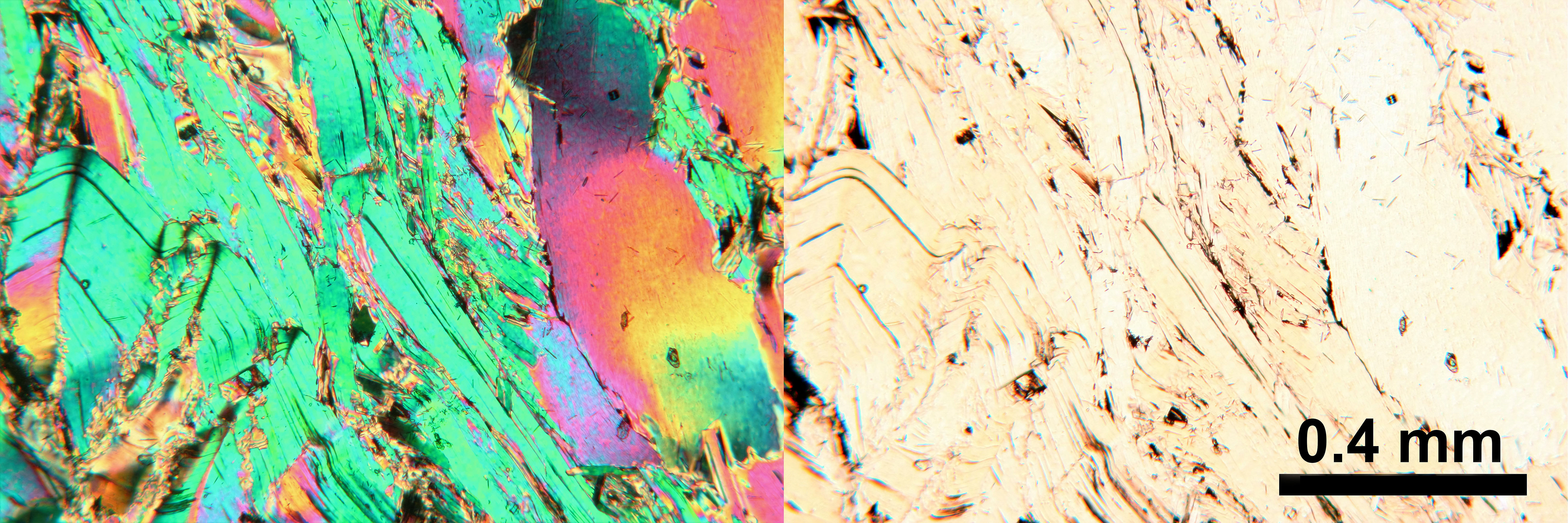
Bird's Eye Extinction
Bird's eye extinction, or bird's eye maple, is a specific type of extinction exhibited by minerals of the mica group Retrieved 2015-07-02 under cross polarized light of the . It gives the a pebbly appearance as it passes into extinction. This is caused when the grinding tools used to creat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinction (optical Mineralogy)
Extinction is a term used in optical mineralogy and petrology, which describes when cross-polarized light dims, as viewed through a thin section of a mineral in a petrographic microscope. Isotropic minerals, opaque (metallic) minerals, and amorphous materials (glass) do not allow light transmission under cross-polarized light (i.e. constant extinction). Anisotropic minerals specifically will show one extinction for each 90 degrees of stage rotation. The extinction angle is the measure between the cleavage direction or habit of a mineral and the extinction. To find this, simply line up the cleavage lines/long direction with one of the crosshairs in the microscope, and turn the mineral until the extinction occurs. The number of degrees the stage was rotated is the extinction angle, between 0-89 degrees. 90 degrees would be considered zero degrees, and is known as parallel extinction. Inclined extinction is a measured angle between 1-89 degrees. Minerals with two cleavages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): Minerals'; p. 1. In the series ''Geology: Landforms, Minerals, and Rocks''. Rosen Publishing Group. The geological definition of mineral normally excludes compounds that occur only in living organisms. However, some minerals are often biogenic (such as calcite) or are organic compounds in the sense of chemistry (such as mellite). Moreover, living organisms often synthesize inorganic minerals (such as hydroxylapatite) that also occur in rocks. The concept of mineral is distinct from rock, which is any bulk solid geologic material that is relatively homogeneous at a large enough scale. A rock may consist of one type of mineral, or may be an aggregate of two or more different types of minerals, spacially segregated into disti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
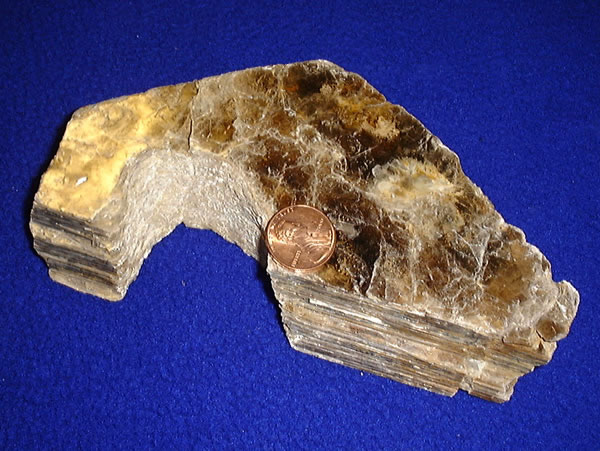
Mica
Micas ( ) are a group of silicate minerals whose outstanding physical characteristic is that individual mica crystals can easily be split into extremely thin elastic plates. This characteristic is described as perfect basal cleavage. Mica is common in igneous and metamorphic rock and is occasionally found as small flakes in sedimentary rock. It is particularly prominent in many granites, pegmatites, and schists, and "books" (large individual crystals) of mica several feet across have been found in some pegmatites. Micas are used in products such as drywalls, paints, fillers, especially in parts for automobiles, roofing and shingles, as well as in electronics. The mineral is used in cosmetics and food to add "shimmer" or "frost." Properties and structure The mica group is composed of 37 phyllosilicate minerals. All crystallize in the monoclinic system, with a tendency towards pseudohexagonal crystals, and are similar in structure but vary in chemical composition. Mic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polarization (waves)
Polarization ( also polarisation) is a property applying to transverse waves that specifies the geometrical orientation of the oscillations. In a transverse wave, the direction of the oscillation is perpendicular to the direction of motion of the wave. A simple example of a polarized transverse wave is vibrations traveling along a taut string ''(see image)''; for example, in a musical instrument like a guitar string. Depending on how the string is plucked, the vibrations can be in a vertical direction, horizontal direction, or at any angle perpendicular to the string. In contrast, in longitudinal waves, such as sound waves in a liquid or gas, the displacement of the particles in the oscillation is always in the direction of propagation, so these waves do not exhibit polarization. Transverse waves that exhibit polarization include electromagnetic waves such as light and radio waves, gravitational waves, and transverse sound waves ( shear waves) in solids. An electromagneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrographic Microscope
A petrographic microscope is a type of optical microscope used in petrology and optical mineralogy to identify rocks and minerals in thin sections. The microscope is used in optical mineralogy and petrography, a branch of petrology which focuses on detailed descriptions of rocks. The method is called " polarized light microscopy" (PLM). __TOC__ Description Depending on the grade of observation required, petrological microscopes are derived from conventional brightfield microscopes of similar basic capabilities by: * Adding a Nicol prism polarizer filter to the light path beneath the sample slide * Replacing the normal stage with a circular rotating stage (typically graduated with vernier scales for reading orientations to better than 1 degree of arc) * Adding a second rotatable and removable Nicol prism filter, called the analyzer, to the light path between objective and eyepiece * Adding a phase telescope, also known as a Bertrand lens, which allows the viewer to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrography
Petrography is a branch of petrology that focuses on detailed descriptions of rocks. Someone who studies petrography is called a petrographer. The mineral content and the textural relationships within the rock are described in detail. The classification of rocks is based on the information acquired during the petrographic analysis. Petrographic descriptions start with the field notes at the outcrop and include macroscopic description of hand specimens. The most important petrographer's tool is the petrographic microscope. The detailed analysis of minerals by optical mineralogy in thin section and the micro-texture and structure are critical to understanding the origin of the rock. Electron microprobe or atom probe tomography analysis of individual grains as well as whole rock chemical analysis by atomic absorption, X-ray fluorescence, and laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy are used in a modern petrographic lab. Individual mineral grains from a rock sample may also be an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thin Section
In optical mineralogy and petrography, a thin section (or petrographic thin section) is a thin slice of a rock or mineral sample, prepared in a laboratory, for use with a polarizing petrographic microscope, electron microscope and electron microprobe. A thin sliver of rock is cut from the sample with a diamond saw and ground optically flat. It is then mounted on a glass slide and then ground smooth using progressively finer abrasive grit until the sample is only 30 μm thick. The method uses the Michel-Lévy interference colour chart to determine thickness, typically using quartz as the thickness gauge because it is one of the most abundant minerals. When placed between two polarizing filters set at right angles to each other, the optical properties of the minerals in the thin section alter the colour and intensity of the light as seen by the viewer. As different minerals have different optical properties, most rock forming minerals can be easily identified. Plagioclase fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleavage (crystal)
Cleavage, in mineralogy and materials science, is the tendency of crystalline materials to split along definite crystallographic structural planes. These planes of relative weakness are a result of the regular locations of atoms and ions in the crystal, which create smooth repeating surfaces that are visible both in the microscope and to the naked eye. If bonds in certain directions are weaker than others, the crystal will tend to split along the weakly bonded planes. These flat breaks are termed "cleavage."Hurlbut, Cornelius S.; Klein, Cornelis, 1985, '' Manual of Mineralogy'', 20th ed., Wiley, The classic example of cleavage is mica, which cleaves in a single direction along the basal pinacoid, making the layers seem like pages in a book. In fact, mineralogists often refer to "books of mica." Diamond and graphite provide examples of cleavage. Both are composed solely of a single element, carbon. But in diamond, each carbon atom is bonded to four others in a tetrahedral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Lattice
In geometry and crystallography, a Bravais lattice, named after , is an infinite array of discrete points generated by a set of discrete translation operations described in three dimensional space by : \mathbf = n_1 \mathbf_1 + n_2 \mathbf_2 + n_3 \mathbf_3, where the ''ni'' are any integers, and a''i'' are ''primitive translation vectors'', or ''primitive vectors'', which lie in different directions (not necessarily mutually perpendicular) and span the lattice. The choice of primitive vectors for a given Bravais lattice is not unique. A fundamental aspect of any Bravais lattice is that, for any choice of direction, the lattice appears exactly the same from each of the discrete lattice points when looking in that chosen direction. The Bravais lattice concept is used to formally define a ''crystalline arrangement'' and its (finite) frontiers. A crystal is made up of one or more atoms, called the ''basis'' or ''motif'', at each lattice point. The ''basis'' may consist of atoms, mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micas
Micas ( ) are a group of silicate minerals whose outstanding physical characteristic is that individual mica crystals can easily be split into extremely thin elastic plates. This characteristic is described as perfect basal cleavage. Mica is common in igneous and metamorphic rock and is occasionally found as small flakes in sedimentary rock. It is particularly prominent in many granites, pegmatites, and schists, and "books" (large individual crystals) of mica several feet across have been found in some pegmatites. Micas are used in products such as drywalls, paints, fillers, especially in parts for automobiles, roofing and shingles, as well as in electronics. The mineral is used in cosmetics and food to add "shimmer" or "frost." Properties and structure The mica group is composed of 37 phyllosilicate minerals. All crystallize in the monoclinic system, with a tendency towards pseudohexagonal crystals, and are similar in structure but vary in chemical composition. Micas ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biotite
Biotite is a common group of phyllosilicate minerals within the mica group, with the approximate chemical formula . It is primarily a solid-solution series between the iron- endmember annite, and the magnesium-endmember phlogopite; more aluminous end-members include siderophyllite and eastonite. Biotite was regarded as a mineral ''species'' by the International Mineralogical Association until 1998, when its status was changed to a mineral ''group''. The term ''biotite'' is still used to describe unanalysed dark micas in the field. Biotite was named by J.F.L. Hausmann in 1847 in honor of the French physicist Jean-Baptiste Biot, who performed early research into the many optical properties of mica. Members of the biotite group are sheet silicates. Iron, magnesium, aluminium, silicon, oxygen, and hydrogen form sheets that are weakly bound together by potassium ions. The term "iron mica" is sometimes used for iron-rich biotite, but the term also refers to a flaky micaceou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phlogopite
Phlogopite is a yellow, greenish, or reddish-brown member of the mica family of phyllosilicates. It is also known as magnesium mica. Phlogopite is the magnesium endmember of the biotite solid solution series, with the chemical formula KMg3AlSi3O10(F,OH)2. Iron substitutes for magnesium in variable amounts leading to the more common biotite with higher iron content. For physical and optical identification, it shares most of the characteristic properties of biotite. Paragenesis Phlogopite is an important and relatively common end-member composition of biotite. Phlogopite micas are found primarily in igneous rocks, although it is also common in contact metamorphic aureoles of intrusive igneous rocks with magnesian country rocks and in marble formed from impure dolomite (dolomite with some siliclastic sediment). The occurrence of phlogopite mica within igneous rocks is difficult to constrain precisely because the primary control is rock composition as expected, but phlogopite is al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |