|
Biotransducer
A biotransducer is the recognition-transduction component of a biosensor system. It consists of two intimately coupled parts; a bio-recognition layer and a physicochemical transducer, which acting together converts a biochemical signal to an electronic or optical signal. The bio-recognition layer typically contains an enzyme or another binding protein such as antibody. However, oligonucleotide sequences, sub-cellular fragments such as organelles (e.g. mitochondria) and receptor carrying fragments (e.g. cell wall), single whole cells, small numbers of cells on synthetic scaffolds, or thin slices of animal or plant tissues, may also comprise the bio-recognition layer. It gives the biosensor selectivity and specificity. The physicochemical transducer is typically in intimate and controlled contact with the recognition layer. As a result of the presence and biochemical action of the analyte (target of interest), a physico-chemical change is produced within the biorecognition layer that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
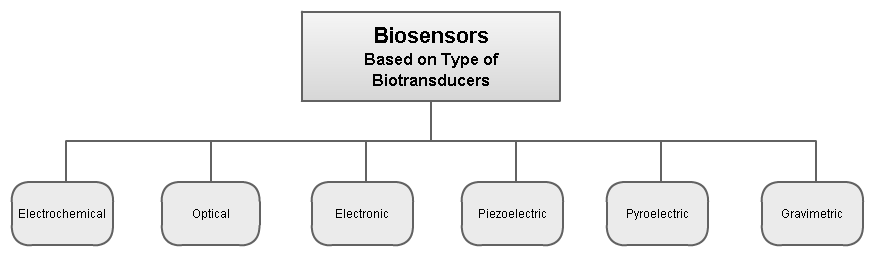
Biosensors Based On Type Of Biotransducers
A biosensor is an analytical device, used for the detection of a chemical substance, that combines a biological component with a physical chemistry, physicochemical detector. The ''sensitive biological element'', e.g. tissue, microorganisms, organelles, cell receptors, enzymes, antibody, antibodies, nucleic acids, etc., is a biologically derived material or biomimetic component that interacts with, binds with, or recognizes the analyte under study. The biologically sensitive elements can also be created by biological engineering. The Biotransducer, ''transducer'' or the ''detector element'', which transforms one signal into another one, works in a physicochemical way: optical, piezoelectric, electrochemical, electrochemiluminescence etc., resulting from the interaction of the analyte with the biological element, to easily measure and quantify. The biosensor reader device connects with the associated electronics or signal processors that are primarily responsible for the display ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biosensor
A biosensor is an analytical device, used for the detection of a chemical substance, that combines a biological component with a physicochemical detector. The ''sensitive biological element'', e.g. tissue, microorganisms, organelles, cell receptors, enzymes, antibodies, nucleic acids, etc., is a biologically derived material or biomimetic component that interacts with, binds with, or recognizes the analyte under study. The biologically sensitive elements can also be created by biological engineering. The ''transducer'' or the ''detector element'', which transforms one signal into another one, works in a physicochemical way: optical, piezoelectric, electrochemical, electrochemiluminescence etc., resulting from the interaction of the analyte with the biological element, to easily measure and quantify. The biosensor reader device connects with the associated electronics or signal processors that are primarily responsible for the display of the results in a user-friendly way. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biosensor
A biosensor is an analytical device, used for the detection of a chemical substance, that combines a biological component with a physicochemical detector. The ''sensitive biological element'', e.g. tissue, microorganisms, organelles, cell receptors, enzymes, antibodies, nucleic acids, etc., is a biologically derived material or biomimetic component that interacts with, binds with, or recognizes the analyte under study. The biologically sensitive elements can also be created by biological engineering. The ''transducer'' or the ''detector element'', which transforms one signal into another one, works in a physicochemical way: optical, piezoelectric, electrochemical, electrochemiluminescence etc., resulting from the interaction of the analyte with the biological element, to easily measure and quantify. The biosensor reader device connects with the associated electronics or signal processors that are primarily responsible for the display of the results in a user-friendly way. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biosensors
A biosensor is an analytical device, used for the detection of a chemical substance, that combines a biological component with a physicochemical detector. The ''sensitive biological element'', e.g. tissue, microorganisms, organelles, cell receptors, enzymes, antibodies, nucleic acids, etc., is a biologically derived material or biomimetic component that interacts with, binds with, or recognizes the analyte under study. The biologically sensitive elements can also be created by biological engineering. The ''transducer'' or the ''detector element'', which transforms one signal into another one, works in a physicochemical way: optical, piezoelectric, electrochemical, electrochemiluminescence etc., resulting from the interaction of the analyte with the biological element, to easily measure and quantify. The biosensor reader device connects with the associated electronics or signal processors that are primarily responsible for the display of the results in a user-friendly way. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biochemical Signaling
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a series of molecular events, most commonly protein phosphorylation catalyzed by protein kinases, which ultimately results in a cellular response. Proteins responsible for detecting stimuli are generally termed receptors, although in some cases the term sensor is used. The changes elicited by ligand binding (or signal sensing) in a receptor give rise to a biochemical cascade, which is a chain of biochemical events known as a signaling pathway. When signaling pathways interact with one another they form networks, which allow cellular responses to be coordinated, often by combinatorial signaling events. At the molecular level, such responses include changes in the transcription or translation of genes, and post-translational and conformational changes in proteins, as well as changes in their location. These molecular events are the basic mechanisms controlling cell growth, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
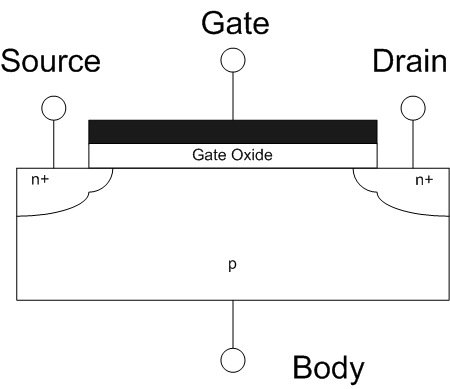
Field-effect Transistors
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the flow of current in a semiconductor. FETs (JFETs or MOSFETs) are devices with three terminals: ''source'', ''gate'', and ''drain''. FETs control the flow of current by the application of a voltage to the gate, which in turn alters the conductivity between the drain and source. FETs are also known as unipolar transistors since they involve single-carrier-type operation. That is, FETs use either electrons (n-channel) or holes (p-channel) as charge carriers in their operation, but not both. Many different types of field effect transistors exist. Field effect transistors generally display very high input impedance at low frequencies. The most widely used field-effect transistor is the MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor). History The concept of a field-effect transistor (FET) was first patented by Austro-Hungarian physicist Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanobiotechnology
Nanobiotechnology, bionanotechnology, and nanobiology are terms that refer to the intersection of nanotechnology and biology. Given that the subject is one that has only emerged very recently, bionanotechnology and nanobiotechnology serve as blanket terms for various related technologies. This discipline helps to indicate the merger of biological research with various fields of nanotechnology. Concepts that are enhanced through nanobiology include: nanodevices (such as biological machines), nanoparticles, and nanoscale phenomena that occurs within the discipline of nanotechnology. This technical approach to biology allows scientists to imagine and create systems that can be used for biological research. Biologically inspired nanotechnology uses biological systems as the inspirations for technologies not yet created. However, as with nanotechnology and biotechnology, bionanotechnology does have many potential ethical issues associated with it. The most important objectives that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioelectronics
Bioelectronics is a field of research in the convergence of biology and electronics. Definitions At the first C.E.C. Workshop, in Brussels in November 1991, bioelectronics was defined as 'the use of biological materials and biological architectures for information processing systems and new devices'. Bioelectronics, specifically bio-molecular electronics, were described as 'the research and development of bio-inspired (i.e. self-assembly) inorganic and organic materials and of bio-inspired (i.e. massive parallelism) hardware architectures for the implementation of new information processing systems, sensors and actuators, and for molecular manufacturing down to the atomic scale'. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), an agency of the United States Department of Commerce, defined bioelectronics in a 2009 report as "the discipline resulting from the convergence of biology and electronics". Sources for information about the field include the Institute of Electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrochemiluminescence
Electrochemiluminescence or electrogenerated chemiluminescence (ECL) is a kind of luminescence produced during electrochemical reactions in solutions. In electrogenerated chemiluminescence, electrochemically generated intermediates undergo a highly exergonic reaction to produce an electronically excited state that then emits light upon relaxation to a lower-level state. This wavelength of the emitted photon of light corresponds to the energy gap between these two states. ECL excitation can be caused by energetic electron transfer (redox) reactions of electrogenerated species. Such luminescence excitation is a form of chemiluminescence where one/all reactants are produced electrochemically on the electrodes. ECL is usually observed during application of potential (several volts) to electrodes of electrochemical cell that contains solution of luminescent species (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, metal complexes, Quantum Dots or Nanoparticles ) in aprotic organic solvent (ECL compos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biointerface
A biointerface is the region of contact between a biomolecule, cell, biological tissue or living organism or organic material considered living with another biomaterial or inorganic/organic material. The motivation for biointerface science stems from the urgent need to increase the understanding of interactions between biomolecules and surfaces. The behavior of complex macromolecular systems at materials interfaces are important in the fields of biology, biotechnology, diagnostics Diagnosis is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in many different disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine "cause and effect". In systems engineer ..., and medicine. Biointerface science is a multidisciplinary field in which biochemists who synthesize novel classes of biomolecules (peptide nucleic acids, peptide, peptidomimetics, aptamers, ribozymes, and engineered proteins) cooperate with scientists who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Field-effect Transistor
A DNA field-effect transistor (DNAFET) is a field-effect transistor which uses the field-effect due to the partial charges of DNA molecules to function as a biosensor. The structure of DNAFETs is similar to that of MOSFETs, with the exception of the gate structure which, in DNAFETs, is replaced by a layer of immobilized ssDNA (single-stranded DNA) molecules which act as surface receptors. When complementary DNA strands hybridize to the receptors, the charge distribution near the surface changes, which in turn modulates current transport through the semiconductor transducer. Arrays of DNAFETs can be used for detecting single nucleotide polymorphisms (causing many hereditary diseases) and for DNA sequencing DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence – the order of nucleotides in DNA. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. T .... Their main advantage compar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physicochemical
Physical chemistry is the study of macroscopic and microscopic phenomena in chemical systems in terms of the principles, practices, and concepts of physics such as motion, energy, force, time, thermodynamics, quantum chemistry, statistical mechanics, analytical dynamics and chemical equilibria. Physical chemistry, in contrast to chemical physics, is predominantly (but not always) a supra-molecular science, as the majority of the principles on which it was founded relate to the bulk rather than the molecular or atomic structure alone (for example, chemical equilibrium and colloids). Some of the relationships that physical chemistry strives to resolve include the effects of: # Intermolecular forces that act upon the physical properties of materials (plasticity, tensile strength, surface tension in liquids). # Reaction kinetics on the rate of a reaction. # The identity of ions and the electrical conductivity of materials. # Surface science and electrochemistry of cell membranes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |