|
Bioorganometallic Chemistry
Bioorganometallic chemistry is the study of biologically active molecules that contain carbon directly bonded to metals or metalloids. The importance of main-group and transition-metal centers has long been recognized as important to the function of enzymes and other biomolecules. However, only a small subset of naturally-occurring metal complexes and synthetically prepared pharmaceuticals are ''organometallic''; that is, they feature a direct covalent bond between the metal(loid) and a carbon atom. The first, and for a long time, the only examples of naturally occurring bioorganometallic compounds were the cobalamin cofactors (vitamin B12) in its various forms. In the 21st century, discovery of new systems containing carbon-metal bonds in biology, bioorganometallic chemistry is rapidly emerging as a distinct subdiscipline of bioinorganic chemistry that straddles organometallic chemistry and biochemistry. Naturally occurring bioorganometallics include enzymes and sensor proteins. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin involved in metabolism. It is one of eight B vitamins. It is required by animals, which use it as a cofactor in DNA synthesis, in both fatty acid and amino acid metabolism. It is important in the normal functioning of the nervous system via its role in the synthesis of myelin, and in the circulatory system in the maturation of red blood cells in the bone marrow. Plants do not need cobalamin and carry out the reactions with enzymes that are not dependent on it. Vitamin B12 is the most chemically complex of all vitamins, and for humans, the only vitamin that must be sourced from animal-derived foods or from supplements. Only some archaea and bacteria can synthesize vitamin B12. Most people in developed countries get enough B12 from the consumption of meat or foods with animal sources. Foods containing vitamin B12 include meat, clams, liver, fish, poultry, eggs, and dairy products. Many breakfast cereals are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
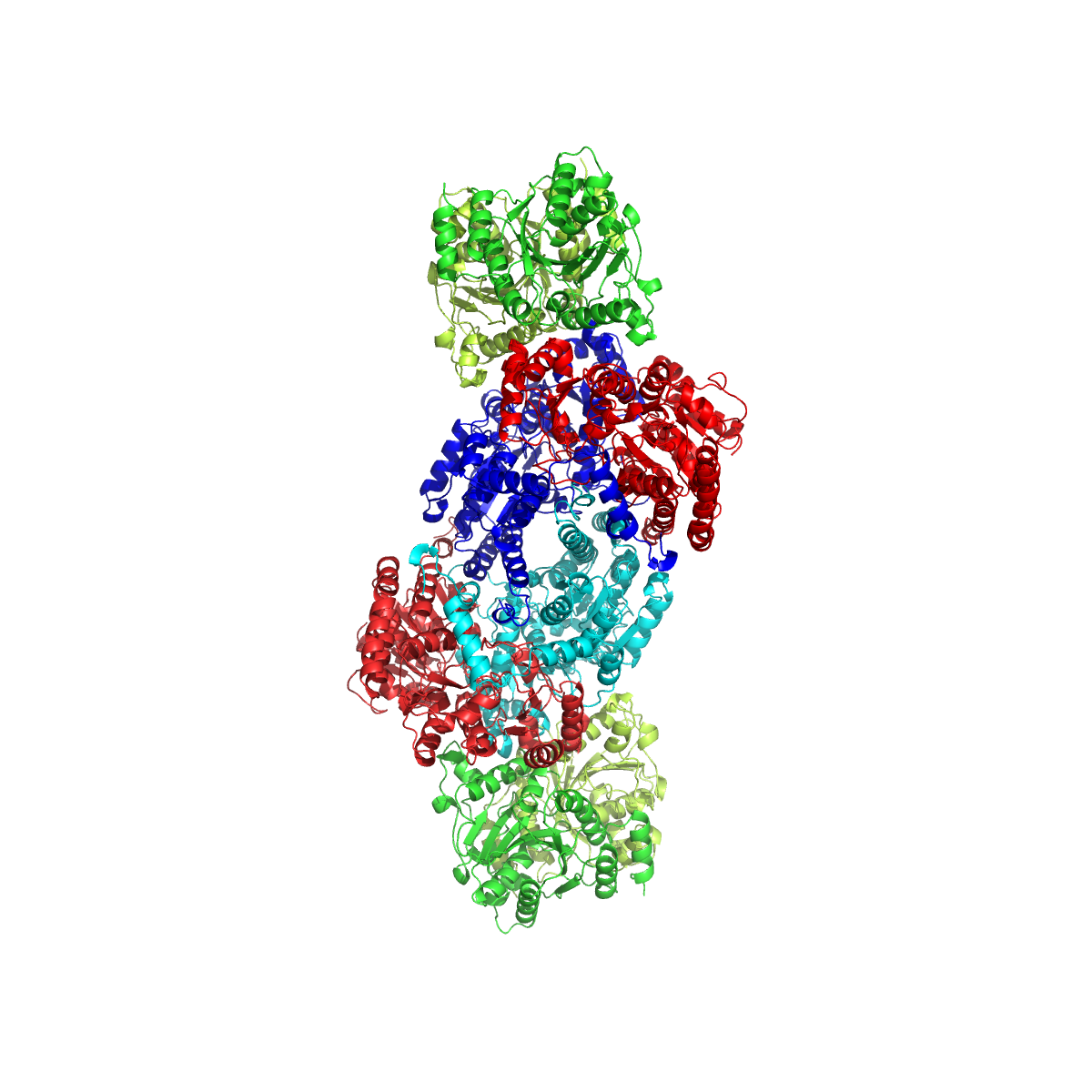
Hydrogenase
A hydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyses the reversible oxidation of molecular hydrogen (H2), as shown below: Hydrogen uptake () is coupled to the reduction of electron acceptors such as oxygen, nitrate, sulfate, carbon dioxide (), and fumarate. On the other hand, proton reduction () is coupled to the oxidation of electron donors such as ferredoxin (FNR), and serves to dispose excess electrons in cells (essential in pyruvate fermentation). Both low-molecular weight compounds and proteins such as FNRs, cytochrome ''c''3, and cytochrome ''c''6 can act as physiological electron donors or acceptors for hydrogenases. Structural classification It has been estimated that 99% of all organisms utilize hydrogen, H2. Most of these species are microbes and their ability to use H2 as a metabolite arises from the expression of metalloenzymes known as hydrogenases. Hydrogenases are sub-classified into three different types based on the active site metal content: iron-iron hydrogenase, ni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable metallic form ( native metals). This led to very early human use in several regions, from circa 8000 BC. Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, circa 5000 BC; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, c. 4000 BC; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactate Racemase
The lactate racemase enzyme (Lar) () interconverts the D- and L-enantiomers of lactic acid. It is classified under the isomerase, racemase, epimerase, and enzyme acting on hydroxyl acids and derivatives classes of enzymes. It is found in certain halophilic archaea, such as ''Haloarcula marismortui'', and in a few species of bacteria, such as several ''Lactobacillus'' species (which produce D- and L- lactate) including ''Lactobacillus sakei'', ''Lactobacillus curvatus'', and ''Lactobacillus plantarum'', as well as in non-lactic acid bacteria such as ''Clostridium beijerinckii''. The gene encoding lactate racemase in ''L. plantarum'' was identified as ''larA'' and shown to be associated with a widespread maturation system involving ''larB'', ''larC1'', ''larC2'', and ''larE''. The optimal pH for its activity is 5.8-6.2 in ''L. sakei''. Structure and properties The molecular weight of lactate racemase differs in the various organisms in which it has been found, ranging from 25,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbide
In chemistry, a carbide usually describes a compound composed of carbon and a metal. In metallurgy, carbiding or carburizing is the process for producing carbide coatings on a metal piece. Interstitial / Metallic carbides The carbides of the group 4, 5 and 6 transition metals (with the exception of chromium) are often described as interstitial compounds. These carbides have metallic properties and are refractory. Some exhibit a range of stoichiometries, being a non-stoichiometric mixture of various carbides arising due to crystal defects. Some of them, including titanium carbide and tungsten carbide, are important industrially and are used to coat metals in cutting tools. The long-held view is that the carbon atoms fit into octahedral interstices in a close-packed metal lattice when the metal atom radius is greater than approximately 135 pm: *When the metal atoms are cubic close-packed, (ccp), then filling all of the octahedral interstices with carbon achieves 1:1 stoich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogenase
Nitrogenases are enzymes () that are produced by certain bacteria, such as cyanobacteria (blue-green bacteria) and rhizobacteria. These enzymes are responsible for the Organic redox reaction, reduction of nitrogen (N2) to ammonia (NH3). Nitrogenases are the only family of enzymes known to catalyze this reaction, which is a key step in the process of nitrogen fixation. Nitrogen fixation is required for all forms of life, with nitrogen being essential for the biosynthesis of molecules (nucleotides, amino acids) that create plants, animals and other organisms. They are encoded by the Nif genes or Homologous chromosome, homologs. They are related to protochlorophyllide reductase. Classification and structure Although the equilibrium formation of ammonia from molecular hydrogen and nitrogen has an overall negative enthalpy of reaction ( \Delta H^ = -45.2 \ \mathrm \, \mathrm \; \mathrm ), the activation energy is very high ( E_\mathrm = 230-420 \ \mathrm \, \mathrm ). Nitrogenase a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FeMoco
FeMoco ( cofactor) is the primary cofactor of nitrogenase. Nitrogenase is the enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen molecules N2 into ammonia (NH3) through the process known as nitrogen fixation. Containing iron and molybdenum, the cofactor is called FeMoco. Its stoichiometry is Fe7MoS9C. Structure The FeMo cofactor is a cluster with composition Fe7MoS9C. Fe is the chemical symbol for the element iron (ferrum), and Mo is the symbol for molybdenum. This large cluster can be viewed as two subunits composed of one Fe4S3 (iron(III) sulfide) cluster and one MoFe3S3 cluster. The two clusters are linked by three sulfide ligands. The unique iron (Fe) is anchored to the protein by a cysteine. It is also bound to three sulfides, resulting in tetrahedral molecular geometry. The additional six Fe centers in the cluster are each bonded to three sulfides. These six internal Fe centers define a trigonal prismatic arrangement around a central carbide center. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cofactor F430
F430 is the cofactor (sometimes called the coenzyme) of the enzyme methyl coenzyme M reductase (MCR). MCR catalyzes the reaction that releases methane in the final step of methanogenesis: : + HS–CoB → + CoB–S–S–CoM It is found only in methanogenic Archaea and anaerobic methanotrophic Archaea. It occurs in relatively high concentrations in archaea that are involved in reverse methanogenesis: these can contain up to 7% by weight of the nickel protein. Structure The trivial name cofactor F430 was assigned in 1978 based on the properties of a yellow sample extracted from ''Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum'', which had a spectroscopic maximum at 430 nm. It was identified as the MCR cofactor in 1982 and the complete structure was deduced by X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy. Coenzyme F430 features a reduced porphyrin in a macrocyclic ring system called a corphin. In addition, it possesses two additional rings in comparison to the standard tetrapyrrole ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl
In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula . In formulas, the group is often abbreviated as Me. This hydrocarbon group occurs in many organic compounds. It is a very stable group in most molecules. While the methyl group is usually part of a larger molecule, bounded to the rest of the molecule by a single covalent bond (), it can be found on its own in any of three forms: methanide anion (), methylium cation () or methyl radical (). The anion has eight valence electrons, the radical seven and the cation six. All three forms are highly reactive and rarely observed. Methyl cation, anion, and radical Methyl cation The methylium cation () exists in the gas phase, but is otherwise not encountered. Some compounds are considered to be sources of the cation, and this simplification is used pervasively in organic chemistry. For example, protonation of methanol gives an elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow to react with air under standard conditions because a passivation layer of nickel oxide forms on the surface that prevents further corrosion. Even so, pure native nickel is found in Earth's crust only in tiny amounts, usually in ultramafic rocks, and in the interiors of larger nickel–iron meteorites that were not exposed to oxygen when outside Earth's atmosphere. Meteoric nickel is found in combination with iron, a reflection of the origin of those elements as major end products of supernova nucleosynthesis. An iron–nickel mixture is thought to compose Earth's outer and inner cores. Use of nickel (as natural meteoric nickel–iron alloy) has been traced as far back as 3500 BCE. Nickel was first isolated and classified as an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanogenesis
Methanogenesis or biomethanation is the formation of methane coupled to energy conservation by microbes known as methanogens. Organisms capable of producing methane for energy conservation have been identified only from the domain Archaea, a group phylogenetically distinct from both eukaryotes and bacteria, although many live in close association with anaerobic bacteria. Other forms of methane production that are not coupled to ATP synthesis exist within all three domains of life. The production of methane is an important and widespread form of microbial metabolism. In anoxic environments, it is the final step in the decomposition of biomass. Methanogenesis is responsible for significant amounts of natural gas accumulations, the remainder being thermogenic. Biochemistry Methanogenesis in microbes is a form of anaerobic respiration. Methanogens do not use oxygen to respire; in fact, oxygen inhibits the growth of methanogens. The terminal electron acceptor in methanogenesis is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalton Transactions
''Dalton Transactions'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal publishing original (primary) research and review articles on all aspects of the chemistry of inorganic, bioinorganic, and organometallic compounds. It is published weekly by the Royal Society of Chemistry. The journal was named after the English chemist, John Dalton, best known for his work on modern atomic theory. Authors can elect to have accepted articles published as open access. The editor is Andrew Shore. ''Dalton Transactions'' was named a "rising star" by ''In-cites'' from Thomson Scientific in 2006. Publication history The journal was established as the ''Journal of the Chemical Society A: Inorganic, Physical, Theoretical'' in 1966. In 1972, the journal was divided into three separate journals: ''Journal of the Chemical Society, Dalton Transactions'' (covering inorganic and organometallic chemistry), '' Journal of the Chemical Society, Faraday Transactions 1: Physical Chemistry in Condensed Phases'', and '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |