|
Biomimetic Material
Biomimetic materials are materials developed using inspiration from nature. This may be useful in the design of composite materials. Natural structures have inspired and innovated human creations. Notable examples of these natural structures include: honeycomb structure of the beehive, strength of spider silks, bird flight mechanics, and shark skin water repellency. The etymological roots of the neologism "biomimetic" derive from Greek, since means "life" and means "imitative". Tissue engineering Biomimetic materials in tissue engineering are materials that have been designed such that they elicit specified cellular responses mediated by interactions with scaffold-tethered peptides from extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins; essentially, the incorporation of cell-binding peptides into biomaterials via chemical or physical modification.Shin, H., S. Jo, and A.G. Mikos, ''Biomimetic materials for tissue engineering''. Biomaterials, 2003. 24: p. 4353-5364. Amino acids located within th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biomimicry
Biomimetics or biomimicry is the emulation of the models, systems, and elements of nature for the purpose of solving complex human problems. The terms "biomimetics" and "biomimicry" are derived from grc, βίος (''bios''), life, and μίμησις ('' mīmēsis''), imitation, from μιμεῖσθαι (''mīmeisthai''), to imitate, from μῖμος (''mimos''), actor. A closely related field is bionics. Living organisms have evolved well-adapted structures and materials over geological time through natural selection. Biomimetics has given rise to new technologies inspired by biological solutions at macro and nanoscales. Humans have looked at nature for answers to problems throughout their existence. Nature has solved engineering problems such as self-healing abilities, environmental exposure tolerance and resistance, hydrophobicity, self-assembly, and harnessing solar energy. History One of the early examples of biomimicry was the study of birds to enable human flight. Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligand (biochemistry)
In biochemistry and pharmacology, a ligand is a substance that forms a complex with a biomolecule to serve a biological purpose. The etymology stems from ''ligare'', which means 'to bind'. In protein-ligand binding, the ligand is usually a molecule which produces a signal by binding to a site on a target protein. The binding typically results in a change of conformational isomerism (conformation) of the target protein. In DNA-ligand binding studies, the ligand can be a small molecule, ion, or protein which binds to the DNA double helix. The relationship between ligand and binding partner is a function of charge, hydrophobicity, and molecular structure. Binding occurs by intermolecular forces, such as ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds and Van der Waals forces. The association or docking is actually reversible through dissociation. Measurably irreversible covalent bonding between a ligand and target molecule is atypical in biological systems. In contrast to the definition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonate
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid (H2CO3), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word ''carbonate'' may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate group C(=O)(O–)2. The term is also used as a verb, to describe carbonation: the process of raising the concentrations of carbonate and bicarbonate ions in water to produce carbonated water and other carbonated beverageseither by the addition of carbon dioxide gas under pressure or by dissolving carbonate or bicarbonate salts into the water. In geology and mineralogy, the term "carbonate" can refer both to carbonate minerals and carbonate rock (which is made of chiefly carbonate minerals), and both are dominated by the carbonate ion, . Carbonate minerals are extremely varied and ubiquitous in chemically precipitated sedimentary rock. The most common are calcite or calcium carbonate, CaCO3, the chief constituent of limestone (as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxylapatite
Hydroxyapatite, also called hydroxylapatite (HA), is a naturally occurring mineral form of calcium apatite with the formula Ca5(PO4)3(OH), but it is usually written Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 to denote that the crystal unit cell comprises two entities. Hydroxyapatite is the hydroxyl endmember of the complex apatite group. The OH− ion can be replaced by fluoride, chloride or carbonate, producing fluorapatite or chlorapatite. It crystallizes in the hexagonal crystal system. Pure hydroxyapatite powder is white. Naturally occurring apatites can, however, also have brown, yellow, or green colorations, comparable to the discolorations of dental fluorosis. Up to 50% by volume and 70% by weight of human bone is a modified form of hydroxyapatite, known as bone mineral. Carbonated calcium-deficient hydroxyapatite is the main mineral of which dental enamel and dentin are composed. Hydroxyapatite crystals are also found in pathological calcifications such as those found in breast tumors, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
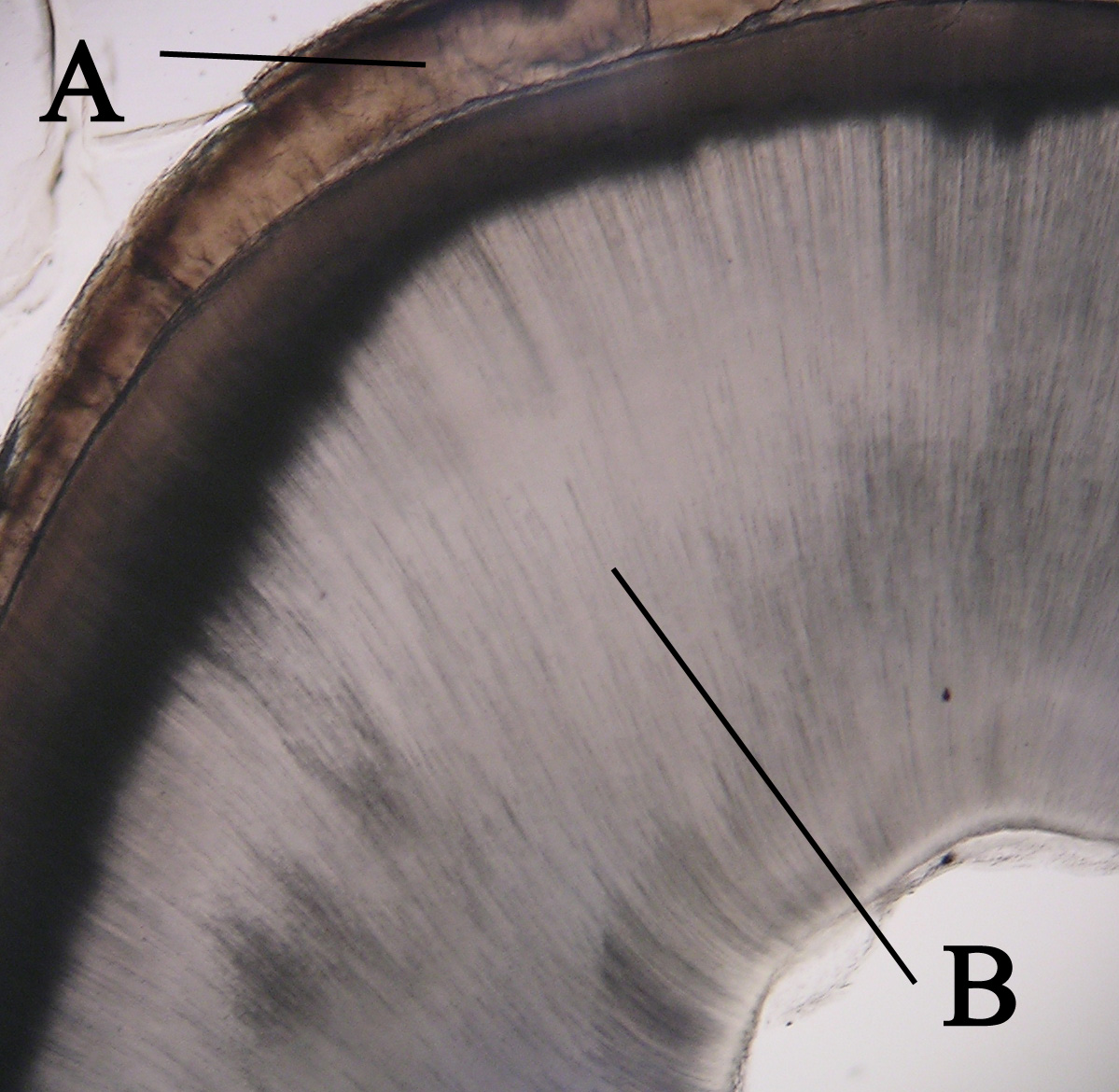
Dentin
Dentin () (American English) or dentine ( or ) (British English) ( la, substantia eburnea) is a calcified tissue of the body and, along with enamel, cementum, and pulp, is one of the four major components of teeth. It is usually covered by enamel on the crown and cementum on the root and surrounds the entire pulp. By volume, 45% of dentin consists of the mineral hydroxyapatite, 33% is organic material, and 22% is water. Yellow in appearance, it greatly affects the color of a tooth due to the translucency of enamel. Dentin, which is less mineralized and less brittle than enamel, is necessary for the support of enamel. Dentin rates approximately 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness. There are two main characteristics which distinguish dentin from enamel: firstly, dentin forms throughout life; secondly, dentin is sensitive and can become hypersensitive to changes in temperature due to the sensory function of odontoblasts, especially when enamel recedes and dentin channels b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type-I Collagen
Type I collagen is the most abundant collagen of the human body. It forms large, eosinophilic fibers known as collagen fibers. It is present in scar tissue, the end product when tissue heals by repair, as well as tendons, ligaments, the endomysium of myofibrils, the organic part of bone, the dermis, the dentin, and organ capsules. Formation The gene produces the pro-alpha1(I) chain. This chain combines with another pro-alpha1(I) chain and also with a pro-alpha2(I) chain (produced by the gene) to make a molecule of type I pro-collagen. These triple-stranded, rope-like pro-collagen molecules must be processed by enzymes outside the cell. Once these molecules are processed, they arrange themselves into long, thin fibrils that cross-link to one another in the spaces around cells. The cross-links result in the formation of very strong mature type I collagen fiber. Clinical significance See Collagen, type I, alpha 1#Clinical significance Markers used to measure bone loss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amelogenesis Imperfecta
Amelogenesis imperfecta (AI) is a congenital disorder which presents with a rare abnormal formation of the enamel or external layer of the crown of teeth, unrelated to any systemic or generalized conditions. Enamel is composed mostly of mineral, that is formed and regulated by the proteins in it. Amelogenesis imperfecta is due to the malfunction of the proteins in the enamel ( ameloblastin, enamelin, tuftelin and amelogenin) as a result of abnormal enamel formation via amelogenesis. People with amelogenesis imperfecta may have teeth with abnormal color: yellow, brown or grey; this disorder can affect any number of teeth of both dentitions. Enamel hypoplasia manifests in a variety of ways depending on the type of AI an individual has (see below), with pitting and plane-form defects common. The teeth have a higher risk for dental cavities and are hypersensitive to temperature changes as well as rapid attrition, excessive calculus deposition, and gingival hyperplasia.American ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleation
In thermodynamics, nucleation is the first step in the formation of either a new thermodynamic phase or structure via self-assembly or self-organization within a substance or mixture. Nucleation is typically defined to be the process that determines how long an observer has to wait before the new phase or self-organized structure appears. For example, if a volume of water is cooled (at atmospheric pressure) below 0°C, it will tend to freeze into ice, but volumes of water cooled only a few degrees below 0°C often stay completely free of ice for long periods (supercooling). At these conditions, nucleation of ice is either slow or does not occur at all. However, at lower temperatures nucleation is fast, and ice crystals appear after little or no delay. Nucleation is a common mechanism which generates first-order phase transitions, and it is the start of the process of forming a new thermodynamic phase. In contrast, new phases at continuous phase transitions start to form im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amelogenin
Amelogenins are a group of protein isoforms produced by alternative splicing or proteolysis from the '' AMELX'' gene, on the X chromosome, and also the '' AMELY'' gene in males, on the Y chromosome. They are involved in amelogenesis, the development of enamel. Amelogenins are type of extracellular matrix protein, which, together with ameloblastins, enamelins and tuftelins, direct the mineralization of enamel to form a highly organized matrix of rods, interrod crystal and proteins. Although the precise role of amelogenin(s) in regulating the mineralization process is unknown, it is known that amelogenins are abundant during amelogenesis. Developing human enamel contains about 70% protein, 90% of which are amelogenins. Function Amelogenins are believed to be involved in the organizing of enamel rods during tooth development. The latest research indicates that these proteins regulate the initiation and growth of hydroxyapatite crystals during the mineralization of enamel. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligand (biochemistry)
In biochemistry and pharmacology, a ligand is a substance that forms a complex with a biomolecule to serve a biological purpose. The etymology stems from ''ligare'', which means 'to bind'. In protein-ligand binding, the ligand is usually a molecule which produces a signal by binding to a site on a target protein. The binding typically results in a change of conformational isomerism (conformation) of the target protein. In DNA-ligand binding studies, the ligand can be a small molecule, ion, or protein which binds to the DNA double helix. The relationship between ligand and binding partner is a function of charge, hydrophobicity, and molecular structure. Binding occurs by intermolecular forces, such as ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds and Van der Waals forces. The association or docking is actually reversible through dissociation. Measurably irreversible covalent bonding between a ligand and target molecule is atypical in biological systems. In contrast to the definition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoskeletal
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is composed of similar proteins in the various organisms. It is composed of three main components, microfilaments, intermediate filaments and microtubules, and these are all capable of rapid growth or disassembly dependent on the cell's requirements. A multitude of functions can be performed by the cytoskeleton. Its primary function is to give the cell its shape and mechanical resistance to deformation, and through association with extracellular connective tissue and other cells it stabilizes entire tissues. The cytoskeleton can also contract, thereby deforming the cell and the cell's environment and allowing cells to migrate. Moreover, it is involved in many cell signaling pathways and in the uptake of extracellular material (endocytosis), the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
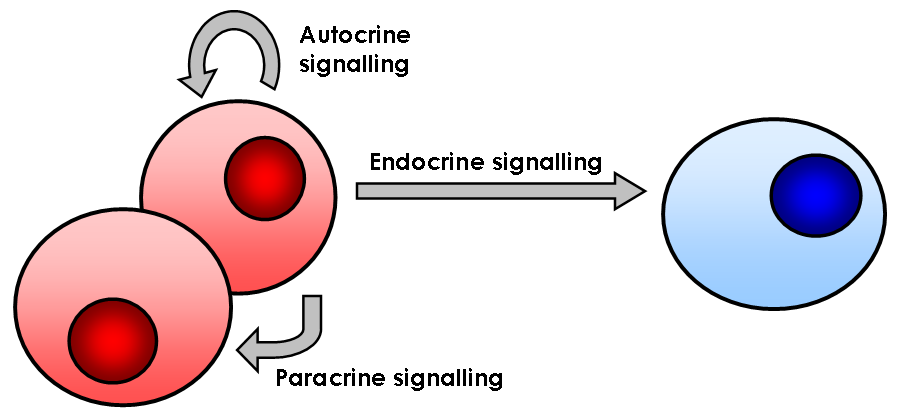
Cell Signaling
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) or cell communication is the ability of a cell to receive, process, and transmit signals with its environment and with itself. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellular life in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Signals that originate from outside a cell (or extracellular signals) can be physical agents like mechanical pressure, voltage, temperature, light, or chemical signals (e.g., small molecules, peptides, or gas). Cell signaling can occur over short or long distances, and as a result can be classified as autocrine, juxtacrine, intracrine, paracrine, or endocrine. Signaling molecules can be synthesized from various biosynthetic pathways and released through passive or active transports, or even from cell damage. Receptors play a key role in cell signaling as they are able to detect chemical signals or physical stimuli. Receptors are generally proteins located on the cell surface or within th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |