|
Biogeography Of Paravian Dinosaurs
The biogeography of Paravian dinosaurs is the study of the global distribution of Paraves through geological history. Paraves is a clade that includes all of the Theropoda that are more closely related to birds than to Oviraptorosauria, oviraptorosaurs. These include Dromaeosauridae and Troodontidae (historically grouped under Deinonychosauria) and Avialae (including crown group birds, i.e. modern birds). The distribution of paraves is closely related to the evolution of the clade. Understanding the changes in their distributions may shed light on problems like how and why paraves evolve, eventually gaining the ability to fly. Paraves first appeared in the fossil record in early Late Jurassic (163–145 million years ago), then rapidly diversified and dispersed during Cretaceous (145–66 million years ago). They emerged during the Pangaea#Rifting and break-up, breakup of Pangea (since Early-Middle Jurassic), which influenced the biogeographic processes such as speciation, geodispe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FMNH Deinonychus
The Field Museum of Natural History (FMNH), also known as The Field Museum, is a natural history museum in Chicago, Illinois, and is one of the largest such museums in the world. The museum is popular for the size and quality of its educational and scientific programs, and its extensive scientific-specimen and artifact collections. The permanent exhibitions, which attract up to two million visitors annually, include fossils, current cultures from around the world, and interactive programming demonstrating today's urgent conservation (ethic), conservation needs. The museum is named in honor of its first major benefactor, Marshall Field, the Department store, department-store magnate. The museum and its collections originated from the 1893 World’s Columbian Exposition, World's Columbian Exposition and the artifacts displayed at the fair. The museum maintains a temporary exhibition program of traveling shows as well as in-house produced topical exhibitions. The professional staff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous–Paleogene Extinction Event
The Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) extinction event (also known as the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction) was a sudden extinction event, mass extinction of three-quarters of the plant and animal species on Earth, approximately 66 million years ago. With the exception of some ectothermic species such as sea turtles and crocodilians, no tetrapods weighing more than survived. It marked the end of the Cretaceous Period, and with it the Mesozoic era, while heralding the beginning of the Cenozoic era, which continues to this day. In the geologic record, the K–Pg event is marked by a thin layer of sediment called the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary, K–Pg boundary, which can be found throughout the world in marine and terrestrial rocks. The boundary clay shows unusually high levels of the metal iridium, which is more common in asteroids than in the Earth's crust. As originally proposed in 1980 by a team of scientists led by Luis Walter Alvarez, Luis Alvarez and his son Walter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plate Tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the la, label= Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large tectonic plates which have been slowly moving since about 3.4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of '' continental drift'', an idea developed during the first decades of the 20th century. Plate tectonics came to be generally accepted by geoscientists after seafloor spreading was validated in the mid to late 1960s. Earth's lithosphere, which is the rigid outermost shell of the planet (the crust and upper mantle), is broken into seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates or "platelets". Where the plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of plate boundary: '' convergent'', '' divergent'', or '' transform''. Earthquakes, volcanic activity, mountain-building, and ocea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
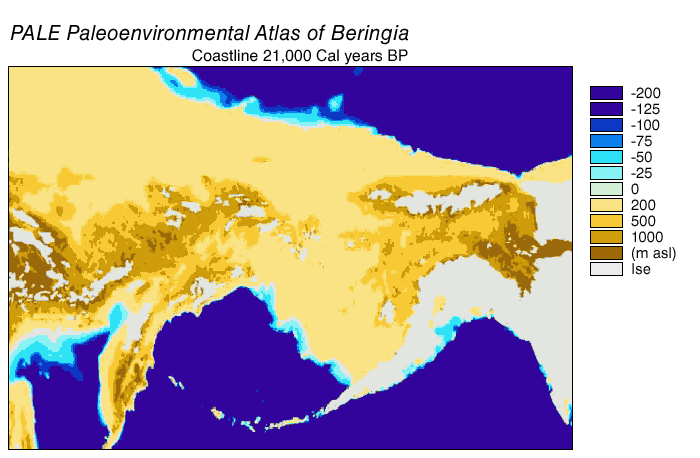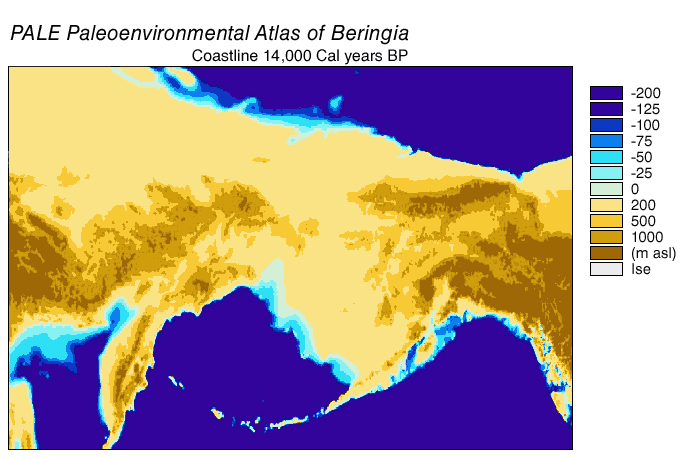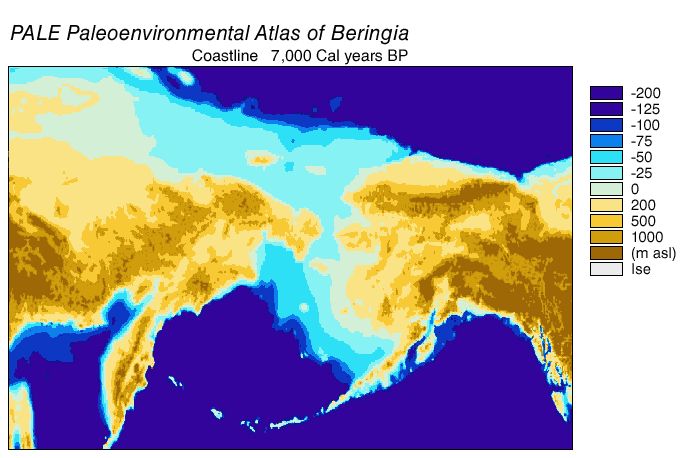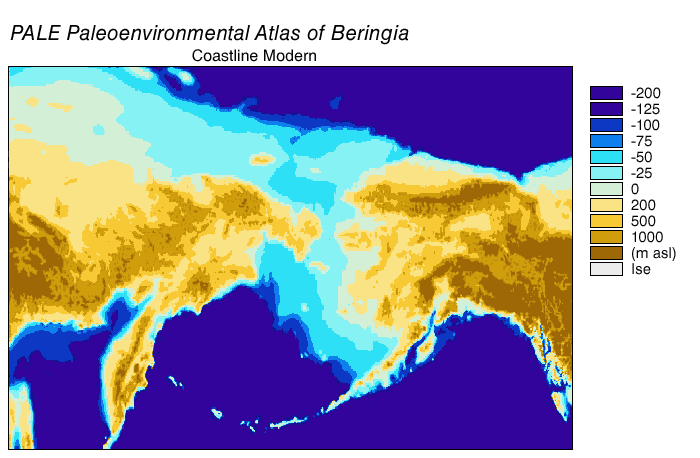
Bering Land Bridge
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 72 degrees north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip of the Kamchatka Peninsula. It includes the Chukchi Sea, the Bering Sea, the Bering Strait, the Chukchi and Kamchatka Peninsulas in Russia as well as Alaska in the United States and the Yukon in Canada. The area includes land lying on the North American Plate and Siberian land east of the Chersky Range. At certain times in prehistory, it formed a land bridge that was up to wide at its greatest extent and which covered an area as large as British Columbia and Alberta together, totaling approximately . Today, the only land that is visible from the central part of the Bering land bridge are the Diomede Islands, the Pribilof Islands of St. Paul and St. George, St. Lawrence Island, St. Matthew Island, and King Island. The term ''Beringia' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Flow
In population genetics, gene flow (also known as gene migration or geneflow and allele flow) is the transfer of genetic material from one population to another. If the rate of gene flow is high enough, then two populations will have equivalent allele frequencies and therefore can be considered a single effective population. It has been shown that it takes only "one migrant per generation" to prevent populations from diverging due to drift. Populations can diverge due to selection even when they are exchanging alleles, if the selection pressure is strong enough. Gene flow is an important mechanism for transferring genetic diversity among populations. Migrants change the distribution of genetic diversity among populations, by modifying allele frequencies (the proportion of members carrying a particular variant of a gene). High rates of gene flow can reduce the genetic differentiation between the two groups, increasing homogeneity. For this reason, gene flow has been thought ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geodispersal
In biogeography, geodispersal is the erosion of barriers to gene flow and biological dispersal (Lieberman, 2005.; Albert and Crampton, 2010.). Geodispersal differs from vicariance, which reduces gene flow through the creation of geographic barriers. In geodispersal, the geographical ranges of individual taxa, or of whole biotas, are merged by erosion of a physical barrier to gene flow or dispersal. Multiple related geodispersal and vicariance events can be mutually responsible for differences among populations. As these geographic barriers break down, organisms of the secluded ecosystems can interact, allowing gene flow between previously separated species, creating more biological variation within a region. A well documented example of geodispersal in between continental ecosystems was the Great American Biotic Interchange (GABI) between the terrestrial faunas and floras of North America and South America, that followed the formation of the Isthmus of Panama about 3 million yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final stages of break-up, involving the separation of Antarctica from South America (forming the Drake Passage) and Australia, occurred during the Paleogene. Gondwana was not considered a supercontinent by the earliest definition, since the landmasses of Baltica, Laurentia, and Siberia were separated from it. To differentiate it from the Indian region of the same name (see ), it is also commonly called Gondwanaland. Gondwana was formed by the accretion of several cratons. Eventually, Gondwana became the largest piece of continental crust of the Palaeozoic Era, covering an area of about , about one-fifth of the Earth's surface. During the Carboniferous Period, it merged with Laurasia to form a larger supercontinent called Pangaea. Gondwana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laurasia
Laurasia () was the more northern of two large landmasses that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from around ( Mya), the other being Gondwana. It separated from Gondwana (beginning in the late Triassic period) during the breakup of Pangaea, drifting farther north after the split and finally broke apart with the opening of the North Atlantic Ocean c. 56 Mya. The name is a portmanteau of Laurentia and Asia. Laurentia, Avalonia, Baltica, and a series of smaller terranes, collided in the Caledonian orogeny c. 400 Ma to form Laurussia (also known as Euramerica, or the Old Red Sandstone Continent). Laurussia then collided with Gondwana to form Pangaea. Kazakhstania and Siberia were then added to Pangaea 290–300 Ma to form Laurasia. Laurasia finally became an independent continental mass when Pangaea broke up into Gondwana and Laurasia. Terminology and origin of the concept Laurentia, the Palaeozoic core of North America and continental fragments that now make ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Periods. It is characterized by the dominance of archosaurian reptiles, like the dinosaurs; an abundance of conifers and ferns; a hot greenhouse climate; and the tectonic break-up of Pangaea. The Mesozoic is the middle of the three eras since Cambrian explosion, complex life evolved: the Paleozoic, the Mesozoic, and the Cenozoic. The era began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, the largest well-documented mass extinction in Earth's history, and ended with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, another mass extinction whose victims included the non-avian dinosaurs, Pterosaur, pterosaurs, Mosasaur, mosasaurs, and Plesiosaur, plesiosaurs. The Mesozoic was a time of significant tectonic, climatic, and evolut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vicariance
Allopatric speciation () – also referred to as geographic speciation, vicariant speciation, or its earlier name the dumbbell model – is a mode of speciation that occurs when biological populations become geographically isolated from each other to an extent that prevents or interferes with gene flow. Various geographic changes can arise such as the movement of continents, and the formation of mountains, islands, bodies of water, or glaciers. Human activity such as agriculture or developments can also change the distribution of species populations. These factors can substantially alter a region's geography, resulting in the separation of a species population into isolated subpopulations. The vicariant populations then undergo genetic changes as they become subjected to different selective pressures, experience genetic drift, and accumulate different mutations in the separated populations' gene pools. The barriers prevent the exchange of genetic information between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geodispersal At Bering Land Bridge
In biogeography, geodispersal is the erosion of barriers to gene flow and biological dispersal (Lieberman, 2005.; Albert and Crampton, 2010.). Geodispersal differs from vicariance, which reduces gene flow through the creation of geographic barriers. In geodispersal, the geographical ranges of individual taxa, or of whole biota (ecology), biotas, are merged by erosion of a physical barrier to gene flow or Biological dispersal, dispersal. Multiple related geodispersal and vicariance events can be mutually responsible for differences among populations. As these geographic barriers break down, organisms of the secluded ecosystems can interact, allowing gene flow between previously separated species, creating more biological variation within a region. A well documented example of geodispersal in between continental ecosystems was the Great American Biotic Interchange (GABI) between the terrestrial faunas and floras of North America and South America, that followed the formation of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |