|
Binary Ethylenimine
Binary ethylenimine (BEI) is a preparation of aziridine. It can be produced by heating bromoethylamine hydrobromide or 2-aminoethyl hydrogen sulfate in the presence of sodium hydroxide ( Gabriel method). It contains at least one three-membered ring which is very reactive because of the ring strain. It is used to inactivate the foot-and-mouth disease virus in vaccines for cattle, as well as other viruses and mycoplasma in blood samples. Contrary to early assumptions that ethylenimines only modified nucleic acids, it was found that trimeric ethylenimine also alters proteins in virus preparations, especially at higher pH values. The modification of the proteins affected viral particle uptake into cells. This should be taken into consideration when using BEI and other ethyleneimines as well. Safety BEI is very hazardous since it attacks nucleic acids and proteins as described above. It can be neutralised by sodium thiosulfate; the thiosulfate is a nucleophile which opens the three-me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aziridine
Aziridine is an organic compound consisting of the three-membered heterocycle . It is a colorless, toxic, volatile liquid that is of significant practical interest. Aziridine was discovered in 1888 by the chemist Siegmund Gabriel. Its derivatives, also referred to as aziridines, are of broader interest in medicinal chemistry. Structure The bond angles in aziridine are approximately 60°, considerably less than the normal hydrocarbon bond angle of 109.5°, which results in angle strain as in the comparable cyclopropane and ethylene oxide molecules. A banana bond model explains bonding in such compounds. Aziridine is less basic than acyclic aliphatic amines, with a pKa of 7.9 for the conjugate acid, due to increased s character of the nitrogen free electron pair. Angle strain in aziridine also increases the barrier to nitrogen inversion. This barrier height permits the isolation of separate ''invertomers'', for example the ''cis'' and ''trans'' invertomers of ''N''-chloro- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations and hydroxide anions . Sodium hydroxide is a highly caustic base and alkali that decomposes proteins at ordinary ambient temperatures and may cause severe chemical burns. It is highly soluble in water, and readily absorbs moisture and carbon dioxide from the air. It forms a series of hydrates . The monohydrate crystallizes from water solutions between 12.3 and 61.8 °C. The commercially available "sodium hydroxide" is often this monohydrate, and published data may refer to it instead of the anhydrous compound. As one of the simplest hydroxides, sodium hydroxide is frequently used alongside neutral water and acidic hydrochloric acid to demonstrate the pH scale to chemistry students. Sodium hydroxide is used in many industries: in the manufacture of pulp and paper, textiles, drinking water, soaps and deterge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aziridine
Aziridine is an organic compound consisting of the three-membered heterocycle . It is a colorless, toxic, volatile liquid that is of significant practical interest. Aziridine was discovered in 1888 by the chemist Siegmund Gabriel. Its derivatives, also referred to as aziridines, are of broader interest in medicinal chemistry. Structure The bond angles in aziridine are approximately 60°, considerably less than the normal hydrocarbon bond angle of 109.5°, which results in angle strain as in the comparable cyclopropane and ethylene oxide molecules. A banana bond model explains bonding in such compounds. Aziridine is less basic than acyclic aliphatic amines, with a pKa of 7.9 for the conjugate acid, due to increased s character of the nitrogen free electron pair. Angle strain in aziridine also increases the barrier to nitrogen inversion. This barrier height permits the isolation of separate ''invertomers'', for example the ''cis'' and ''trans'' invertomers of ''N''-chloro- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
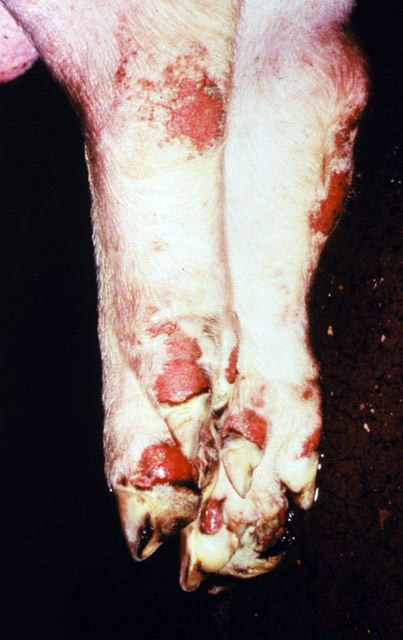
Foot-and-mouth Disease
Foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) or hoof-and-mouth disease (HMD) is an infectious and sometimes fatal viral disease that affects cloven-hoofed animals, including domestic and wild bovids. The virus causes a high fever lasting two to six days, followed by blisters inside the mouth and near the hoof that may rupture and cause lameness. FMD has very severe implications for animal farming, since it is highly infectious and can be spread by infected animals comparatively easily through contact with contaminated farming equipment, vehicles, clothing, and feed, and by domestic and wild predators. Its containment demands considerable efforts in vaccination, strict monitoring, trade restrictions, quarantines, and the culling of both infected and healthy (uninfected) animals. Susceptible animals include cattle, water buffalo, sheep, goats, pigs, antelope, deer, and bison. It has also been known to infect hedgehogs and elephants; llamas and alpacas may develop mild symptoms, but are resistant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaccine
A vaccine is a biological Dosage form, preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease, infectious or cancer, malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verified. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism and is often made from weakened or Antigen, killed forms of the microbe, its toxins, or one of its surface proteins. The agent stimulates the body's immune system to recognize the agent as a threat, destroy it, and to further recognize and destroy any of the microorganisms associated with that agent that it may encounter in the future. Vaccines can be prophylaxis, prophylactic (to prevent or ameliorate the effects of a future infection by a natural or "wild" pathogen), or therapeutic vaccines, therapeutic (to fight a disease that has already occurred, such as cancer vaccine, cancer). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus ''Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult males are referred to as bulls. Cattle are commonly raised as livestock for meat (beef or veal, see beef cattle), for milk (see dairy cattle), and for hides, which are used to make leather. They are used as riding animals and draft animals ( oxen or bullocks, which pull carts, plows and other implements). Another product of cattle is their dung, which can be used to create manure or fuel. In some regions, such as parts of India, cattle have significant religious significance. Cattle, mostly small breeds such as the Miniature Zebu, are also kept as pets. Different types of cattle are common to different geographic areas. Taurine cattle are found primarily in Europe and temperate areas of Asia, the Americas, and Australia. Zebus (also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycoplasma
''Mycoplasma'' is a genus of bacteria that, like the other members of the class ''Mollicutes'', lack a cell wall around their cell membranes. Peptidoglycan (murein) is absent. This characteristic makes them naturally resistant to antibiotics that target cell wall synthesis (like the beta-lactam antibiotics). They can be parasitic or saprotrophic. Several species are pathogenic in humans, including '' M. pneumoniae'', which is an important cause of "walking" pneumonia and other respiratory disorders, and '' M. genitalium'', which is believed to be involved in pelvic inflammatory diseases. ''Mycoplasma'' species (like the other species of the class ''Mollicutes'') are among the smallest organisms yet discovered, can survive without oxygen, and come in various shapes. For example, ''M. genitalium'' is flask-shaped (about 300 x 600 nm), while ''M. pneumoniae'' is more elongated (about 100 x 1000 nm), many ''Mycoplasma'' species are coccoid. Hundreds of ''Mycoplasma'' species i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the circulatory system is also known as ''peripheral blood'', and the blood cells it carries, ''peripheral blood cells''. Blood is composed of blood cells suspended in blood plasma. Plasma, which constitutes 55% of blood fluid, is mostly water (92% by volume), and contains proteins, glucose, mineral ions, hormones, carbon dioxide (plasma being the main medium for excretory product transportation), and blood cells themselves. Albumin is the main protein in plasma, and it functions to regulate the colloidal osmotic pressure of blood. The blood cells are mainly red blood cells (also called RBCs or erythrocytes), white blood cells (also called WBCs or leukocytes) and platelets (also called thrombocytes). The most abundant cells in vertebrate blo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleic Acid
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, macromolecules, essential to all known forms of life. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomers made of three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). If the sugar is ribose, the polymer is RNA; if the sugar is the ribose derivative deoxyribose, the polymer is DNA. Nucleic acids are naturally occurring chemical compounds that serve as the primary information-carrying molecules in cells and make up the genetic material. Nucleic acids are found in abundance in all living things, where they create, encode, and then store information of every living cell of every life-form on Earth. In turn, they function to transmit and express that information inside and outside the cell nucleus to the interior operations of the cell and ultimately to the next generation of each living organism. The encoded information is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Thiosulfate
Sodium thiosulfate (sodium thiosulphate) is an inorganic compound with the formula . Typically it is available as the white or colorless pentahydrate, . The solid is an efflorescent (loses water readily) crystalline substance that dissolves well in water. Sodium thiosulfate is used in gold mining, water treatment, analytical chemistry, the development of silver-based photographic film and prints, and medicine. The medical uses of sodium thiosulfate include treatment of cyanide poisoning and pityriasis. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Uses Sodium thiosulfate is used predominantly in industry. For example, it is used to convert dyes to their soluble colorless forms, which are called leuco. It is also used to bleach "wool, cotton, silk, ...soaps, glues, clay, sand, bauxite, and... edible oils, edible fats, and gelatin." Medical uses Sodium thiosulfate is used in the treatment of cyanide poisoning. Other uses include topical treatment of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver Nitrate
Silver nitrate is an inorganic compound with chemical formula . It is a versatile precursor to many other silver compounds, such as those used in photography. It is far less sensitive to light than the halides. It was once called ''lunar caustic'' because silver was called ''luna'' by ancient alchemists who associated silver with the moon. In solid silver nitrate, the silver ions are three- coordinated in a trigonal planar arrangement. Synthesis and structure Albertus Magnus, in the 13th century, documented the ability of nitric acid to separate gold and silver by dissolving the silver. Indeed silver nitrate can be prepared by dissolving silver in nitric acid followed by evaporation of the solution. The stoichiometry of the reaction depends upon the concentration of nitric acid used. :3 Ag + 4 HNO3 (cold and diluted) → 3 AgNO3 + 2 H2O + NO :Ag + 2 HNO3 (hot and concentrated) → AgNO3 + H2O + NO2 The structure of silver nitrate has been examined by X-ray crystallography sever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |