|
Bhopalgarh Tehsil
Bhopalgarh tehsil is a tehsil in Jodhpur District of Rajasthan state in western India. Headquarters for the tehsil is the town of Bhopalgarh. Bhopalgarh tehsil is an eastern tehsil among the 13 tehsils in Jodhpur District. It borders Nagaur District to the north and east, Piparcity, Pipar city tehsil to the south, Jodhpur tehsil to the southwest, and Bawadi tehsil to the west. Bhopalgarh Panchayat samiti (block), panchayat samiti has 35 gram panchayats & 116 villages. The mineral and the stone used for Emery Stone are found in Bhopalgarh. Rabi crops are mainly cultivated in the Bhopalgarh Tehsil with Bajra, Moong, Moth, Sesamum (Til), Jowar and Cotton being the most common crops. Bhopalgarh tehsil has a total area of 174623.74 hectares with total cultivable area of 63.92% of total area & 21.27% of total cultivable area as irrigated area as per land use 2011. Jats are the dominant community in bhopalgarh . There number vary close to one lakh in the entire constituency . Demographic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jodhpur Rural District
Jodhpur Gramin is district in Rajasthan, Rajashtan. This district was formed in 7 August 2023. Its administrative headquarters is Jodhpur district. References Districts of Rajasthan Districts in Jodhpur division {{Rajasthan-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piparcity
Pipar city ( hi, पीपाड़ सिटी या पीपाड़ शहर) is a town and a municipality in Jodhpur district in the Indian state of Rajasthan Rajasthan (; lit. 'Land of Kings') is a state in northern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern si .... Jojari River, the tributary of Luni River passes through this town. Demographics Piparcity had a population of 36,810. Males constitute 52% of the population and females 48%. Piparcity has an average literacy rate of 52%, lower than the national average of 59.5%: male literacy is 66%, and female literacy is 36%. In Piparcity, 18% of the population is under 6 years of age. Education It has a government women's college, Smt. Sita Dewi Chunni Lal Bardiya Mahila Mahavidyalay and three senior secondary level government schools along with other private colleges and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sopra, Bhopalgarh
Sopara or Sopra or Hopra is a village located in the Bhopalgarh tehsil of Jodhpur District, Rajasthan, India. History The habitation is around 500 years old. It is said that the village was established by the two brothers and their nephew who travelled to the place long back ago from Kurchi (another village). All the people of the village are the progeny of the three gentlemen. As a result, the village is divided in three major "baas" (habitations), namely "Uperly Baas", "Bhichily Baas" and "Khurali Baas". The name "Sopra" It is said that the three men reached the place at time of dusk, so they called the place , or , meaning "dusk is approached" in the local language, Marwari. Later it corrupted to Sopda and Sopra. Demographics Sopra has population of 1264 of which 658 are males while 606 are females as per Population Census 2011. In Sopra village population of children with age 0–6 is 140. 659 of the population are literate. Languages: People predominantly speak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ratkuria
Ratkuria is a village in Bhopalgarh tehsil, Jodhpur district, Rajasthan, India located at . Its PIN code A personal identification number (PIN), or sometimes redundantly a PIN number or PIN code, is a numeric (sometimes alpha-numeric) passcode used in the process of authenticating a user accessing a system. The PIN has been the key to facilitati ... is 342606. It is the location of a Ch. Gullaram Government Senior Secondary School. References Villages in Jodhpur district {{Rajasthan-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuri, Bhopalgarh
Kuri is a small village located in the Bhopalgarh tehsil of the Jodhpur District of the State of Rajasthan in western India. About Kuri is a large village in the Bhopalgarh tehsil of the Jodhpur District of the State of Rajasthan, India. It is located 62 km to the east of the Jodhpur District headquarters, 13 km from Bhopalgarh and 277 km from the state capital of Jaipur Kuri Pin code is 342606 and postal head office is Pipar Road. Near Kuri are the cities of Pipar City, Phalodi, Bilara, and Jodhpur. Population According to 2011 census, the Kuri population is :Male Population 1675 :Female Population 1566 :;Total Population 3241 Language Marwari is the dominant local language and Hindi is used. Geography It is among the larger villages of the area: : Tambariya Kalan (8 km) : Bhundana (9 km) : Malar (9 km) : Kagal (10 km) : Dewatra (11 km) : Sopra (6 km) Surrounding Kuri is: :West - Mandor tehsil :West - Jodhpur tehs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kur, Rajasthan
Kur is a panchayat village in Rajasthan in western India. Administratively, it is under Bhopalgarh tehsil, Jodhpur District of the state of Rajasthan.2011 Census Village code for Koor = 084887, There are three villages in the Kood gram panchayat Gram Panchayat () is a basic village-governing institute in Indian villages. It is a democratic structure at the grass-roots level in India. It is a political institute, acting as cabinet of the village. The Gram Sabha work as the general bod ...: Kur, Hinganiya (Hingania) and Khokhariya (Khokharia). Demographics In the 2001 census, the village of Kur had 2,042 inhabitants, with 1,044 males (51.1%) and 998 females (48.9%), for a gender ratio of 956 females per thousand males. Notes Villages in Jodhpur district {{Rajasthan-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panchayat Village
Gram Panchayat () is a basic village-governing institute in Indian villages. It is a democratic structure at the grass-roots level in India. It is a political institute, acting as cabinet of the village. The Gram Sabha work as the general body of the Gram Panchayat. The members of the Gram Panchayat are elected by the Gram Sabha. There are about 250,000+ Gram Panchayats in India. History Established in various states of India, the Panchayat Raj system has three tiers: Zila Parishad, at the district level; Panchayat Samiti, at the block level; and Gram Panchayat, at the village level. Rajasthan was the first state to establish Gram Panchayat, Bagdari Village (Nagaur District) being the first village where Gram Panchayat was established, on 2 October 1959. The failed attempts to deal with local matters at the national level caused, in 1992, the reintroduction of Panchayats for their previously used purpose as an organisation for local self-governance. Structure Gram P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scheduled Castes And Scheduled Tribes
The Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs) are officially designated groups of people and among the most disadvantaged socio-economic groups in India. The terms are recognized in the Constitution of India and the groups are designated in one or other of the categories. For much of the period of British rule in the Indian subcontinent, they were known as the Depressed Classes. In modern literature, the ''Scheduled Castes'' are sometimes referred to as Dalit, meaning "broken" or "dispersed", having been popularised by B. R. Ambedkar (1891–1956), a Dalit himself, an economist, reformer, chairman of the Constituent Assembly of India, and Dalit leader during the independence struggle. Ambedkar preferred the term Dalit to Gandhi's term, Harijan, meaning "person of Hari/Vishnu" (or Man of God). In September 2018, the government "issued an advisory to all private satellite channels asking them to 'refrain' from using the nomenclature 'Dalit'", though "rights groups and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
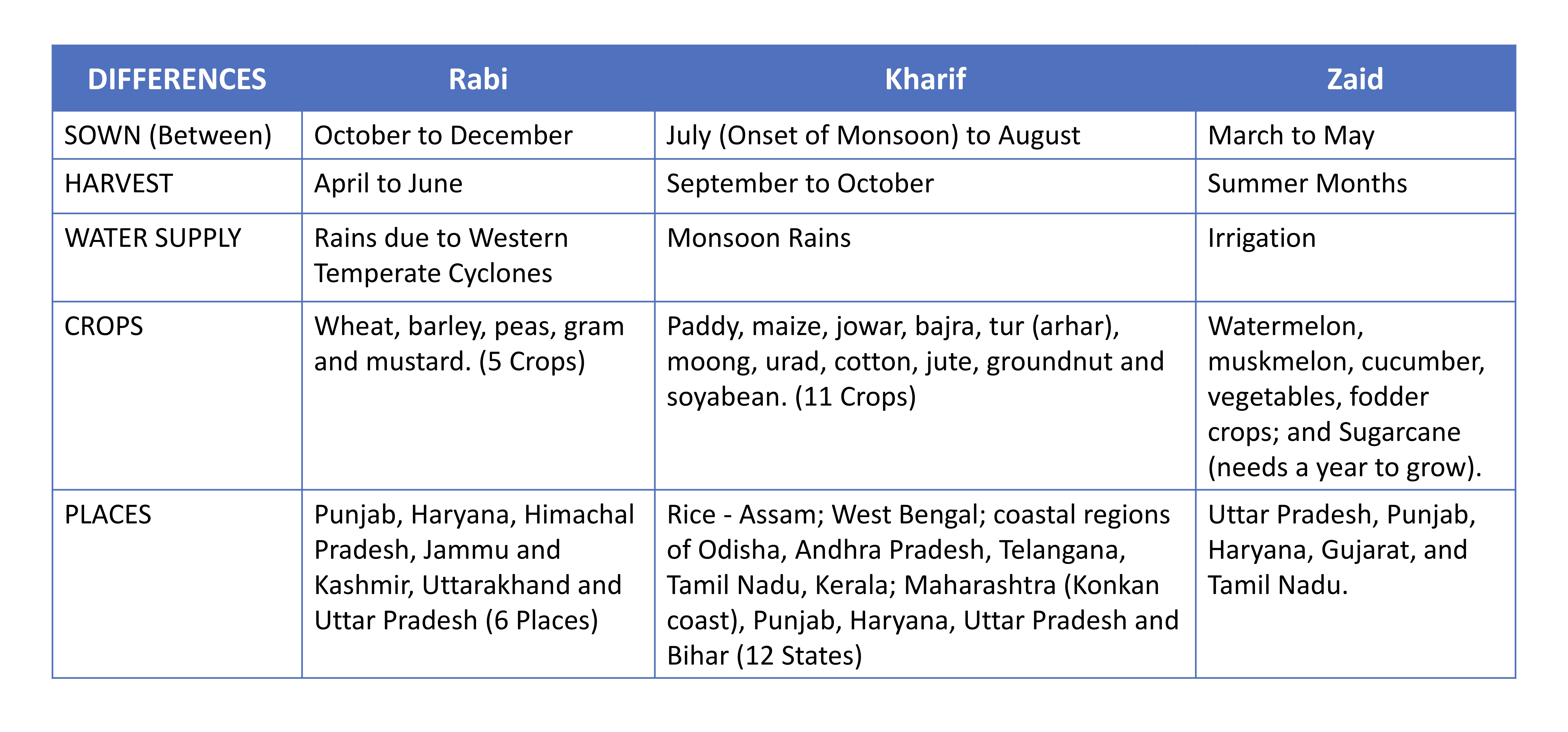
Rabi Crop
Rabi crops or rabi harvest, also known as winter crops, are agricultural crops that are sown in winter and harvested in the spring in India, Pakistan and Bangladesh. The complimentary of the rabi crop is the kharif crop, which is grown after the rabi and zaid (zaa-id) crops are harvested one after another respectively. Etymology The words ''Kharif'' and ''rabi'' have their origins in Arabic. These came to be used in India with the ascent of the Mughal empire in the Indian subcontinent and have been widely used ever since. The term is derived from the Arabic word for "spring", which is used in the Indian subcontinent, where it is the spring harvest (also known as the "winter crop"). Rabi season in India The rabi crops are sown around mid-November, preferably after the monsoon rains are over, and harvesting begins in April / May. The crops are grown either with rainwater that has percolated into the ground or using irrigation. Good rain in winter spoils the rabi crops but is go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram Panchayat
Gram Panchayat () is a basic village-governing institute in Indian villages. It is a democratic structure at the grass-roots level in India. It is a political institute, acting as cabinet of the village. The Gram Sabha work as the general body of the Gram Panchayat. The members of the Gram Panchayat are elected by the Gram Sabha. There are about 250,000+ Gram Panchayats in India. History Established in various states of India, the Panchayat Raj system has three tiers: Zila Parishad, at the district level; Panchayat Samiti, at the block level; and Gram Panchayat, at the village level. Rajasthan was the first state to establish Gram Panchayat, Bagdari Village (Nagaur District) being the first village where Gram Panchayat was established, on 2 October 1959. The failed attempts to deal with local matters at the national level caused, in 1992, the reintroduction of Panchayats for their previously used purpose as an organisation for local self-governance. Structure Gram P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |