|
Bhoota Kola
Būta Kōlā,/buːt̪ʌ/ is the local pronunciation while the standardised Kannada pronunciation is /bʱuːt̪ʌ koːlɑː/ also referred to as daiva kōlā or nēmā, is a ritual dance performance prevalent among the Hindus of Tulu Nadu and parts of Kasargod in northern Kerala, India. The dance is highly stylized and performed as part of 'Bhootaradhana' or worship of the local deities worshipped by the Tulu speaking population. It has influenced Yakshagana folk theatre. Būta kōlā is closely related to Theyyam of neighbouring Malayalam-speaking populations. List of Daivas Panjurli, a boar spirit that is worshipped to ward off the menace of wild boars in order to protect the crops. Bobbarya, the God of the seas who is worshipped mostly by members of the fishing community. Kallurti Kalkuda Guliga Koragajja Etymology The word is derived from ''būta'' (Tulu for ‘spirit’, ‘deity’; in turn derived from Sanskrit भूत for ‘free elements’, 'which is pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koraga People
The Koraga are a tribal community found mainly in the Dakshina Kannada, Udupi districts of Karnataka and the Kasaragod district of Kerala, south India. These areas in Karnataka, are altogether often referred to as Tulunaad, which roughly corresponds to the boundaries of the erstwhile South Canara district. They are also found in small numbers in adjoining districts of Uttara Kannada, Shimoga and Kodagu. The Koraga are classified by the Government of India as a Scheduled Tribe. The Koraga, who numbered 16,071 according to the 2001 census of India, have their own language, classified as an independent Dravidian language, which is strongly influenced by Tulu, Kannada, Malayalam, languages commonly found in their area. Social status The 1901 census report noted the Koraga as being a lowly tribe of basket-makers and labourers, some of whom were employed as scavengers. They remain today among the untouchables, being considered as ritually polluted by Hindus, but there have in the pas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mogaveera
The Mogaveera, or Mogavira is a subcaste of the Koli caste living in the Karnataka state of India. They dominated maritime activities in coastal Karnataka. History Mogaveera means a warrior who after the demolition of the kingdom continued to live on river belts and coastal belts and pursue their traditional occupation of fishing. Mogaveera people form a community who dominate fishing and marine activities in and around Mangalore. The Mogaveeras who have taken up fishing as their profession are called ''Marakalas''. Some have also found occupation as peasants and artisans. Community organisations A community organisation called Dakshina Kannada Mogaveera Mahajana Sabha (DKMMS) was established in 1923 with 146 gram sabha. There were other such associations previously, including one in Bombay that was founded in 1902; others included those at Mangalore, Barkur and Udupi, some of which merged. The various groups became distinguishable by the different languages. The Mogavee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banga Arasa
Banga Arasa or Banga Raja is the dynastic title of a medieval ruling family of coastal Karnataka, India. The word ''Banga'' is the name of a clan and a surname of the Bunts and the word ''Arasa'' or ''Raja'' means a ruler in the Tulu language. The dynasty followed the Bunt custom of matrilineal inheritance (Aliyasantana). The Banga Arasas claimed descent from the ancient Alupas and the rulers bore the Alupa royal title ''Pandyapparasa''. The Banga Arasas were said to have been given control of 15 sub-divisions (Magane) of Southern Tulu Nadu by the Hoysala Ballal Emperor, Vira Narasimha. The Banga Arasas ruled from 1224 C.E until the conquest of South Canara by the British in 1799 CE. Descendants of the dynasty survive. However, the family seems to have stopped the coronation ritual after 1889 CE. Since the cessation of the coronation ritual no member of the family has borne the princely title ''Banga Arasa'' or ''Banga Raja'' instead preferring the aristocratic title Ballal. The dyn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belle, Udupi
Belle (also known as Bollay) is a village in the southern state of Karnataka, India.Village code=01308800 It is located in the Udupi taluk of Udupi district. The village is known for its historic Moodu-Belle Mahalingeshwara Temple dedicated to Shiva. Demographics As of the 2001 India census, Belle had a population of 5324 with 2441 males and 2883 females. Economy The village economy is predominantly based on agriculture, with plenty of rice cultivation. Some modern changes are apparent. Cultivation of Jasmine flowers, coconut, arecanut, sugarcane and poultry farming is on the rise. The weekly market of Belle is on Tuesdays. Belle is connected to Udupi, the district and Taluka headquarters, Karkala, Shirva, and Katapadi by a bus service. The economic prosperity of the village may be due to the employment of a significant a number of people from the village in the Gulf countries. History and culture Moodubelle Mahalingeshwara Temple The village has a thousand year old ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kantara (film)
''Kantara'' () is a 2022 Indian Kannada-language action thriller film written and directed by Rishab Shetty, and produced by Vijay Kiragandur, under Hombale Films. The film stars Shetty as a Kambala champion who is at loggerheads with an upright forest officer, Murali (played by Kishore). Set and filmed in Keradi in coastal Karnataka, principal photography began in August 2021. The cinematography was handled by Arvind S. Kashyap, with B. Ajaneesh Loknath scoring music for the film and the action sequences were choreographed by the action director Vikram More. The production design was handled by debutant, Dharani Gange Putra. ''Kantara'' was released on 30 September 2022 and received acclaim from critics, who praised the cast performances (particularly those of Shetty and Kishore), direction, writing, production design, cinematography, proper showcasing of the Bhoota Kola, action sequences, editing, soundtrack, and musical score. The film was a huge commercial success and eme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patrilineality
Patrilineality, also known as the male line, the spear side or agnatic kinship, is a common kinship system in which an individual's family membership derives from and is recorded through their father's lineage. It generally involves the inheritance of property, rights, names, or titles by persons related through male kin. This is sometimes distinguished from cognate kinship, through the mother's lineage, also called the spindle side or the distaff side. A patriline ("father line") is a person's father, and additional ancestors, as traced only through males. Traditionally and historically people would identify the person's ethnicity with the father's heritage and ignore the maternal ancestry in the ethnic factor. In the Bible In the Bible, family and tribal membership appears to be transmitted through the father. For example, a person is considered to be a priest or Levite, if his father is a priest or Levite, and the members of all the Twelve Tribes are called Israelites because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrilineality
Matrilineality is the tracing of kinship through the female line. It may also correlate with a social system in which each person is identified with their matriline – their mother's lineage – and which can involve the inheritance of property and/or titles. A matriline is a line of descent from a female ancestor to a descendant (of either sex) in which the individuals in all intervening generations are mothersin other words, a "mother line". In a matrilineal descent system, an individual is considered to belong to the same descent group as their mother. This ancient matrilineal descent pattern is in contrast to the currently more popular pattern of patrilineal descent from which a family name is usually derived. The ''matriline'' of historical nobility was also called their enatic or uterine ancestry, corresponding to the patrilineal or "agnatic" ancestry. Early human kinship In the late 19th century, almost all prehistorians and anthropologists believed, followi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Billava
The Billava, Billoru, Biruveru people are an ethnic group of India. They are found traditionally in Tulu Nadu region and engaged in toddy tapping, cultivation and other activities. They have used both missionary education and Sri Narayana Guru's reform movement to upgrade themselves. Etymology and origins L. K. Ananthakrishna Iyer recounted the community's belief that ''billava'' means ''bowmen'' and that it "applied to the castemen who were largely employed as soldiers by the native rulers of the district". Edgar Thurston had reached a similar conclusion in 1909. The Billavas are first recorded in inscriptions dating from the fifteenth century AD but Amitav Ghosh notes that "... this is merely an indication of their lack of social power; there is every reason to suppose that all the major Tuluva castes share an equally long history of settlement in the region". The earliest epigraphy for the Tuluva Bunt community dates to around 400 years earlier. Language There is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
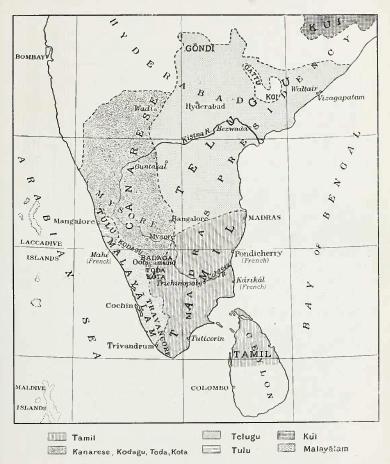
Castes And Tribes Of Southern India
''Castes and Tribes of Southern India'' is a seven-volume encyclopedia of social groups of Madras Presidency and the princely states of Travancore, Mysore, Coorg and Pudukkottai published by British museologist Edgar Thurston and K. Rangachari in 1909. Background The seven-volume work was one of several such publications resulting from the Ethnographic Survey of India project which was formally instituted by the Government of British India in 1901. The Survey was intended to record details of the manners, customs and physical features of Indian castes and tribes using in part the anthropometric methods that had first been used in India by Herbert Hope Risley for his own survey of the tribes and castes of Bengal. An eight-year period of funding was allotted for the purpose. The British government in India appointed a Superintendent of Ethnography for each province. Thurston, who had been Superintendent of the Madras Government Museum since 1885, had already conducted some e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global population, known as Hindus. The word ''Hindu'' is an exonym, and while Hinduism has been called the oldest religion in the world, many practitioners refer to their religion as '' Sanātana Dharma'' ( sa, सनातन धर्म, lit='the Eternal Dharma'), a modern usage, which refers to the idea that its origins lie beyond human history, as revealed in the Hindu texts. Another endonym is ''Vaidika dharma'', the dharma related to the Vedas. Hinduism is a diverse system of thought marked by a range of philosophies and shared concepts, rituals, cosmological systems, pilgrimage sites, and shared textual sources that discuss theology, metaphysics, mythology, Vedic yajna, yoga, agamic rituals, and temple building, among other to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |