|
Beta Function (accelerator Physics)
The beta function in accelerator physics is a function related to the transverse size of the particle beam at the location s along the nominal beam trajectory. It is related to the transverse beam size as follows:https://www.cockcroft.ac.uk/wp-content/uploads/2014/12/Neil_3.pdf \sigma(s) = \sqrt where * s is the location along the nominal beam trajectory * the beam is assumed to have a Gaussian shape in the transverse direction * \sigma(s) is the width parameter of this Gaussian * \epsilon is the RMS geometrical beam emittance, which is normally constant along the trajectory when there is no acceleration Typically, separate beta functions are used for two perpendicular directions in the plane transverse to the beam direction (e.g. horizontal and vertical directions). The beta function is one of the Courant–Snyder parameters (also called Twiss parameters). Beta star The value of the beta function at an interaction point is referred to as beta star. The beta function is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accelerator Physics
Accelerator physics is a branch of applied physics, concerned with designing, building and operating particle accelerators. As such, it can be described as the study of motion, manipulation and observation of relativistic charged particle beams and their interaction with accelerator structures by electromagnetic fields. It is also related to other fields: *Microwave engineering (for acceleration/deflection structures in the radio frequency range). *Optics with an emphasis on geometrical optics (beam focusing and bending) and laser physics (laser-particle interaction). *Computer technology with an emphasis on digital signal processing; e.g., for automated manipulation of the particle beam. *Plasma physics, for the description of intense beams. The experiments conducted with particle accelerators are not regarded as part of accelerator physics, but belong (according to the objectives of the experiments) to, e.g., particle physics, nuclear physics, condensed matter physics or m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
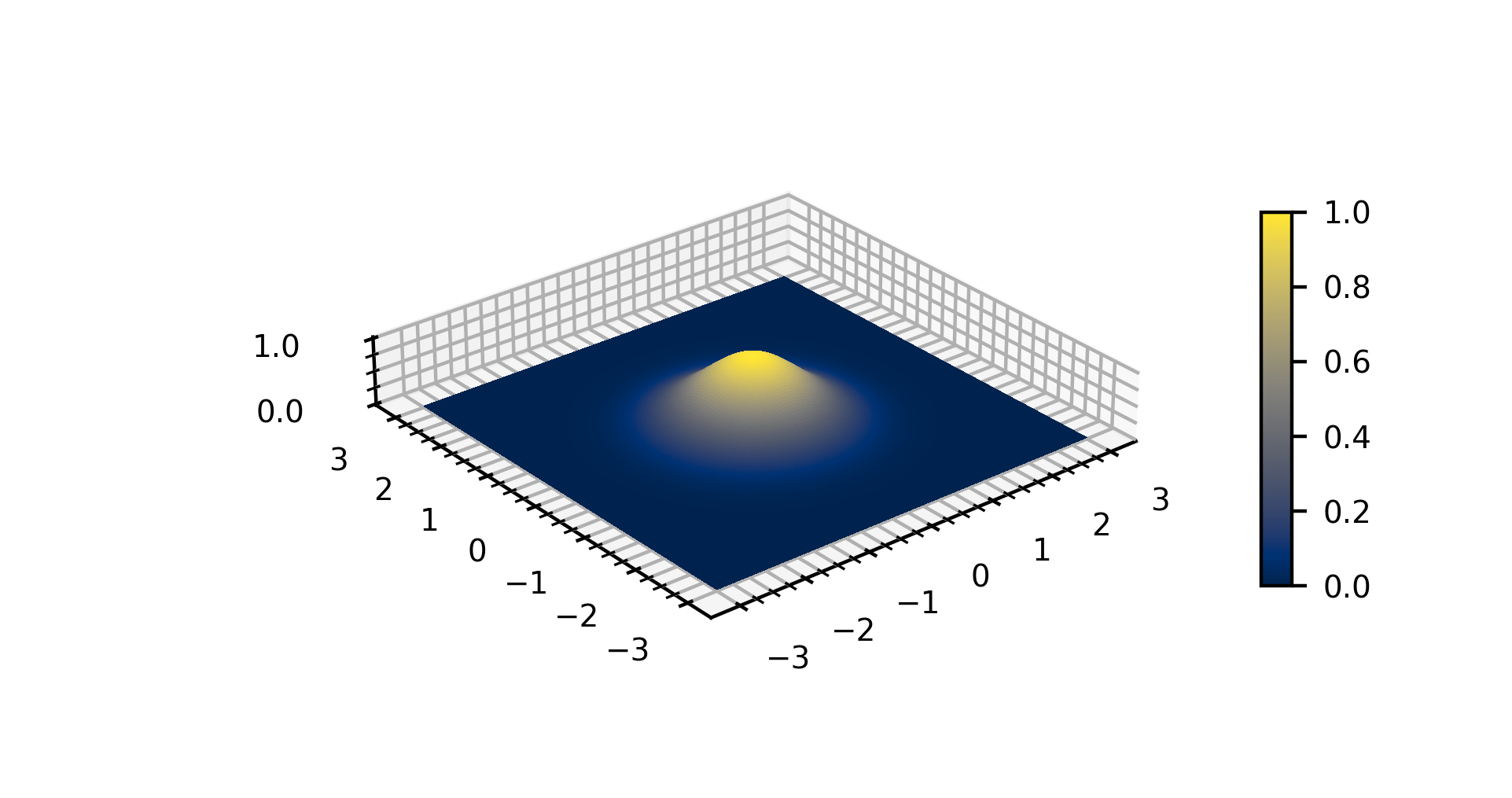
Gaussian Function
In mathematics, a Gaussian function, often simply referred to as a Gaussian, is a function of the base form f(x) = \exp (-x^2) and with parametric extension f(x) = a \exp\left( -\frac \right) for arbitrary real constants , and non-zero . It is named after the mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss. The graph of a Gaussian is a characteristic symmetric " bell curve" shape. The parameter is the height of the curve's peak, is the position of the center of the peak, and (the standard deviation, sometimes called the Gaussian RMS width) controls the width of the "bell". Gaussian functions are often used to represent the probability density function of a normally distributed random variable with expected value and variance . In this case, the Gaussian is of the form g(x) = \frac \exp\left( -\frac \frac \right). Gaussian functions are widely used in statistics to describe the normal distributions, in signal processing to define Gaussian filters, in image processing where two-dimensio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beam Emittance
In accelerator physics, emittance is a property of a charged particle beam. It refers to the area occupied by the beam in a position-and-momentum phase space. Each particle in a beam can be described by its position and momentum along each of three orthogonal axes, for a total of six position and momentum coordinates. When the position and momentum for a single axis are plotted on a two dimensional graph, the average spread of the coordinates on this plot are the emittance. As such, a beam will have three emittances, one along each axis, which can be described independently. As particle momentum along an axis is usually described as an angle relative to that axis, an area on a position-momentum plot will have dimensions of length × angle (for example, millimeters × milliradian). Emittance is important for analysis of particle beams. As long as the beam is only subjected to conservative forces, Liouville's Theorem shows that emittance is a conserved quantity. If t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Courant–Snyder Parameters
In accelerator physics, the Courant–Snyder parameters (frequently referred to as Twiss parameters or CS parameters) are a set of quantities used to describe the distribution of positions and velocities of the particles in a beam. When the positions along a single dimension and velocities (or momenta) along that dimension of every particle in a beam are plotted on a phase space diagram, an ellipse enclosing the particles can be given by the equation: :\gamma x^2 + 2 \alpha x x' + \beta x'^2 = \epsilon where x is the position axis and x' is the velocity axis. In this formulation, \alpha, \beta, and \gamma are the Courant–Snyder parameters for the beam along the given axis, and \epsilon is the emittance. Three sets of parameters can be calculated for a beam, one for each orthogonal direction, x, y, and z. History The use of these parameters to describe the phase space properties of particle beams was popularized in the accelerator physics community by Ernest Courant and Har ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aperture (other)
The aperture of an optical system is the opening that limits the amount of light that can pass through. Aperture may also refer to: Science and technology *In anatomy, a number of apertures in the human body: ** Apertura nasalis posterior ** Apertura pelvis inferior ** Apertura pelvis minoris ** Apertura pelvis superior ** Apertura thoracis inferior ** Apertura thoracis superior **Lateral aperture (foramen of Luschka), an opening in each lateral extremity of the lateral recess of the fourth ventricle of the human brain **Median aperture (foramen of Magendie), which drains cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the fourth ventricle into the cisterna magna *Antenna aperture, a physical parameter of an antenna *Aperture (mollusc), the main opening in the shell of a gastropod or scaphopod (mollusc) *Aperture (botany), a weaker spot in the wall of a pollen grain *Numerical aperture is a parameter used to describe optical systems *Aperture (computer memory), a region of the physical address spac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |