|
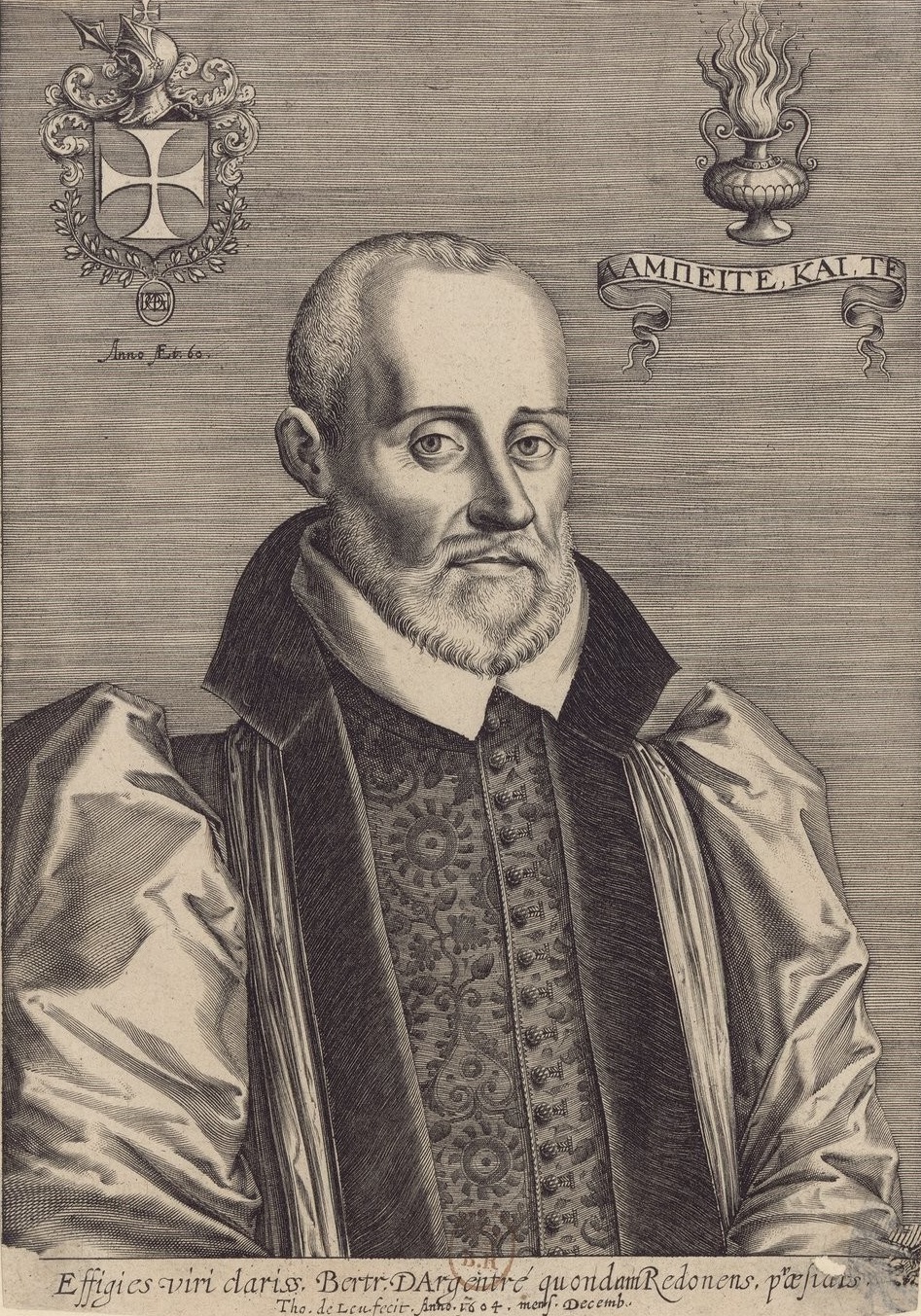
Bertrand D'Argentré
Bertrand d'Argentré (or Argentraeus) (19 May 1519 in Vitré, Ille-et-Vilaine – 13 February 1590) was a Breton jurist and historian. Argentraeus was born the son of Pierre d'Argentré, seneschal of Rennes, and the nephew of historian Pierre Le Baud. After studies of law in Bourges, he was named seneschal of Vitré in 1541 and seneschal of Rennes in 1547. Dismissed from that post, he was named head of the présidial court of Rennes in 1582 instead, but refused to leave Brittany even when offered coveted court positions in Paris. In his judicial capacity, he frequently clashed with other jurisdictions such as that of the Parlement, which he considered ignorant of Breton customs. His principal legal work is the influential ''Nouvelle coutume de Bretagne'' (1580), a compilation of customary Breton law. In that work, D'Argentré fought against the influence of French and Roman law, which he considered overly procedural and inquisitive, unmerciful to the weak, and detrimental to in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Law
Roman law is the law, legal system of ancient Rome, including the legal developments spanning over a thousand years of jurisprudence, from the Twelve Tables (c. 449 BC), to the ''Corpus Juris Civilis'' (AD 529) ordered by Eastern Roman emperor Justinian I. Roman law forms the basic framework for Civil law (legal system), civil law, the most widely used legal system today, and the terms are sometimes used synonymously. The historical importance of Roman law is reflected by the continued use of List of legal Latin terms, Latin legal terminology in many legal systems influenced by it, including common law. After the dissolution of the Western Roman Empire, the Roman law remained in effect in the Eastern Roman Empire. From the 7th century onward, the legal language in the East was Greek. ''Roman law'' also denoted the legal system applied in most of Western Europe until the end of the 18th century. In Germany, Roman law practice remained in place longer under the Holy Roman Empire ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16th-century French Lawyers
The 16th century begins with the Julian year 1501 ( MDI) and ends with either the Julian or the Gregorian year 1600 ( MDC) (depending on the reckoning used; the Gregorian calendar introduced a lapse of 10 days in October 1582). The 16th century is regarded by historians as the century which saw the rise of Western civilization and the Islamic gunpowder empires. The Renaissance in Italy and Europe saw the emergence of important artists, authors and scientists, and led to the foundation of important subjects which include accounting and political science. Copernicus proposed the heliocentric universe, which was met with strong resistance, and Tycho Brahe refuted the theory of celestial spheres through observational measurement of the 1572 appearance of a Milky Way supernova. These events directly challenged the long-held notion of an immutable universe supported by Ptolemy and Aristotle, and led to major revolutions in astronomy and science. Galileo Galilei became a champion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Vitré, Ille-et-Vilaine
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its use as a plural form of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1590 Deaths
Year 159 (CLIX) was a common year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time in Roman territories, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Quintillus and Priscus (or, less frequently, year 912 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 159 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place India * In India, the reign of Shivashri Satakarni, as King Satavahana of Andhra, begins. Births * December 30 – Lady Bian, wife of Cao Cao (d. 230) * Annia Aurelia Fadilla, daughter of Marcus Aurelius * Gordian I, Roman emperor (d. 238) * Lu Zhi, Chinese general (d. 192) Deaths * Liang Ji, Chinese general and regent * Liang Nüying Liang Nüying () (died 159), formally Empress Yixian (懿獻皇后, literally "the meek and wise empress") was an empress during Han Dynasty. She was Emperor Huan of Han, Emper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1519 Births
__NOTOC__ Year 1519 ( MDXIX) was a common year starting on Saturday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar, the 1519th year of the Common Era (CE) and ''Anno Domini'' (AD) designations, the 519th year of the 2nd millennium, the 19th year of the 16th century, and the 10th and last year of the 1510s decade. Events January–June * January 1 – Ulrich Zwingli preaches for the first time, as people's priest of the Great Minister in Zürich. * March 4 – Hernán Cortés and his conquistadores land in Mexico. * April 21 (Maundy Thursday) – Hernán Cortés reaches San Juan de Ulúa; next day (Good Friday) he sets foot on the beach of modern-day Veracruz. * May 2 – 67-year-old Leonardo da Vinci dies. * June 28 – Charles I of Spain becomes Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor (rules until 1556). July–December * July 4 – Martin Luther joins the debate regarding papal authority, against Johann Eck at Leipzig. * July ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cujas Library
Cujas Library (french: Bibliothèque Cujas), named after the French jurist and scholar Jacques Cujas (1520–1590), is an academic research library, and the largest law library in Europe.Oswald, Godfrey (2008). '' Library world records'' (2nd ed.) McFarland & Company, p. 97. It is located in the Latin Quarter, next to the Panthéon and Sainte-Geneviève Library, in the 5th arrondissement of Paris. History Cujas Library was originally the library of the Law School of the University of Paris (which dates back to 1215). The collections of the library were dispersed during the French Revolution . Consequently the current collections have been built since 1829 only. From 1876 to 1914, Paul Viollet, head librarian, dedicated much effort to developing the library’s collections. At that time, the library was located in the main building of the Law School of Paris, on the Place du Panthéon. In 1958, a new building was opened to house the Library. In 1970, the University of Paris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicolas Buon
Nicolas or Nicolás may refer to: People Given name * Nicolas (given name) Mononym * Nicolas (footballer, born 1999), Brazilian footballer * Nicolas (footballer, born 2000), Brazilian footballer Surname Nicolas * Dafydd Nicolas (c.1705–1774), Welsh poet * Jean Nicolas (1913–1978), French international football player * Nicholas Harris Nicolas (1799–1848), English antiquary * Paul Nicolas (1899–1959), French international football player * Robert Nicolas (1595–1667), English politician Nicolás * Adolfo Nicolás (1936–2020), Superior General of the Society of Jesus * Eduardo Nicolás (born 1972), Spanish former professional tennis player Other uses * Nicolas (wine retailer), a French chain of wine retailers * ''Le Petit Nicolas'', a series of children's books by René Goscinny See also * San Nicolás (other) * Nicholas (other) * Nicola (other) * Nikola Nikola () is a given name which, like Nicholas, is a version of the Greek ''Nikolaos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippe Emmanuel, Duke Of Mercœur
Philippe is a masculine sometimes feminin given name, cognate to Philip. It may refer to: * Philippe of Belgium (born 1960), King of the Belgians (2013–present) * Philippe (footballer) (born 2000), Brazilian footballer * Prince Philippe, Count of Flanders, father to Albert I of Belgium * Philippe d'Orléans (other), multiple people * Philippe A. Autexier (1954–1998), French music historian * Philippe Blain, French volleyball player and coach * Philippe Najib Boulos (1902–1979), Lebanese lawyer and politician * Philippe Coutinho, Brazilian footballer * Philippe Daverio (1949–2020), Italian art historian * Philippe Dubuisson-Lebon, Canadian football player * Philippe Ginestet (born 1954), French billionaire businessman, founder of GiFi * Philippe Gilbert, Belgian bicycle racer * Philippe Petit, French performer and tightrope artist * Philippe Petitcolin (born 1952/53), French businessman, CEO of Safran * Philippe Russo, French singer * Philippe Sella, French rugby pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry III Of France
Henry III (french: Henri III, né Alexandre Édouard; pl, Henryk Walezy; lt, Henrikas Valua; 19 September 1551 – 2 August 1589) was King of France from 1574 until his assassination in 1589, as well as King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1573 to 1575. As the fourth son of King Henry II of France, he was not expected to inherit the French throne and thus was a good candidate for the vacant throne of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, where he was elected List of Polish rulers#Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, 1569–1795, monarch in 1573. During his brief rule, he signed the Henrician Articles into law, recognizing the szlachta's right to Royal elections in Poland, freely elect their monarch. Aged 22, Henry abandoned Poland–Lithuania upon inheriting the French throne when his brother, Charles IX of France, Charles IX, died without issue. France was at the time plagued by the French Wars of Religion, Wars of Religion, and Henry's authority was undermi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
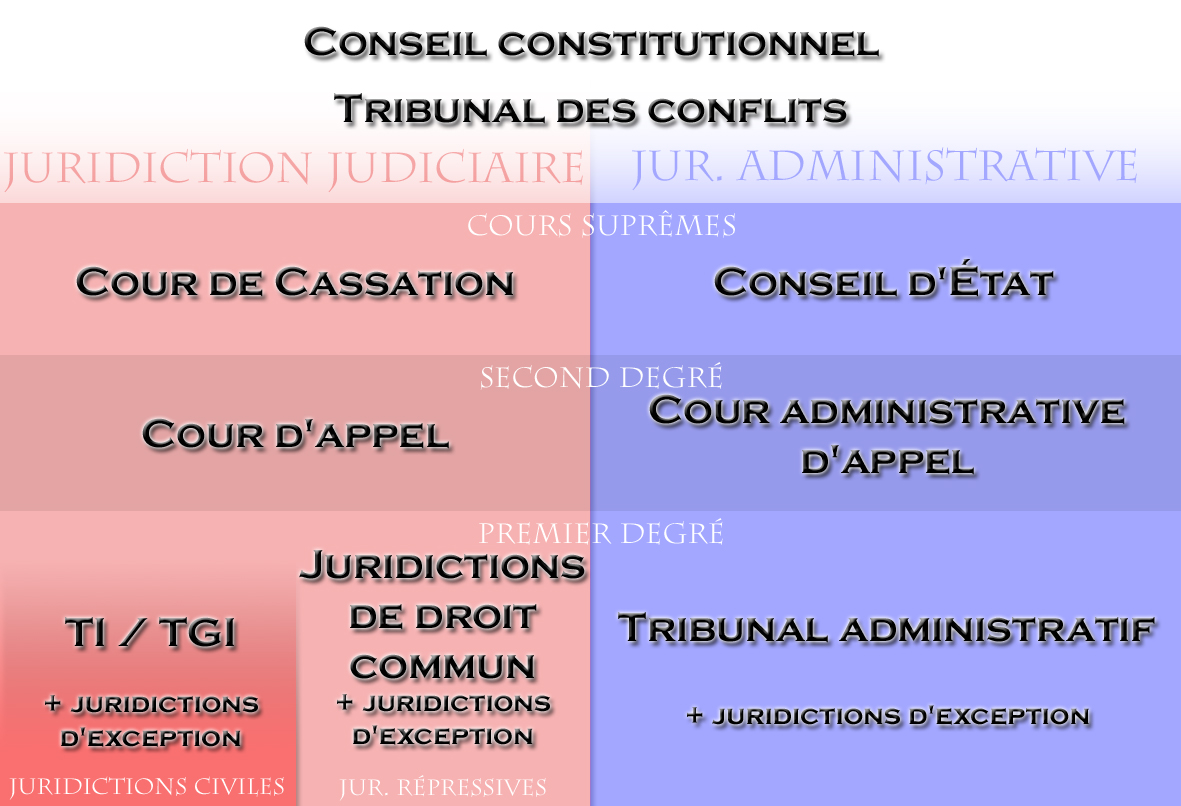
French Law
The Law of France refers to the legal system in the French Republic, which is a civil law legal system primarily based on legal codes and statutes, with case law also playing an important role. The most influential of the French legal codes is the Napoleonic Civil Code, which inspired the civil codes of Europe and later across the world. The Constitution of France adopted in 1958 is the supreme law in France. European Union law is becoming increasingly important in France, as in other EU member states. In academic terms, French law can be divided into two main categories: private law (''Droit privé'') and public law (''droit public''). This differs from the traditional common law concepts in which the main distinction is between criminal law and civil law. Private law governs relationships between individuals. It includes, in particular: * Civil law ('). This branch refers to the field of private law in common law systems. This branch encompasses the fields of inheritance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_1938.jpg)