|
Bere Alston Railway Station
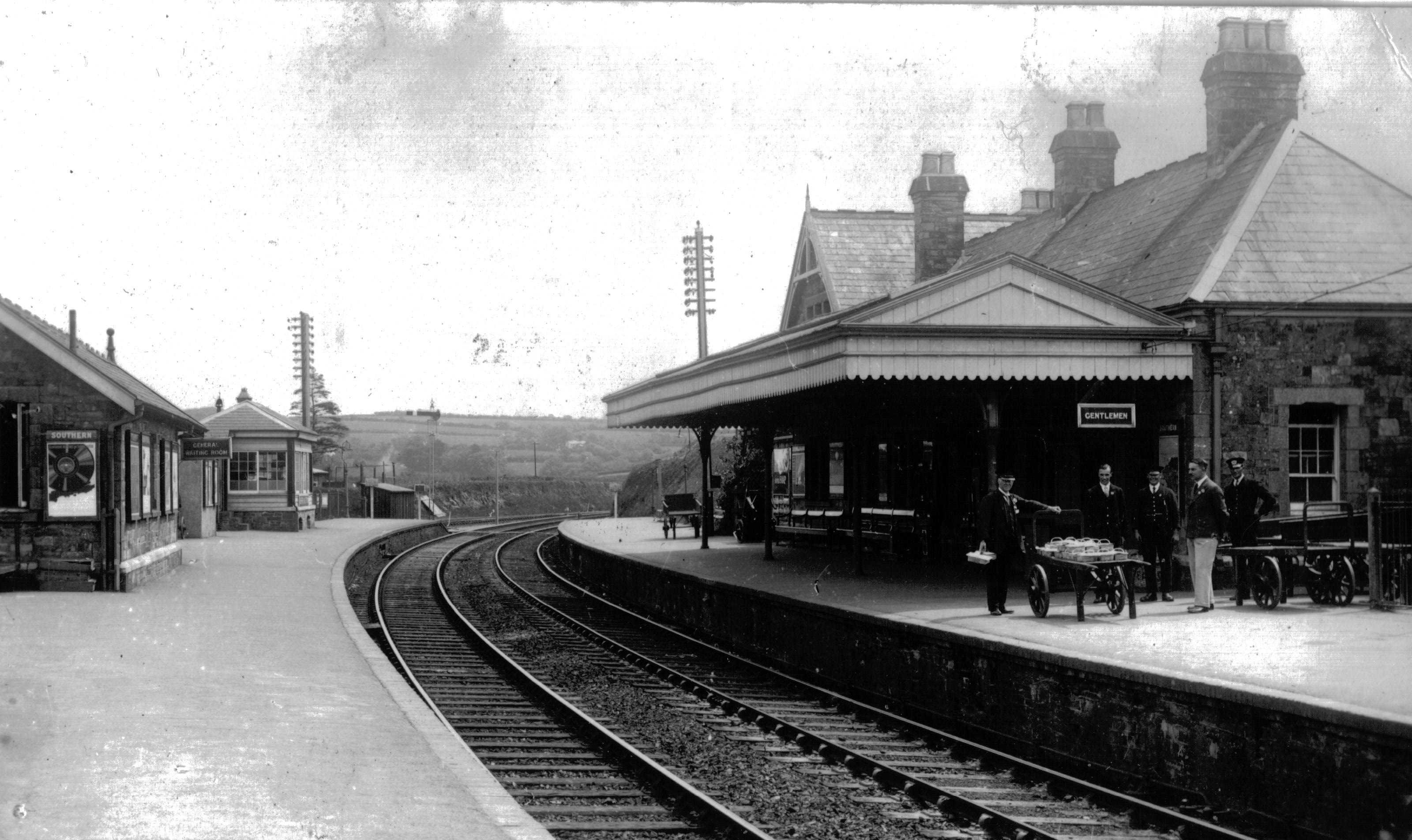
Bere Alston railway station serves the village of Bere Alston in Devon, England, north of Plymouth on the Tamar Valley Line to Gunnislake. The route escaped complete closure in the 1960s mainly because places on the line have relatively poor road connections. However, one section of the branch, beyond Gunnislake to Callington, did not survive. History Beer Alston station was opened for passengers on 2 June 1890 by the Plymouth, Devonport and South Western Junction Railway as an intermediate station on that company's line from Lydford to Devonport, which – being in effect an extension of the London and South Western Railway's main line from London Waterloo station to Lydford, enabling the LSWR to reach Plymouth independently of the Great Western Railway – was immediately leased to the LSWR. Bere Alston station was 220 miles and 15 chains (354.35 km) from Waterloo. The station was originally called Beer Alston after the local Beer family who owned several near ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bere Alston
Bere Alston is a village in West Devon in the county of Devon in England. It forms part of the civil parish of Bere Ferrers. History and geography With a population of about 2,000, the village lies in the Bere peninsula, between the rivers Tamar and Tavy. Its origins lie in the once thriving local mining industry, including silver and lead, and the market gardening sector. At one time, the mainline trains to London would stop at the village to pick up locally grown produce destined for the capital. Bere Alston is about 12 km north of the centre of Plymouth as the crow flies, but the road trip requires either a long detour via Tavistock or else negotiating narrow lanes and a narrow bridge. Trains still run to Bere Alston railway station on the picturesque Tamar Valley Line between Plymouth and Gunnislake, and trains reverse at this station. There has been discussion of making the station a junction once again by reopening the former 'main line' to Tavistock, the largest tow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, received its enabling Act of Parliament on 31 August 1835 and ran its first trains in 1838 with the initial route completed between London and Bristol in 1841. It was engineered by Isambard Kingdom Brunel, who chose a broad gauge of —later slightly widened to —but, from 1854, a series of amalgamations saw it also operate standard-gauge trains; the last broad-gauge services were operated in 1892. The GWR was the only company to keep its identity through the Railways Act 1921, which amalgamated it with the remaining independent railways within its territory, and it was finally merged at the end of 1947 when it was nationalised and became the Western Region of British Railways. The GWR was called by some "God's Wonderful Railway" and by others the "Great Way Round" but it was famed as the "Holiday ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bere Ferrers Railway Station
Bere Ferrers station on the Tamar Valley Line is situated near the village of Bere Ferrers in Devon, England. The station is on the former Southern main line between Exeter and via . It is currently operated by Great Western Railway (GWR). History The Plymouth, Devonport and South Western Junction Railway opened the station on 2 June 1890 with its main line from to Devonport, which gave the London and South Western Railway a route into Plymouth that was independent of the Great Western Railway. The station was originally called Beer Ferris after the local Beer family who owned several nearby villages. However, in 1897, the railway authorities of the time decided that this name promoted an unrefined image of the village due to the association with beer, and therefore changed the name to Bere Ferrers. The original spelling can still be seen on the sign on the signal box in the heritage centre. The station was host to a Southern Railway camping coach from 1936 to 1939. A cam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bere Alston 150127
Bere may refer to: Places * Bere, Botswana, a village * Béré, Burkina Faso, a city * Bere Department, Burkina Faso * Béré, Chad, a city * Béré Region, Woroba District, Ivory Coast * Bere Bay, Nunavut, Canada * Early name for the village of Beercrocombe in Somerset, England * Alternative spelling for Beer, Somerset in Aller, Somerset, England * Forest of Bere, Hampshire, England * Bere or Beara peninsula, Ireland ** Bere or Bear (barony), County Cork; on the peninsula ** Bere Island, in the barony * ''Bere'', the Hungarian name for Berea village, Ciumești Commune, Satu Mare County, Romania Other uses * Bere (surname) (including a list of people with the name) * Bere (grain), a barley cultivar See also * De la Bere baronets * Beres (other) * Beer (other) Beer is an alcoholic drink. Beer may also refer to: Places * Beer, Devon, England, a coastal village * Beer, Somerset, England, a hamlet * Beer, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan, a union council * Bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tavistock Railway Station (proposed)
Tavistock railway station is a proposed new station to serve Tavistock in Devon, England, in order to reinstate a rail connection between the town and Plymouth, about to the south. History Tavistock used to have two railway stations, both now closed, with trains to Plymouth: * Tavistock North was the Plymouth, Devonport and South Western Junction Railway station, operated by the London and South Western Railway. * Tavistock South was the Great Western Railway station, on the other side of the river Tavy, opposite the town. Current situation The trackbed of the Tavistock North route for around a mile south of Tavistock North station is open to the public as a footpath and nature reserve. The route is almost intact to Bere Alston where it joins today's Tamar Valley Line between Gunnislake and Plymouth. An engineering assessment in 2009 showed that the rail-bed, bridges and tunnels between Bere Alston and Tavistock were in sound condition. The Tamar Valley line, with which the lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tavistock, Devon
Tavistock ( ) is an ancient stannary and market town within West Devon, England. It is situated on the River Tavy from which its name derives. At the 2011 census the three electoral wards (North, South and South West) had a population of 13,028. It traces its recorded history back to at least 961 when Tavistock Abbey, whose ruins lie in the centre of the town, was founded. Its most famous son is Sir Francis Drake. History Middle Ages The area around Tavistock (formerly Tavistoke), where the River Tavy runs wide and shallow allowing it to be easily crossed, and near the secure high ground of Dartmoor, was inhabited long before historical records. The surrounding area is littered with archaeological remains from the Bronze and Iron Ages and it is believed a hamlet existed on the site of the present town long before the town's official history began, with the founding of the Abbey. The abbey of Saint Mary and Saint Rumon was founded in 961 by Ordgar, Earl of Devon. After destruct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilbride Community Rail
Kilbride may refer to the following places: Canada *Kilbride, St. John's, Newfoundland and Labrador *Kilbride (electoral district), for the House of Assembly of Newfoundland and Labrador * Kilbride, Ontario, community near Burlington *Castle Kilbride, historic house in Baden, Ontario Ireland and Northern Ireland *Kilbride, County Antrim, village in County Antrim, Northern Ireland * Kilbride, Trim, County Meath, settlement near Trim in Dunderry parish * Kilbride, Ratoath, County Meath * Kilbride, County Cavan, townland and civil parish in County Cavan, Ireland * Kilbride, County Down, townland in County Down, Northern Ireland *Kilbride, County Waterford, townland in Ireland *Kilbride, County Westmeath (civil parish), in Fartullagh, County Westmeath, Ireland *Kilbride, County Westmeath, townland in Kilbride, Fartullagh, County Westmeath, Ireland *Kilbride, County Wicklow, village in Leinster, Ireland, also called Manor Kilbride *Kilbride, County Wicklow, a townland in the Barony o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beeching Axe
The Beeching cuts (also Beeching Axe) was a plan to increase the efficiency of the nationalised railway system in Great Britain. The plan was outlined in two reports: ''The Reshaping of British Railways'' (1963) and ''The Development of the Major Railway Trunk Routes'' (1965), written by Richard Beeching and published by the British Railways Board. The first report identified 2,363 stations and of railway line for closure, amounting to 55% of stations, 30% of route miles, and 67,700 British Rail positions, with an objective of stemming the large losses being incurred during a period of increasing competition from road transport and reducing the rail subsidies necessary to keep the network running. The second report identified a small number of major routes for significant investment. The 1963 report also recommended some less well-publicised changes, including a switch to the now-standard practice of containerisation for rail freight, and the replacement of some services wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Okehampton Railway Station
Okehampton railway station is a terminus railway station on the Dartmoor line serving the town of Okehampton in Devon, England. The station closed to regular traffic in 1972, but heritage and occasional mainline services ran from 1997 to 2019. Regular railway services resumed in November 2021. History The station opened in 1871 when the London and South Western Railway (LSWR) extended its line from . Services were extended further west to with the inauguration of Meldon Viaduct in 1874. Constructed to rival the South Devon Railway route to Plymouth, the completion of the LSWR's own route to Plymouth saw Okehampton become an important junction with lines to Padstow and as well as . Boat trains carrying passengers from ocean liners calling at Stonehouse Pool, Plymouth and prestige services such as the Atlantic Coast Express and Devon Belle all used the route. From 1960 to 1964 it was the terminus of a car-carrying train from . With the publication of the Beeching Repo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
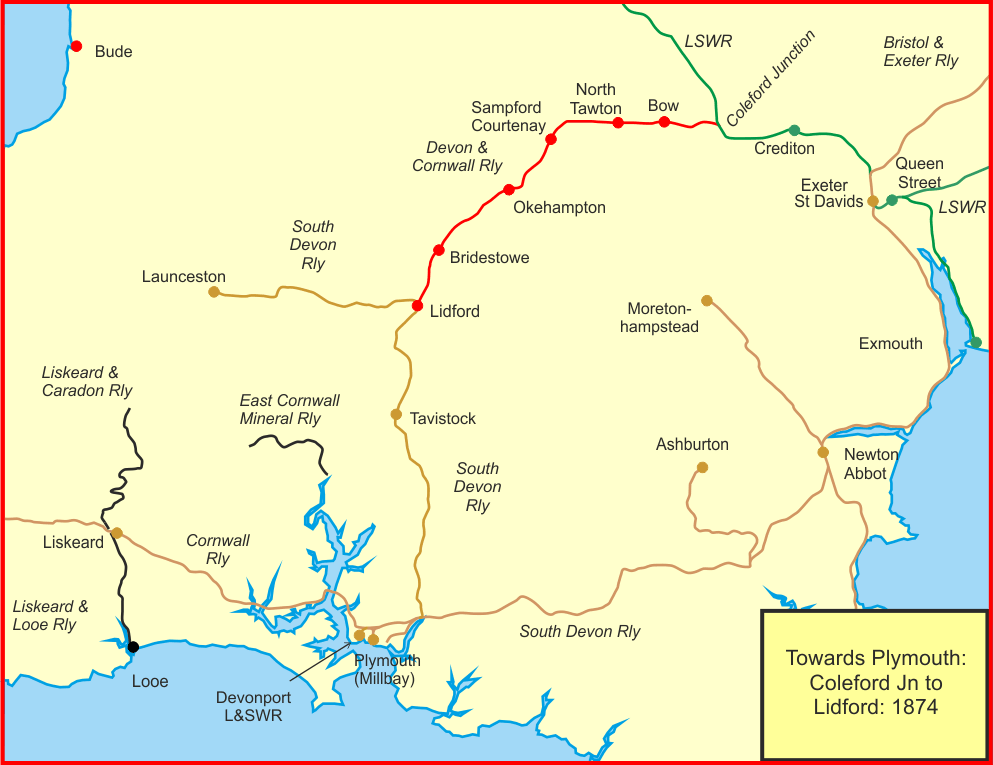
Exeter To Plymouth Railway Of The LSWR
The Exeter to Plymouth railway of the London and South Western Railway (LSWR) was the westernmost part of a route competing with that of the Great Western Railway (GWR) and its 'associated companies' from London and Exeter to Plymouth in Devon, England. Whereas the GWR route from Exeter followed the coast to Newton Abbot and then went around the southern edge of Dartmoor, the LSWR route followed the northern and western margins of Dartmoor, passing through the towns of Crediton, Okehampton, and Tavistock. The route was constructed piecemeal by independent companies, in most cases supported by the LSWR. LSWR trains first reached Plymouth in 1876 and the route took on its final form in 1891. The central part of the line closed in 1968, leaving just local services at either end. History Railways to Exeter The broad gauge Bristol and Exeter Railway (B&ER) was the first line to reach Exeter. It had reached St Davids station in Exeter in 1844 and was allied with the Great We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Railways
British Railways (BR), which from 1965 traded as British Rail, was a state-owned company that operated most of the overground rail transport in Great Britain from 1948 to 1997. It was formed from the nationalisation of the Big Four British railway companies, and was privatised in stages between 1994 and 1997. Originally a trading brand of the Railway Executive of the British Transport Commission, it became an independent statutory corporation in January 1963, when it was formally renamed the British Railways Board. The period of nationalisation saw sweeping changes in the railway. A process of dieselisation and electrification took place, and by 1968 steam locomotives had been entirely replaced by diesel and electric traction, except for the Vale of Rheidol Railway (a narrow-gauge tourist line). Passengers replaced freight as the main source of business, and one-third of the network was closed by the Beeching cuts of the 1960s in an effort to reduce rail subsidies. On privatis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Railway (Great Britain)
The Southern Railway (SR), sometimes shortened to 'Southern', was a British railway company established in the 1923 Grouping. It linked London with the Channel ports, South West England, South coast resorts and Kent. The railway was formed by the amalgamation of several smaller railway companies, the largest of which were the London and South Western Railway (LSWR), the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway (LB&SCR) and the South Eastern and Chatham Railway (SE&CR).Bonavia (1987) pp. 26-28 The construction of what was to become the Southern Railway began in 1838 with the opening of the London and Southampton Railway, which was renamed the London & South Western Railway. The railway was noted for its astute use of public relations and a coherent management structure headed by Sir Herbert Walker. At , the Southern Railway was the smallest of the '' Big Four'' railway companies and, unlike the others, the majority of its revenue came from passenger traffic rather than freight. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)
