|
Battle Of The Chosin Reservoir
The Battle of Chosin Reservoir, also known as the Chosin Reservoir Campaign or the Battle of Lake Changjin (), was an important battle in the Korean War. The name "Chosin" is derived from the Japanese pronunciation "''Chōshin'', instead of the Korean pronunciation. The battle took place about a month after the People's Republic of China entered the conflict and sent the People's Volunteer Army (PVA) 9th Army to infiltrate the northeastern part of North Korea. On 27 November 1950, the Chinese force surprised the US X Corps (United States), X Corps commanded by Major General Edward Almond in the Chosin Reservoir area. A brutal 17-day battle in freezing weather soon followed. Between 27 November and 13 December, 30,000 United Nations Command troops (later nicknamed "The Chosin Few") under the field command of Major General Oliver P. Smith were encircled and attacked by about 120,000 Chinese troops under the command of Song Shilun, who had been ordered by Mao Zedong to d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Phase Offensive
The Second Phase Offensive (25 November – 24 December 1950) or Second Phase Campaign () of the Korean War was an offensive by the People's Republic of China, Chinese People's Volunteer Army (PVA) against United Nations Command (U.S./UN) forces, most of which were soldiers of First Republic of Korea, South Korea and the United States. The two major engagements of the campaign were the Battle of the Ch'ongch'on River in the western part of North Korea and the Battle of Chosin Reservoir in the eastern part of North Korea. Casualties were heavy on both sides. The battles were fought in temperatures as low as and casualties from frostbite may have exceeded those from battle wounds. On 23 December 1950 Lieutenant General Walton Walker died in a vehicle accident in Seoul while in command of the U.S. 8th Army. He was the highest ranked U.S. military service member killed in the Korean War. U.S. intelligence and air reconnaissance failed to detect the large numbers of Chinese soldiers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People's Republic Of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and borders fourteen countries by land, the most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four municipalities, and two Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the most populous city and financial center is Shanghai. Modern Chinese trace their origins to a cradle of civilization in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. The semi-legendary Xia dynasty in the 21st century BCE and the well-attested Shang and Zhou dynasties developed a bureaucratic political system to serve hereditary monarchies, or dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UN September 1950 Counteroffensive
The UN September 1950 counteroffensive was a large-scale offensive by United Nations Command (UN) forces against North Korean forces commencing on 23 September 1950. Following the UN counterattack at Inchon on 15 September, on 16 September UN forces within the Pusan Perimeter broke out of the perimeter, driving back the North Koreans and moved north linking up with the UN forces coming from Inchon near Osan on 27 September. Background By 23 September the Korean People's Army (KPA) was everywhere in retreat from the Pusan Perimeter. US Eighth Army, motorized and led by armored spearheads, was ready to sweep forward along the main axes of advance. On 22 September Eighth Army commander General Walton Walker issued his order for the pursuit. The Eighth Army order stated: Enemy resistance has deteriorated along the Eighth Army front permitting the assumption of a general offensive from present positions. In view of this situation it is mandatory that all efforts be directed toward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Inchon
The Battle of Incheon (), also spelled Battle of Inchon, was an amphibious invasion and a battle of the Korean War that resulted in a decisive victory and strategic reversal in favor of the United Nations Command (UN). The operation involved some 75,000 troops and 261 naval vessels and led to the recapture of the South Korean capital of Seoul two weeks later. The code name for the operation was Operation Chromite. The battle began on 15 September 1950 and ended on 19 September. Through a surprise amphibious assault far from the Pusan Perimeter that UN and Republic of Korea Army (ROK) forces were desperately defending, the largely undefended city of Incheon was secured after being bombed by UN forces. The battle ended a string of victories by the North Korean Korean People's Army (KPA). The subsequent UN recapture of Seoul partially severed the KPA's supply lines in South Korea. The UN and ROK forces were commanded by General of the Army Douglas MacArthur of the United States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
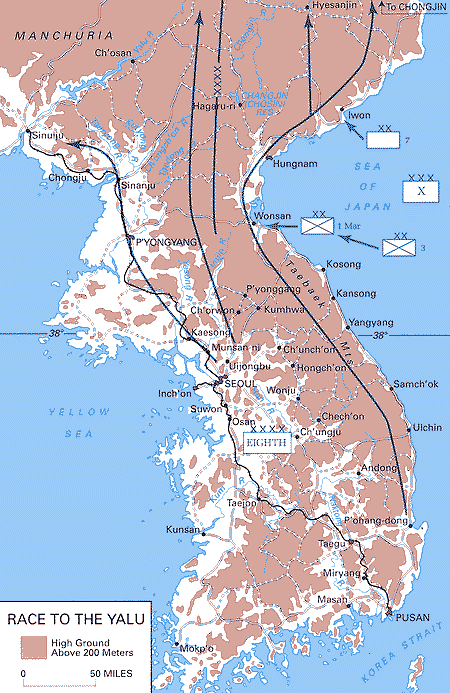
Race To Yalu Map
Race, RACE or "The Race" may refer to: * Race (biology), an informal taxonomic classification within a species, generally within a sub-species * Race (human categorization), classification of humans into groups based on physical traits, and/or social relations * Racing, a competition of speed Rapid movement * The Race (yachting race) * Mill race, millrace, or millrun, the current of water that turns a water wheel, or the channel (sluice) conducting water to or from a water wheel * Tidal race, a fast-moving tide passing through a constriction Acronyms * RACE encoding, a syntax for encoding non-ASCII characters in ASCII * Radio Amateur Civil Emergency Service, in the US, established in 1952 for wartime use * Rapid amplification of cDNA ends, a technique in molecular biology * RACE (Remote Applications in Challenging Environments), a robotics development center in the UK * RACE Racing Academy and Centre of Education, a jockey and horse-racing industry training centre in Kildare t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungnam Evacuation
The Hungnam evacuation' (), also known as the Miracle of Christmas, was the evacuation of United Nations Command, United Nations (UN) forces and North Korean civilians from the port of Hungnam, North Korea, between 15 and 24 December 1950 during the Korean War. As part of the Withdrawal (military)#Tactical withdrawal, fighting withdrawal of UN forces against the People's Volunteer Army (PVA) during the Battle of the Chosin Reservoir (27 November to 13 December), they abandoned some 59,000 square kilometers of North Korean territory to enemy forces and retreated to Hungnam from where they were evacuated to South Korea. Background On 8 December 1950 US X Corps (United States), X Corps commander General Edward Almond received UN Commander General Douglas MacArthur’s order to evacuate X Corps through Hungnam. Following the earlier decision to concentrate X Corps forces at Hungnam, the evacuation of Wonsan had begun on 3 December. In a week’s time, without interference from PVA or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eighth United States Army
The Eighth Army is a U.S. field army which is the commanding formation of all United States Army United States Forces Korea, forces in South Korea. It commands U.S. and South Korean units and is headquartered at the Camp Humphreys,Yongsan garrison move pushed back to 2019 in the Anjeong-ri of Pyeongtaek, Pyeongtaek, South Korea. It is the only field army in the U.S. Army. History World War II The unit first activated on 10 June 1944 in the United States, under the command of Lieutenant General Robert Eichelberger. The Eighth Army took part in many of the amphibious landings in the Southwest Pacific Theater of World War II, eventually participating in no less than sixty of them. The first mission of the Eighth Army, in September 1944, was to ta ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungnam
Hŭngnam is a district of Hamhung, the second largest city in North Korea. It is a port city on the eastern coast on the Sea of Japan. It is only from the slightly inland city of Hamhung. In 2005 it became a ward of Hamhung. History The port at Hŭngnam was the site of the Hŭngnam evacuation, a major evacuation of both United Nations military and North Korean civilians during the Korean War in late December 1950. Approximately 100,000 troops and material and 100,000 civilians were loaded onto a variety of merchant ships and military transports totaling 193 shiploads over the weeks leading up to Christmas 1950, and were transported to safety in Pusan and other destinations in South Korea. The evacuation included 14,000 refugees who were transported on one ship, the SS ''Meredith Victory'' - the largest evacuation from land by a single ship. This was made possible by a declaration of national emergency by President Truman issued on 16 December 1950 with Presidential Proclamati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Withdrawal (military)
A tactical withdrawal or retreating defensive action is a type of military operation, generally meaning that retreating forces draw back while maintaining contact with the enemy. A withdrawal may be undertaken as part of a general retreat, to consolidate forces, to occupy ground that is more easily defended, force the enemy to overextend to secure a decisive victory, or to lead the enemy into an ambush. It is considered a relatively risky operation, requiring discipline to keep from turning into a disorganized rout or at the very least doing severe damage to the military's morale. Tactical withdrawal A withdrawal may be anticipated, as when a defending force is outmatched or on disadvantageous ground, but must cause as much damage to an enemy as possible. In such a case, the retreating force may employ a number of tactics and strategies to further impede the enemy's progress. This could include setting mines or booby traps during or before withdrawal, leading the enemy into p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong pronounced ; also romanised traditionally as Mao Tse-tung. (26 December 1893 – 9 September 1976), also known as Chairman Mao, was a Chinese communist revolutionary who was the founder of the People's Republic of China (PRC), which he led as the chairman of the Chinese Communist Party from the establishment of the PRC in 1949 until his death in 1976. Ideologically a Marxist–Leninist, his theories, military strategies, and political policies are collectively known as Maoism. Mao was the son of a prosperous peasant in Shaoshan, Hunan. He supported Chinese nationalism and had an anti-imperialist outlook early in his life, and was particularly influenced by the events of the Xinhai Revolution of 1911 and May Fourth Movement of 1919. He later adopted Marxism–Leninism while working at Peking University as a librarian and became a founding member of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP), leading the Autumn Harvest Uprising in 1927. During the Chinese Civil War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X Corps (United States)
X Corps was a corps of the United States Army in World War II and the Korean War. World War II The X Corps was activated in May 1942 at Sherman, Texas. Elements of the corps embarked aboard ''Klipfontein'', a Dutch ship operating under charter through the War Shipping Administration for the Army. The ship departed the San Francisco Port of Embarkation for the Pacific Theater 14 July 1944 after two changes of station and participation in maneuvers in Louisiana and at the California-Arizona maneuver area. X Corps took part in the following campaigns: New Guinea, Leyte, and Southern Philippines. As part of the Sixth Army, X Corps took part in the Philippines campaign of 1944–45, beginning with the invasion of Leyte. For its involvement, the X Corps received the Philippine Presidential Unit Citation with a streamer embroidered 17 October 1944 – 4 July 1945. X Corps became inactive in 1946. Korean War Inchon landing During the Korean War, it took part in Operation Chrom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |