|
Battle Of Vellica
The Battle of Vellica was a battle of the Cantabrian Wars fought in the year 25 BC by the emperor Augustus and his Roman legions against the Cantabri forces who resided in the area. The most generally accepted location for the battle is the area around Monte Cildá, Olleros de Pisuerga, Palencia. Location of the Battle Cildá was populated by the Cantabri people. Claudius Ptolemy (II,6,51) mentions ''Vellika'' first amongst the Cantabrian towns. Certain authors such as Adolf Schulten, Miguel Ángel García Guinea and Iglesias Gil have placed the battle and the town of Vellica in an area near Monte Cildá. According to Joaquín González Echegaray, this town corresponded with the fortifications built on Monte Cildá (where there appeared an inscription that cites the clan of the ''Vellicum''), and that had to be taken by the Romans from the south, after capture of Amaya but before the battle at Castro de Monte Bernorio. It has likewise been inferred that Vellica and Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantabrian Wars
The Cantabrian Wars (29–19 BC) (''Bellum Cantabricum''), sometimes also referred to as the Cantabrian and Asturian Wars (''Bellum Cantabricum et Asturicum''), were the final stage of the two-century long Roman conquest of Hispania, in what today are the provinces of Cantabria, Asturias and León in northwestern Spain. During the reign of Emperor Augustus, Rome waged a bloody conflict against the Cantabri and the Astures, the last independent Celtic nations of Hispania. These warlike peoples fiercely resisted Roman domination; ten years of war and eight legions with their auxiliary troops – more than 50,000 soldiers in total – were needed to subdue the region. Augustus moved to Segisama (modern Sasamon, Burgos) in 26 BC to supervise the campaign in person. The major fighting was completed in 19 BC, although there were minor rebellions until 16 BC and the Romans had to station two legions there for seventy more years. Antecedents The Cantabri first appear in histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joaquín González Echegaray
Joaquín or Joaquin is a male given name, the Spanish language, Spanish version of Joachim (given name), Joachim. Given name * Joaquín (footballer, born 1956), Spanish football midfielder * Joaquín (footballer, born 1981), Spanish football winger * Joaquín (footballer, born 1982), Spanish football forward * Joaquín Almunia, Spanish politician * Joaquín Andújar, professional baseball player in the Houston Astros organization * Joaquín Arias (baseball), Joaquín Arias, professional baseball player in the San Francisco Giants organization * Joaquín Balaguer, President of the Dominican Republic * Joaquín Belgrano, Argentine patriot * Joaquín Benoit, professional baseball player for the San Diego Padres * Joaquin Castro, American politician from San Antonio, Texas * Joaquín Cortés, Spanish flamenco dancer * Joaquín De Luz, Spanish New York City Ballet principal dancer * Joaquin Domagoso, Filipino actor and model * Joaquín "El Chapo" Guzmán, Mexican drug lord * Joaquín ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Involving The Roman Empire
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
20s BC Conflicts
S, or s, is the nineteenth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''ess'' (pronounced ), plural ''esses''. History Origin Northwest Semitic šîn represented a voiceless postalveolar fricative (as in 'ip'). It originated most likely as a pictogram of a tooth () and represented the phoneme via the acrophonic principle. Ancient Greek did not have a phoneme, so the derived Greek letter sigma () came to represent the voiceless alveolar sibilant . While the letter shape Σ continues Phoenician ''šîn'', its name ''sigma'' is taken from the letter ''samekh'', while the shape and position of ''samekh'' but name of ''šîn'' is continued in the '' xi''. Within Greek, the name of ''sigma'' was influenced by its association with the Greek word (earlier ) "to hiss". The original name of the letter "sigma" may have been ''san'', but due to the complica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
25 BC
__NOTOC__ Year 25 BC was either a common year starting on Wednesday, Thursday or Friday or a leap year starting on Wednesday or Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar (the sources differ, see leap year error for further information) and a leap year starting on Tuesday of the Proleptic Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Augustus and Silanus (or, less frequently, year 729 '' Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 25 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman empire * Imperator Caesar Augustus becomes Consul for the ninth time. His partner is Marcus Junius Silanus. * The temple to Neptune on the Circus Flaminius is built. * Estimation: Rome, capital of the Roman Empire becomes the largest city in the world, taking the lead from Chang'an, capital of China. * Galatia bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Roman Wars And Battles
The following is a List of Roman wars and battles fought by the ancient Roman Kingdom, Roman Republic and Roman Empire against external enemies, organized by date. For civil wars, revolts and rebellions, see List of Roman civil wars and revolts. 8th century BC * Wars with the Latins and the Sabines (for the Rape of the Sabine Women) * Conquest of Cameria * War with Fidenae and Veii 7th century BC * Second war with Fidenae and Veii * Second Sabine War *Roman–Latin wars 6th century BC * Roman-Sabine wars * War with the Volsci * War with Gabii * War with the Rutuli * Roman-Etruscan wars ** 509 BC – Battle of Silva Arsia – The Romans defeated the forces of Tarquinii and Veii led by the deposed king Lucius Tarquinius Superbus. One of the Roman consuls, Lucius Junius Brutus, is killed in battle. ** 508 BC – War with Clusium – King Lars Porsena of Clusium besieges Rome on behalf of Tarquinius Superbus. The outcome is debated, but tradition states that it was a Roman vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legio IX Hispana
Legio IX Hispana ("9th Spanish Legion"), also written Legio VIIII Hispana, was a legion of the Imperial Roman army that existed from the 1st century BC until at least 120 AD. The legion fought in various provinces of the late Roman Republic and early Roman Empire. It was stationed in Britain following the Roman invasion in 43 AD. The legion disappears from surviving Roman records after and there is no extant account of what happened to it. The unknown fate of the legion has been the subject of considerable research and speculation. One theory (per historian Theodor Mommsen) was that the legion was wiped out in action in northern Britain soon after 108 AD, the date of the latest datable inscription of the Ninth found in Britain, perhaps during a rising of northern tribes against Roman rule. This view was popularised by the 1954 novel ''The Eagle of the Ninth'' in which the legion is said to have marched into Caledonia (modern day Scotland), after which it w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legio IV Macedonica
Legio IV Macedonica ("Macedonian Fourth Legion"), was a legion of the Imperial Roman army founded in 48 BC by Gaius Julius Caesar (dictator of Rome 49–44 BC) with Italian legionaries. The legion was disbanded in AD 70 by Emperor Vespasian. The legion symbols were a bull (as with all of Caesar's legions) and a capricorn. History Early history This legion was possibly founded in Italy during the 48 BCE Julius Caesar, who needed it in his war against Pompey. It saw its first action at the Battle of Dyrrhachium. After the civil war the legion was stationed in Macedonia. It was supposed to serve in Caesar's campaign against the Parthian Empire. However, the expedition was canceled after Caesar's death. This legion would go onto fight in the civil war between Antony and Augustus.Before the conflict erupted, the legion was moved to Italy by Mark Antony, although this did not deter them from siding with Augustusduring the Battle of Mutina, where they fought against Antony and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orosius
Paulus Orosius (; born 375/385 – 420 AD), less often Paul Orosius in English, was a Roman priest, historian and theologian, and a student of Augustine of Hippo. It is possible that he was born in '' Bracara Augusta'' (now Braga, Portugal), then capital of the Roman province of Gallaecia, which would have been the capital of the Kingdom of the Suebi by his death. Although there are some questions regarding his biography, such as his exact date of birth, it is known that he was a person of some prestige from a cultural point of view, as he had contact with the greatest figures of his time such as Augustine of Hippo and Jerome of Stridon. In order to meet with them Orosius travelled to cities on the southern coast of the Mediterranean Sea, such as Hippo Regius, Alexandria, and Jerusalem. These journeys defined his life and intellectual output. Orosius did not just discuss theological matters with Augustine; he also collaborated with him on the book '' City of God''. In addition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Principate, which is the first phase of the Roman Empire, and Augustus is considered one of the greatest leaders in human history. The reign of Augustus initiated an imperial cult as well as an era associated with imperial peace, the ''Pax Romana'' or '' Pax Augusta''. The Roman world was largely free from large-scale conflict for more than two centuries despite continuous wars of imperial expansion on the empire's frontiers and the year-long civil war known as the "Year of the Four Emperors" over the imperial succession. Originally named Gaius Octavius, he was born into an old and wealthy equestrian branch of the plebeian ''gens'' Octavia. His maternal great-uncle Julius Caesar was assassinated in 44 BC, and Octavius was named in Caesar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
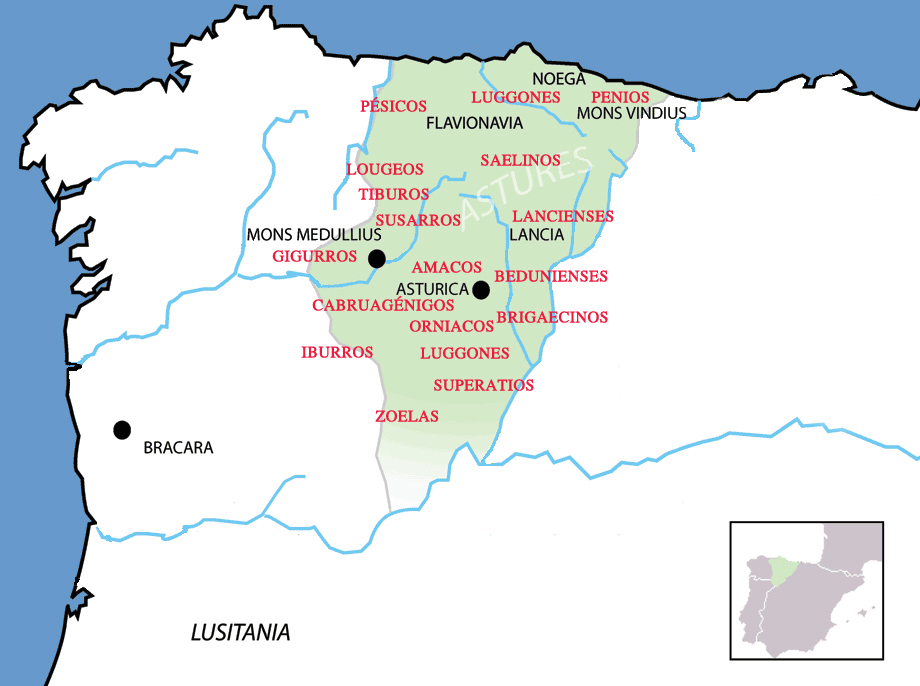
Astures
The Astures or Asturs, also named Astyrs, were the Hispano-Celtic inhabitants of the northwest area of Hispania that now comprises almost the entire modern autonomous community of Principality of Asturias, the modern province of León, and the northern part of the modern province of Zamora (all in Spain), and eastern Trás os Montes in Portugal. They were a horse-riding highland cattle-raising people who lived in circular huts of stone drywall construction. The Albiones were a major tribe from western Asturias. Isidore of Seville gave an etymology as coming from a ''river Asturia'', identified by David Magie with Órbigo river in the plain of León, by others the modern Esla river. Location The Asturian homeland encompassed the modern autonomous community of Asturias and the León, eastern Lugo, Orense, and northern Zamora provinces, along with the northeastern tip of the Portuguese region of Trás-os-Montes. Here they held the towns of ''Lancia'' (Villasabariego – Leó ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_(7685208580)_2.jpg)