|
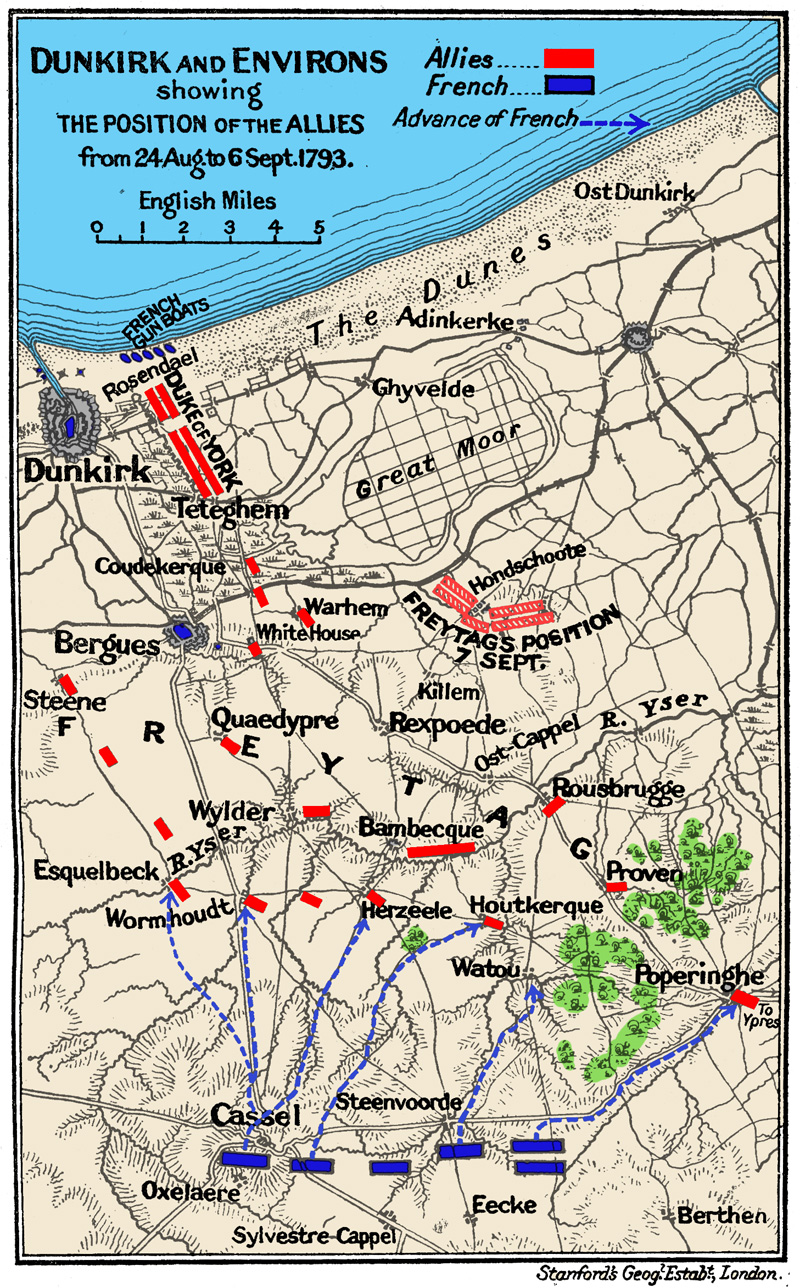
Battle Of Tourcoing (1794)
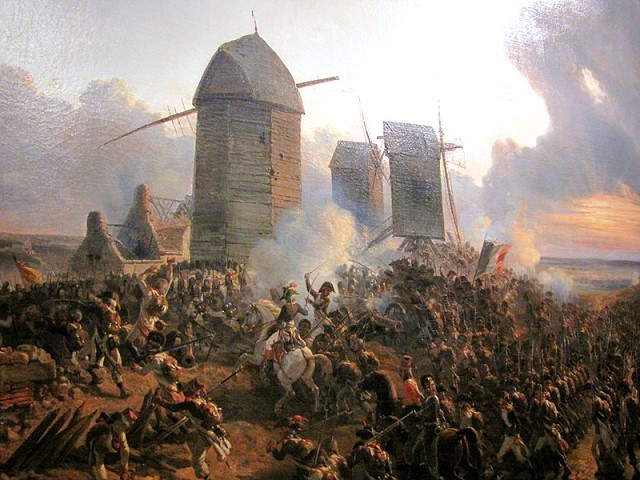
The Battle of Tourcoing (17–18 May 1794) saw a Republican French army directed by General of Division Joseph Souham defend against an attack by a Coalition army led by Emperor Francis II and Austrian Prince Josias of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld. The French army was temporarily led by Souham in the absence of its normal commander Jean-Charles Pichegru. Threatened with encirclement, Souham and division commanders Jean Victor Marie Moreau and Jacques Philippe Bonnaud improvised a counterattack which defeated the Coalition's widely separated and poorly coordinated columns. The War of the First Coalition action was fought near the town of Tourcoing, north of Lille in northeastern France. The Coalition battle plan drawn up by Karl Mack von Leiberich launched six columns that attempted to envelop part of the French army holding an awkward bulge at Menen (Menin) and Kortrijk (Courtrai). On 17 May, the French defeated Georg Wilhelm von dem Bussche's small column while the columns of Count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flanders Campaign
The Flanders Campaign (or Campaign in the Low Countries) was conducted from 20 April 1792 to 7 June 1795 during the first years of the War of the First Coalition. A coalition of states representing the Ancien Régime in Western Europe – Austria (including the Southern Netherlands), Prussia, Great Britain, the Dutch Republic (the Northern Netherlands), Hanover and Hesse-Kassel – mobilised military forces along all the French frontiers, with the intention to invade Revolutionary France and end the French First Republic. The radicalised French revolutionaries, who broke the Catholic Church's power (1790), abolished the monarchy (1792) and even executed the deposed king Louis XVI of France (1793), vied to spread the Revolution beyond France's borders, by violent means if necessary. A quick French success in the Battle of Jemappes in November 1792 was followed by a major Coalition victory at Neerwinden in March 1793. After this initial stage, the largest of these forces ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques Philippe Bonnaud
Jacques Philippe Bonnaud or Bonneau (11 September 1757 – 30 March 1797) commanded a French combat division in a number of actions during the French Revolutionary Wars. He enlisted in the French Royal Army as cavalryman in 1776 and was a non-commissioned officer in 1789. He became a captain in the 12th Chasseurs à Cheval Regiment in 1792. The unit fought at Valmy, Jemappes, Aldenhoven, Neerwinden, Raismes, Caesar's Camp and Wattignies, and he was wounded twice. In January 1794 he was promoted to general officer. In April 1794, he reluctantly accepted command of a division that had been cut to pieces at Villers-en-Cauchies and Troisvilles, and this at a time when failed generals often were sent to the guillotine. He led his troops at Courtrai, Tourcoing and in the invasion of the Dutch Republic. He fought in the War in the Vendée the following year, briefly leading the ''Army of the Coasts of Cherbourg''. In the Rhine Campaign of 1796 he led a cavalry division in combat at Ambe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Committee Of Public Safety
The Committee of Public Safety (french: link=no, Comité de salut public) was a committee of the National Convention which formed the provisional government and war cabinet during the Reign of Terror, a violent phase of the French Revolution. Supplementing the Committee of General Defence created after the execution of King Louis XVI in January 1793, the Committee of Public Safety was created in April 1793 by the National Convention. It was charged with protecting the new republic against its foreign and domestic enemies, fighting the First Coalition and the Vendée revolt. As a wartime measure, the committee was given broad supervisory and administrative powers over the armed forces, judiciary and legislature, as well as the executive bodies and ministers of the Convention. As the committee, restructured in July, raised the defense ('' levée en masse'') against the monarchist coalition of European nations and counter-revolutionary forces within France, it became more and more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lazare Carnot
Lazare Nicolas Marguerite, Count Carnot (; 13 May 1753 – 2 August 1823) was a French mathematician, physicist and politician. He was known as the "Organizer of Victory" in the French Revolutionary Wars and Napoleonic Wars. Education and early life Carnot was born on 13 May 1753 in the village of Nolay, in Burgundy, as the son of a local judge and royal notary, Claude Carnot and his wife, Marguerite Pothier. He was the second oldest of seven children. At the age of fourteen, Lazare and his brother were enrolled at the ''Collège d'Autun'', where he focused on the study of philosophy and the classics. He held a strong belief in stoic philosophy and was deeply influenced by Roman civilization. When he turned fifteen, he left school in Autun to strengthen his philosophical knowledge and study under the Society of the Priests of Saint Sulpice. During his short time with them, he studied logic, mathematics and theology under the Abbe Bison. After being impressed with Lazare's work a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Great Britain
The Kingdom of Great Britain (officially Great Britain) was a Sovereign state, sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, which united the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England (which included Wales) and Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland to form a single kingdom encompassing the whole island of Great Britain and its outlying islands, with the exception of the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands. The unitary state was governed by a single Parliament of Great Britain, parliament at the Palace of Westminster, but distinct legal systems – English law and Scots law – remained in use. The formerly separate kingdoms had been in personal union since the 1603 "Union of the Crowns" when James VI of Scotland became King of England and King of Ireland. Since James's reign, who had been the first to refer to himself as "king of Great Britain", a political un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudolf Ritter Von Otto
Rudolf Ritter von Otto (1735 – 7 August 1811) began his military career in the army of the Electorate of Saxony, transferred to the Austrian army and had a distinguished combat record during the Seven Years' War and the French Revolutionary Wars. Early career Born in Weißenfels in the Electorate of Saxony in 1735, Otto joined the Saxon army in 1753 as a cavalryman. In the Seven Years' War he fought at the battles of Kolín and the Breslau in 1757. He was also present at several sieges and skirmishes. He joined an Austrian Freikorps raised by his brother Wilhelm and participated in several successful ambushes and raids in 1760-1762. Austrian service At the end of the war he formally entered the Austrian army, joining the Hesse-Darmstadt Dragoon Regiment # 19 as an ''Oberleutnant''. Promoted to captain in 1769 and major in 1777, he transferred to the Graeven Hussar Regiment # 34. Because he improved his new regiment's efficiency, he was rapidly promoted, first to ''Oberstleutnan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Frederick, Duke Of York And Albany
Prince Frederick, Duke of York and Albany (Frederick Augustus; 16 August 1763 – 5 January 1827) was the second son of George III, King of the United Kingdom and Hanover, and his consort Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz. A soldier by profession, from 1764 to 1803 he was Prince-Bishop of Osnabrück in the Holy Roman Empire. From the death of his father in 1820 until his own death in 1827, he was the heir presumptive to his elder brother, George IV, in both the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and the Kingdom of Hanover. Frederick was thrust into the British Army at a very early age and was appointed to high command at the age of thirty, when he was given command of a notoriously ineffectual campaign during the War of the First Coalition, a continental war following the French Revolution. Later, as Commander-in-Chief during the Napoleonic Wars, he oversaw the reorganisation of the British Army, establishing vital structural, administrative and recruiting reformsGlo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archduke Charles, Duke Of Teschen
Archduke Charles Louis John Joseph Laurentius of Austria, Duke of Teschen (german: link=no, Erzherzog Karl Ludwig Johann Josef Lorenz von Österreich, Herzog von Teschen; 5 September 177130 April 1847) was an Austrian field-marshal, the third son of Emperor Leopold II and his wife, Maria Luisa of Spain. He was also the younger brother of Francis II, Holy Roman Emperor. Despite being epileptic, Charles achieved respect both as a commander and as a reformer of the Austrian army. He was considered one of Napoleon's more formidable opponents and one of the greatest generals of the French Revolutionary Wars. He began his career fighting the revolutionary armies of France. Early in the wars of the First Coalition, he saw victory at Neerwinden in 1793, before being defeated at Wattignies 1793 and Fleurus 1794. In 1796, as chief of all Austrian forces on the Rhine, Charles defeated Jean-Baptiste Jourdan at Amberg, Würzburg and Limburg, and then won victories at Wetzlar, Emmendingen a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Joseph, Count Kinsky
Franz Joseph, Count Kinsky of Wchinitz and Tettau (6 December 1739 – 9 June 1805) was a Habsburg Austrian general in the War of the Bavarian Succession and the French Revolutionary Wars. A nobleman from the House of Kinsky, he began his military service in 1759 and within ten years he commanded an infantry regiment. Ahead of his time, he began a school in his regiment to train officer cadets. As a general officer he led troops in a successful action against Prussia in 1778. A year later he was appointed Inhaber of an infantry regiment and Director of the Theresian Military Academy in Wiener Neustadt; he held both posts during the remainder of his life. In the Flanders Campaign in 1794, he commanded an infantry division against the French. He led an attack column at Tourcoing where he failed to support Prince Frederick, Duke of York and Albany. He was promoted to Feldzeugmeister in September 1794. He held no more active commands and died at Vienna in 1805. Early career Franz Josep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
François Sébastien Charles Joseph De Croix, Count Of Clerfayt
François Sébastien Charles Joseph de Croix, Count of Clerfayt (14 October 1733 – 21 July 1798),His title is also spelled Count of Clairfayt and Count of Clairfait a Walloon, joined the army of the Habsburg monarchy and soon fought in the Seven Years' War. Later in his military career, he led Austrian troops in the war against Ottoman Turkey. During the French Revolutionary Wars he saw extensive fighting and rose to the rank of Field Marshal. Early career Born at the Castle of Bruille in Hainaut in the Austrian Netherlands, he entered the Austrian army in 1753. In the Seven Years' War (1756–1763) he distinguished himself, earning rapid promotion, and received the Military Order of Maria Theresa decoration. At the conclusion of the peace (Treaty of Hubertusburg, 15 February 1763), though still under thirty, he had already become an Oberst (colonel). During the revolt in the Netherlands in 1787, Clerfayt, as a Walloon by birth, came under great pressure to abandon Emperor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Wilhelm Von Dem Bussche
Georg Wilhelm Baron von dem Bussche-Haddenhausen (19 July 1726 – 11 December 1794) was a general officer of Hanoverian soldiers during the War of the First Coalition who famously led one of the Coalition columns at the Battle of Tourcoing. In 1743 he joined the Hanoverian military service and fought in the War of the Austrian Succession and Seven Years' War, fighting at Minden and Lutterberg. He led a battalion at Gibraltar in the American Revolutionary War. In the War of the First Coalition he led his soldiers at Valenciennes, Hondschoote, Mouscron, Tourcoing and Tournai. On 11 December 1794 while defending the Bommelerwaard in the Dutch Republic, his hand was taken off by a cannonball and he died shortly afterward. Early career Bussche was born in Minden, then part of the Kingdom of Prussia, on 19 July 1726. His father, Albrecht Hilmar von dem Bussche, who was a member of the judicial council, descended from a long line of Westphalian nobility. The Bussche family was a noble f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kortrijk
Kortrijk ( , ; vls, Kortryk or ''Kortrik''; french: Courtrai ; la, Cortoriacum), sometimes known in English as Courtrai or Courtray ( ), is a Belgian City status in Belgium, city and Municipalities in Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region, Flemish Provinces of Belgium, province of West Flanders. It is the capital and largest city of the judicial and administrative arrondissement of Kortrijk. The wider municipality comprises the city of Courtrai proper and the villages of Aalbeke, Bellegem, Bissegem, Heule, Kooigem, Marke (Belgium), Marke, and Rollegem. Courtrai is also part of the cross-border Lille-Kortrijk-Tournai metropolitan area. The city is on the river Leie, southwest of Ghent and northeast of Lille. Mouscron in Wallonia is just south of Courtrai. Courtrai originated from a Gallo-Roman town, ''Cortoriacum'', at a crossroads near the Leie river and two Roman roads. In the Middle Ages, Courtrai grew significantly thanks to the flax and wool industry with France ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |