|
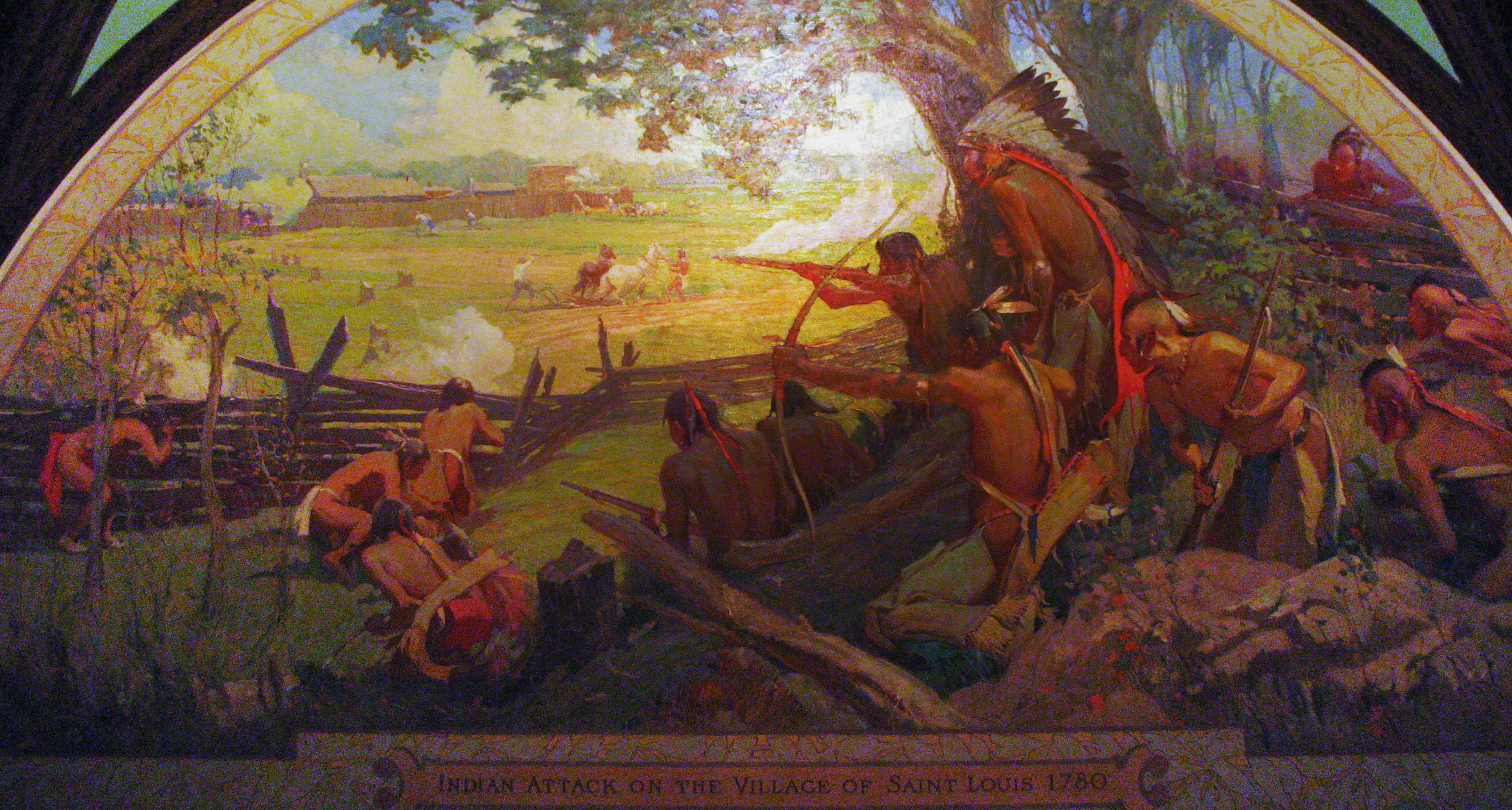
Battle Of St. Louis
The Battle of St. Louis ( es, Batalla de San Luis), also known as the Battle of Fort San Carlos, was an unsuccessful attack by British-allied Indians on St. Louis (a French settlement in Spanish Louisiana, founded on the West Bank of the Mississippi River after the 1763 Treaty of Paris) on May 26, 1780, during the American Revolutionary War. A Loyalist fur trader led a large force of Indians and attacked the settlement. Fernando de Leyba, the Lieutenant Governor of Upper Louisiana, led the local militia to fortify the town as best as they could and successfully withstood the attack. On the opposite bank of the Mississippi, a second simultaneous attack on the nearby Patriot outpost of Cahokia was also repulsed. The retreating Indians destroyed the crops and took captive civilians outside the protected area. The British failed to defend their side of the river and, thus, effectively ended any attempts to gain control of the Mississippi River during the war. Background ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missouri State Capitol
The Missouri State Capitol is the home of the Missouri General Assembly and the executive branch of government of the U.S. state of Missouri. Located in Jefferson City at 201 West Capitol Avenue, it is the third capitol to be built in the city. (The previous two were demolished after they were damaged by fire.) The domed building, designed by the New York City architectural firm of Tracy and Swartwout, was completed in 1917. The capitol’s dome is the first thing travelers see when approaching Jefferson City from the north. In addition to the state Senate and House of Representatives, the capitol also contains offices of the governor, lieutenant governor, secretary of state, state treasurer, state auditor, and some administrative agencies. It is individually listed on the National Register of Historic Places and is a contributing property in the Missouri State Capitol Historic District. Architecture, paintings, and statuary The capitol exterior The exterior of the Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matchekewis
Matchekewis (c.1735 – July 1805), also known as Madjeckewiss, Mash-i-pi-nash-i-wish or Bad Bird, was a respected Ojibwe war chief in present-day northern Michigan. He became famous for his role in the 1763 capture of Fort Michilimackinac from the British during Pontiac's War. However, he subsequently became a staunch ally of Great Britain throughout the American Revolutionary War. Military career In 1763, he took part in Pontiac's Rebellion in the capture of Fort Michilimackinac from the British. But in 1780 he commanded his tribes in the American Revolutionary War as an ally of Great Britain against Spain. At the Battle of St. Louis, in charge of all of the native American troops, he was defeated by the Spanish gunpowder weapons. After the war, he signed the Treaty of Greenville with the young United States, ceding Bois Blanc Island in Lake Huron Lake Huron ( ) is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. Hydrology, Hydrologically, it comprises the eas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Mississippi River
The Upper Mississippi River is the portion of the Mississippi River upstream of St. Louis, Missouri, United States, at the confluence of its main tributary, the Missouri River. History In terms of geologic and hydrographic history, the Upper Mississippi east and south of Fort Snelling is a portion of the now-extinct Glacial River Warren which carved the valley of the Minnesota River, permitting the immense Glacial Lake Agassiz to join the world's oceans at the Gulf of Mexico. The collapse of ice dams holding back Glacial Lake Duluth and Glacial Lake Grantsburg carved out the Dalles of the St. Croix River at Interstate Park. The Upper Mississippi River valley likely originated as an ice-marginal stream during the Pre-Illinoian Stage. The Driftless Area is a portion of North America left unglaciated at that ice age's height, hence not smoothed out or covered over by previous geological processes. Inasmuch as the Wisconsin glaciation formed lobes that met (and blocked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Orleans
New Orleans ( , ,New Orleans . ; french: La Nouvelle-Orléans , es, Nueva Orleans) is a consolidated city-parish located along the in the southeastern region of the U.S. state of Louisiana. With a population of 383,997 according to the 2020 U.S. census, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
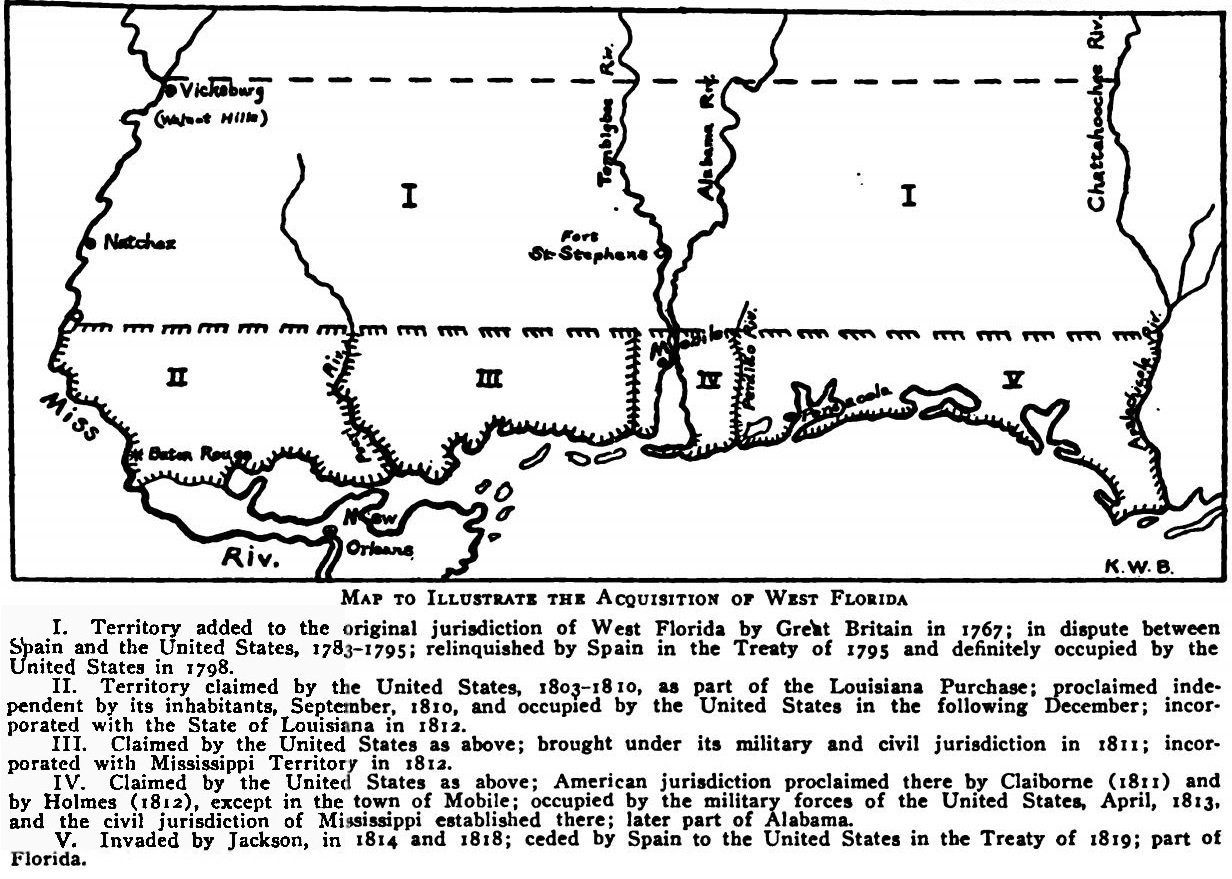
West Florida
West Florida ( es, Florida Occidental) was a region on the northern coast of the Gulf of Mexico that underwent several boundary and sovereignty changes during its history. As its name suggests, it was formed out of the western part of former Spanish Florida ( East Florida formed the eastern part, with the Apalachicola River as the border), along with lands taken from French Louisiana; Pensacola became West Florida's capital. The colony included about two thirds of what is now the Florida Panhandle, as well as parts of the modern U.S. states of Louisiana, Mississippi, and Alabama. Great Britain established West and East Florida in 1763 out of land acquired from France and Spain after the Seven Years' War. As the newly acquired territory was too large to govern from one administrative center, the British divided it into two new colonies separated by the Apalachicola River. British West Florida included the part of formerly Spanish Florida which lay west of the Apalachicola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for two millennia. The City of London, its ancient core and financial centre, was founded by the Roman Empire, Romans as ''Londinium'' and retains its medieval boundaries.See also: Independent city#National capitals, Independent city § National capitals The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has for centuries hosted the national Government of the United Kingdom, government and Parliament of the United Kingdom, parliament. Since the 19th century, the name "London" has also referred to the metropolis around this core, historically split between the Counties of England, counties of Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent, and Hertfordshire, which largely comprises Greater London ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its predecessor states between 1492 and 1976. One of the largest empires in history, it was, in conjunction with the Portuguese Empire, the first to usher the European Age of Discovery and achieve a global scale, controlling vast portions of the Americas, territories in Western Europe], Africa, and various islands in Spanish East Indies, Asia and Oceania. It was one of the most powerful empires of the early modern period, becoming the first empire known as " the empire on which the sun never sets", and reached its maximum extent in the 18th century. An important element in the formation of Spain's empire was the dynastic union between Isabella I of Castile and Ferdinand II of Aragon in 1469, known as the Catholic Monarchs, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patriot (American Revolution)
Patriots, also known as Revolutionaries, Continentals, Rebels, or American Whigs, were the colonists of the Thirteen Colonies who rejected British rule during the American Revolution, and declared the United States of America an independent nation in July 1776. Their decision was based on the political philosophy of republicanism—as expressed by such spokesmen as Thomas Jefferson, John Adams, and Thomas Paine. They were opposed by the Loyalists, who supported continued British rule. Patriots represented the spectrum of social, economic, and ethnic backgrounds. They included lawyers such as John Adams, students such as Alexander Hamilton, planters such as Thomas Jefferson and George Mason, merchants such as Alexander McDougall and John Hancock, and farmers such as Daniel Shays and Joseph Plumb Martin. They also included slaves and freemen such as Crispus Attucks, one of the first casualties of the American Revolution; James Armistead Lafayette, who served as a double ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Paris (1763)
The Treaty of Paris, also known as the Treaty of 1763, was signed on 10 February 1763 by the kingdoms of Great Britain, France and Spain, with Portugal in agreement, after Great Britain and Prussia's victory over France and Spain during the Seven Years' War. The signing of the treaty formally ended conflict between France and Great Britain over control of North America (the Seven Years' War, known as the French and Indian War in the United States), and marked the beginning of an era of British dominance outside Europe. Great Britain and France each returned much of the territory that they had captured during the war, but Great Britain gained much of France's possessions in North America. Additionally, Great Britain agreed to protect Roman Catholicism in the New World. The treaty did not involve Prussia and Austria as they signed a separate agreement, the Treaty of Hubertusburg, five days later. Exchange of territories During the war, Great Britain had conquered the French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it flows generally south for to the Mississippi River Delta in the Gulf of Mexico. With its many tributaries, the Mississippi's watershed drains all or parts of 32 U.S. states and two Canadian provinces between the Rocky and Appalachian mountains. The main stem is entirely within the United States; the total drainage basin is , of which only about one percent is in Canada. The Mississippi ranks as the thirteenth-largest river by discharge in the world. The river either borders or passes through the states of Minnesota, Wisconsin, Iowa, Illinois, Missouri, Kentucky, Tennessee, Arkansas, Mississippi, and Louisiana. Native Americans have lived along the Mississippi River and its tributaries for thousands of years. Most were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Louisiana
Spanish Louisiana ( es, link=no, la Luisiana) was a governorate and administrative district of the Viceroyalty of New Spain from 1762 to 1801 that consisted of a vast territory in the center of North America encompassing the western basin of the Mississippi River plus New Orleans. The area had originally been claimed and controlled by France, which had named it '' La Louisiane'' in honor of King Louis XIV in 1682. Spain secretly acquired the territory from France near the end of the Seven Years' War by the terms of the Treaty of Fontainebleau (1762). The actual transfer of authority was a slow process, and after Spain finally attempted to fully replace French authorities in New Orleans in 1767, French residents staged an uprising which the new Spanish colonial governor did not suppress until 1769. Spain also took possession of the trading post of St. Louis and all of Upper Louisiana in the late 1760s, though there was little Spanish presence in the wide expanses of the " Il ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |