|
Battle Of Sedemünder
The Battle of Sedemünder () was a military conflict between the episcopal army of the Bishopric of Minden, Bishop of Minden, Wedekind I of Hoya, Wedekind, and an army of Hamelin's townsfolk. It took place on 28 July 1260 or, according to other sources, on 28 July 1259, near the abandoned village of Sedemünder, south of the Deister Gate in what is now Lower Saxony. The battle ended in a crushing defeat of the townsfolk, whose survivors were taken into captivity in Minden. The strengths and casualties of the two sides are unknown. The reason for the dispute, which is referred to as the Minden Feud, was a deed of purchase agreed in 1259, in which the Abbot of Fulda transferred sovereign rights over the town and beneficiary of Hamelin to the Bishop of Minden for 500 silver Mark (unit), marks. This was seen by the townsfolk of Hamelin as threatening their independence; they refused to cooperate and took up arms. After the battle, the reigning Dukes of Brunswick-Lüneburg, Albert I (Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishopric Of Minden
The Prince-Bishopric of Minden (german: Fürstbistum Minden; Bistum Minden; Hochstift Minden; Stift Minden) was an ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire. It was progressively secularized following the Protestant Reformation when it came under the rule of Protestant rulers, and by the Peace of Westphalia of 1648 given to Brandenburg as the Principality of Minden. It must not be confused with the Roman Catholic diocese of Minden, which was larger, and over which the prince-bishop exercised spiritual authority. History The diocese was founded by Charlemagne in 803, after he had conquered the Saxons. It was subordinate to the Archbishopric-Electorate of Cologne. It became the Prince-Bishopric of Minden (german: Fürstbistum Minden) in 1180, when the Duchy of Saxony was dissolved. As to the diocese of Minden, it ceased to exist following the Swedish takeover of 1648. Prior to its dissolution, the diocesan area comprised, in addition to the temporal prince-bishopri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John I (Brunswick-Lüneburg)
John I may refer to: People * John I (bishop of Jerusalem) * John Chrysostom (349 – c. 407), Patriarch of Constantinople * John of Antioch (died 441) * Pope John I, Pope from 523 to 526 * John I (exarch) (died 615), Exarch of Ravenna * John I of Naples (died c. 719) * John of Abkhazia (ruled 878/879–880) * John I of Gaeta (died c. 933) * John I Tzimiskes (c. 925 – 976), Byzantine Emperor * John I of Amalfi (died 1007) * John I of Ponthieu (c. 1147 – 1191) * John I (archbishop of Trier) (c. 1140-1212), Archbishop of Trier from 1190 to 1212 * John of England (1166–1216), King of England, Lord of Ireland, Duke of Normandy and Aquitaine and Count of Anjou * John I of Sweden (c. 1201 – 1222) * John of Brienne (c. 1148 – 1237), king of Jerusalem * John I of Trebizond (died 1238) * John I of Dreux (1215–1249) * John I of Avesnes (1218–1257), Count of Hainaut * John of Brunswick, Duke of Lüneburg (c. 1242–1277) * John I, Count of Blois (died 1280) * John I, Duke of Saxo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1260
Year 1260 ( MCCLX) was a leap year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. Events By place Africa * October 24 – Saif ad-Din Qutuz, Mamluk sultan of Egypt, is assassinated by Baibars, who seizes power for himself. * The civil servant and bard longing for lost al-Andalus, Ibn al-Abbar, is burnt at the stake by the Marinid ruler. * The Arba'a Rukun Mosque was completed in Mogadishu. The Arba'a Rukun Mosque (Arabic: أربع روكون), also known as Arba Rucun, is a mosque in the medieval district Shangani, Mogadishu, Somalia. Asia * The Toluid Civil War begins between Kublai Khan and Ariq Böke, for the title of Great Khan. * May 5 – Kublai Khan becomes a claimant to the Mongol Empire, after the death of Möngke Khan. * May 21 – Kublai sends his envoy Hao Jing to negotiate with Song Dynasty Chancellor Jia Sidao, after the small force left by Kublai south of the Yangtze River is destroyed, by a Chinese army of the South ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1260s In The Holy Roman Empire
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
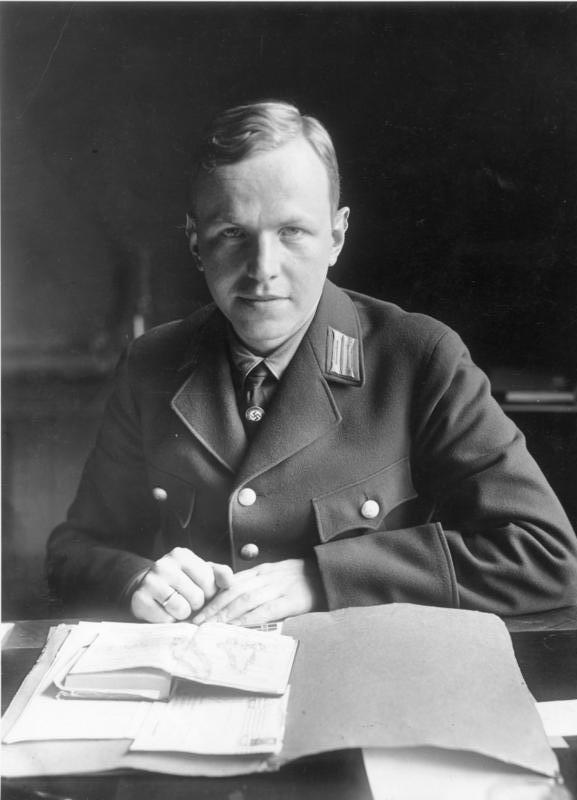
Achim Gercke
Achim Gercke (3 August 1902 – 27 October 1997) was a German politician. Born in Greifswald, Gercke became a department head of the NSDAP in Munich on 1 January 1932. In April 1933 he was appointed to the Ministry of the Interior, where he served as an expert on racial matters. Gercke devised the system of "racial prophylaxis", forbidding the intermarriage between Jews and Aryans. As a student, he had attempted to develop a card index listing all Jews in Germany. His articles outlined Nazi policy on what to do to the Jews during the early phase of the Third Reich, which included expulsion from Germany. He described the just-enacted Nuremberg Laws restricting Jews as provisional measures, which indicated the direction future measures would take. Gercke argued for defining "Jew" as including any person with one-sixteenth Jewish blood. Later in 1942, the Wannsee Conference ultimately defined "Jew" quite differently: Persons having one Jewish grandparent were mostly excluded an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memorial Stone
A headstone, tombstone, or gravestone is a stele or marker, usually stone, that is placed over a grave. It is traditional for burials in the Christian, Jewish, and Muslim religions, among others. In most cases, it has the deceased's name, date of birth, and date of death inscribed on it, along with a personal message, or prayer, but may contain pieces of funerary art, especially details in stone relief. In many parts of Europe, insetting a photograph of the deceased in a frame is very common. Use The stele (plural stelae), as it is called in an archaeological context, is one of the oldest forms of funerary art. Originally, a tombstone was the stone lid of a stone coffin, or the coffin itself, and a gravestone was the stone slab that was laid over a grave. Now, all three terms are also used for markers placed at the head of the grave. Some graves in the 18th century also contained footstones to demarcate the foot end of the grave. This sometimes developed into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Brunswick-Lüneburg
The Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg (german: Herzogtum Braunschweig und Lüneburg), or more properly the Duchy of Brunswick and Lüneburg, was a historical duchy that existed from the late Middle Ages to the Late Modern era within the Holy Roman Empire, until the year of its dissolution. The duchy was located in what is now northwestern Germany. Its name came from the two largest cities in the territory: Brunswick and Lüneburg. The dukedom emerged in 1235 from the allodial lands of the House of Welf in Saxony and was granted as an imperial fief to Otto the Child, a grandson of Henry the Lion. The duchy was divided several times during the High Middle Ages amongst various lines of the House of Welf, but each ruler was styled "Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg" in addition to his own particular title. By 1692, the territories had consolidated to two: the Electorate of Brunswick-Lüneburg (commonly known as Electorate of Hanover) and the Principality of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landstadt
A town is a human settlement. Towns are generally larger than villages and smaller than cities, though the criteria to distinguish between them vary considerably in different parts of the world. Origin and use The word "town" shares an origin with the German word , the Dutch word , and the Old Norse . The original Proto-Germanic word, *''tūnan'', is thought to be an early borrowing from Proto-Celtic *''dūnom'' (cf. Old Irish , Welsh ). The original sense of the word in both Germanic and Celtic was that of a fortress or an enclosure. Cognates of ''town'' in many modern Germanic languages designate a fence or a hedge. In English and Dutch, the meaning of the word took on the sense of the space which these fences enclosed, and through which a track must run. In England, a town was a small community that could not afford or was not allowed to build walls or other larger fortifications, and built a palisade or stockade instead. In the Netherlands, this space was a gard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Welf
The House of Welf (also Guelf or Guelph) is a European dynasty that has included many German and British monarchs from the 11th to 20th century and Emperor Ivan VI of Russia in the 18th century. The originally Franconia, Franconian family from the Meuse-Moselle area was closely related to the imperial family of the Carolingians. Origins The (Younger) House of Welf is the older branch of the House of Este, a dynasty whose earliest known members lived in Veneto and Lombardy in the late 9th/early 10th century, sometimes called Welf-Este. The first member was Welf I, Duke of Bavaria, also known as Welf IV. He inherited the property of the Elder House of Welf when his maternal uncle Welf, Duke of Carinthia, Welf III, Duke of Carinthia and Verona, the last male Welf of the Elder House, died in 1055. Welf IV was the son of Welf III's sister Kunigunde of Altdorf and her husband Albert Azzo II, Margrave of Milan. In 1070, Welf IV became Duke of Bavaria. Welf II, Duke of Bavaria marrie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weser
The Weser () is a river of Lower Saxony in north-west Germany. It begins at Hannoversch Münden through the confluence of the Werra and Fulda. It passes through the Hanseatic city of Bremen. Its mouth is further north against the ports of Bremerhaven and Nordenham. The latter is on the Butjadingen Peninsula. It then merges into the North Sea via two highly saline, estuarine mouths. It connects to the canal network running east-west across the North German Plain. The river, when combined with the Werra (a dialectal form of "Weser"), is long and thus, the longest river entirely situated within Germany (the Main, however, is the longest if the Weser and Werra are not combined). The Weser itself is long. The Werra rises in Thuringia, the German state south of the main projection (tongue) of Lower Saxony. Etymology "Weser" and "Werra" are the same words in different dialects. The difference reflects the old linguistic border between Central and Low German, passin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privilege (legal Ethics)
A privilege is a certain entitlement to immunity granted by the state or another authority to a restricted group, either by birth or on a conditional basis. Land-titles and taxi medallions are examples of transferable privilege – they can be revoked in certain circumstances. In modern democratic states, a ''privilege'' is conditional and granted only after birth. By contrast, a ''right'' is an inherent, irrevocable entitlement held by all citizens or all human beings from the moment of birth. Various Examples of old common law privilege still exist – to title deeds, for example. Etymologically, a privilege (''privilegium'') means a "private law", or rule relating to a specific individual or institution. The principles of conduct that members of the legal profession observe in their practice are called legal ethics. Boniface's abbey of Fulda, to cite an early and prominent example, was granted '' privilegium'', setting the abbot in direct contact with the pope, bypassing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert I (Brunswick)
Albert the Tall ( lat, Albertus Longus, german: Albrecht der Große; 1236 – 15 August 1279), a member of the House of Welf, was Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg from 1252 and the first ruler of the newly created Principality of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel from 1269 until his death. Life Albert was the oldest surviving son of the first Brunswick duke Otto the Child and his wife, Matilda of Brandenburg. When his father died in 1252, he took over the rule of the duchy; later his younger brother John joined him. Albert's rule was initially troubled by several armed conflicts as the Welf dukes still had to cope with the followers of the extinct Hohenstaufen dynasty within their dominions. In 1260/61 Albert's troops fought against the Danish duke Eric I of Schleswig on behalf of Queen Margaret Sambiria and her minor son King Eric V of Denmark. In 1263 the duke quite luckless interfered in the War of the Thuringian Succession to support the claims raised by his mother-in-law Sophie of Braban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)
.jpg)