|
Battle Of Pered
The Battle of Pered, fought on 20–21 June 1849, was one of the battles which took place in the Summer Campaign of the Hungarian War of Independence from 1848 to 1849, fought between the Hungarian Revolutionary Army and the Habsburg Empire helped by Russian troops. The Hungarian army was led by General Artúr Görgei, while the imperial army by Lieutenant field marshal Julius Jacob von Haynau. After several preliminary minor battles of the Hungarian and Austrian troops along the Vág river, in which the attacking Hungarians could not achieve success, Görgei took the command of his troops, and after receiving reinforcements, on 20 June, put his troops to attack again towards West. Although the II. Hungarian army corps occupied in heavy fights the village of Pered, the other two corps (the III. and the VIII.) were unsuccessful, and could not advance. The angered Görgei removed the commander of the III. corps, General Károly Knezić because of his inactivity, and Colonel Lajos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian Revolution Of 1848
The Hungarian Revolution of 1848 or fully Hungarian Civic Revolution and War of Independence of 1848–1849 () was one of many European Revolutions of 1848 and was closely linked to other revolutions of 1848 in the Habsburg areas. Although the revolution failed, it is one of the most significant events in Hungary's modern history, forming the cornerstone of modern Hungarian national identity. In April 1848, Hungary became the third country of Continental Europe (after France (1791), and Belgium (1831)) to enact law about democratic parliamentary elections. The new suffrage law (Act V of 1848) transformed the old feudal parliament ( Estates General) into a democratic representative parliament. This law offered the widest suffrage right in Europe at the time. The crucial turning point of events was when the new young Austrian monarch Franz Joseph I arbitrarily revoked the April laws (ratified by King Ferdinand I) without any legal competence. This unconstitutional act irrever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonel
Colonel (abbreviated as Col., Col or COL) is a senior military officer rank used in many countries. It is also used in some police forces and paramilitary organizations. In the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries, a colonel was typically in charge of a regiment in an army. Modern usage varies greatly, and in some cases, the term is used as an honorific title that may have no direct relationship to military service. The rank of colonel is typically above the rank of lieutenant colonel. The rank above colonel is typically called brigadier, brigade general or brigadier general. In some smaller military forces, such as those of Monaco or the Vatican, colonel is the highest rank. Equivalent naval ranks may be called captain or ship-of-the-line captain. In the Commonwealth's air force ranking system, the equivalent rank is group captain. History and origins By the end of the late medieval period, a group of "companies" was referred to as a "column" of an army. According to Raymond Ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Buda (1849)
The siege of Buda took place at Buda castle (called ''Festung Ofen'' in German), part of the twin capital cities of the Kingdom of Hungary. The Hungarian revolutionary army was led by General Artúr Görgei during the Hungarian War of Independence. Part of the Spring Campaign, the siege began on 4 May 1849, ending with the Hungarian capture of the castle by assault on 21 May. Buda Castle was the only fortress throughout the entire war to be taken by storm by the besiegers on either side. All other fortresses capitulated following agreements between besiegers and besieged. The siege of Buda was also the shortest siege of the war (18 days). The senseless bombardment of Pest by Austrian commander Major General Heinrich Hentzi caused destruction of classic buildings on the shores of the Danube. Other regions of the capitals also suffered heavy damage due to the artillery duels between the two sides. The capture of Buda Castle completed the liberation of the Hungarian capital cities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry John Temple, 3rd Viscount Palmerston
Henry John Temple, 3rd Viscount Palmerston, (20 October 1784 – 18 October 1865) was a British statesman who was twice Prime Minister of the United Kingdom in the mid-19th century. Palmerston dominated British foreign policy during the period 1830 to 1865, when Britain stood at the height of its imperial power. He held office almost continuously from 1807 until his death in 1865. He began his parliamentary career as a Tory, defected to the Whigs in 1830, and became the first prime minister from the newly formed Liberal Party in 1859. He was highly popular with the British public. David Brown argues that "an important part of Palmerston's appeal lay in his dynamism and vigour". Henry Temple succeeded to his father's Irish peerage (which did not entitle him to a seat in the House of Lords, leaving him eligible to sit in the House of Commons) as the 3rd Viscount Palmerston in 1802. He became a Tory MP in 1807. From 1809 to 1828 he served as Secretary at War, organising the finan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lajos Kossuth
Lajos Kossuth de Udvard et Kossuthfalva (, hu, udvardi és kossuthfalvi Kossuth Lajos, sk, Ľudovít Košút, anglicised as Louis Kossuth; 19 September 1802 – 20 March 1894) was a Hungarian nobleman, lawyer, journalist, politician, statesman and governor-president of the Kingdom of Hungary during the revolution of 1848–1849. With the help of his talent in oratory in political debates and public speeches, Kossuth emerged from a poor gentry family into regent-president of the Kingdom of Hungary. As the influential contemporary American journalist Horace Greeley said of Kossuth: "Among the orators, patriots, statesmen, exiles, he has, living or dead, no superior." Kossuth's powerful English and American speeches so impressed and touched the famous contemporary American orator Daniel Webster, that he wrote a book about Kossuth's life. He was widely honoured during his lifetime, including in Great Britain and the United States, as a freedom fighter and bellwet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bertalan Szemere
Bertalan Szemere (27 August 1812 – 18 January 1869) was a Hungarian poet and nationalist who became the third Prime Minister of Hungary during the short period of the Hungarian Revolution of 1848 when Hungary was independent of rule by the Austrian Empire. Early years Szemere was born in Vatta into a poor noble family. His father was Major László Szemere, his mother was Erzsébet Karove. Szemere studied in Miskolc, Késmárk and Sárospatak. He was interested in writing poems and his works were published in the periodical ("Upper-Hungarian Minerva"). He was influenced by Ferenc Kölcsey and Mihály Vörösmarty. In the reform era In 1832 Szemere graduated as a jurist and started to work as an apprentice in Pressburg (now Bratislava, Slovakia) and became a member of the Parliamentary Young Members' Group and advocated liberal principles. After he finished his pupillage, Szemere went back to Borsod where he was elected as an honorary notary public. In 1835 Szemere tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas I Of Russia
Nicholas I , group=pron ( – ) was List of Russian rulers, Emperor of Russia, Congress Poland, King of Congress Poland and Grand Duke of Finland. He was the third son of Paul I of Russia, Paul I and younger brother of his predecessor, Alexander I of Russia, Alexander I. Nicholas inherited his brother's throne despite the failed Decembrist revolt against him. He is mainly remembered in history as a reactionary whose controversial reign was marked by geographical expansion, economic growth, and massive industrialisation on the one hand, and centralisation of administrative policies and repression of dissent on the other. Nicholas had a happy marriage that produced a large family; all of their seven children survived childhood. Nicholas's biographer Nicholas V. Riasanovsky said that he displayed determination, singleness of purpose, and an iron will, along with a powerful sense of duty and a dedication to very hard work. He saw himself as a soldier—a junior officer totally consumed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Joseph I Of Austria
Franz Joseph I or Francis Joseph I (german: Franz Joseph Karl, hu, Ferenc József Károly, 18 August 1830 – 21 November 1916) was Emperor of Austria, King of Hungary, and the Grand title of the Emperor of Austria, other states of the Habsburg monarchy from 2 December 1848 until his death on 21 November 1916. In the early part of his reign, his realms and territories were referred to as the Austrian Empire, but were reconstituted as the dual monarchy of the Austro-Hungarian Empire in 1867. From 1 May 1850 to 24 August 1866, Franz Joseph was also President of the German Confederation. In December 1848, Franz Joseph's uncle Ferdinand I of Austria, Emperor Ferdinand abdicated the throne at Olomouc, as part of Minister President Felix zu Schwarzenberg's plan to end the Revolutions of 1848 in Hungary. Franz Joseph then acceded to the throne. Largely considered to be a reactionary, he spent his early reign resisting constitutionalism in his domains. The Austrian Empire was forced to c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Józef Bem
Józef Zachariasz Bem ( hu, Bem József, tr, Murat Pasha; March 14, 1794 – December 10, 1850) was a Polish engineer and general, an Ottoman pasha and a national hero of Poland and Hungary, and a figure intertwined with other European patriotic movements. Like Tadeusz Kościuszko (who fought in the American War of Independence) and Jan Henryk Dąbrowski (who fought alongside Napoleon Bonaparte in Italy and in the French Invasion of Russia), Bem fought outside Poland's borders anywhere his leadership and military skills were needed. Early life He was born on 14 March 1794 in Tarnów in Galicia, the area of Poland that had become part of the Habsburg monarchy through the First Partition in 1772. After the creation of the Duchy of Warsaw from the territories captured by Napoleon, he moved with his parents to Kraków, where after finishing military school (where he distinguished himself in mathematics) and joined the ducal forces as a fifteen-year-old cadet. He joined a P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lieutenant General
Lieutenant general (Lt Gen, LTG and similar) is a three-star military rank (NATO code OF-8) used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages, where the title of lieutenant general was held by the second-in-command on the battlefield, who was normally subordinate to a captain general. In modern armies, lieutenant general normally ranks immediately below general and above major general; it is equivalent to the navy rank of vice admiral, and in air forces with a separate rank structure, it is equivalent to air marshal. A lieutenant general commands an army corps, made up of typically three army divisions, and consisting of around 60 000 to 70 000 soldiers (U.S.). The seeming incongruity that a lieutenant general outranks a major general (whereas a major outranks a lieutenant) is due to the derivation of major general from sergeant major general, which was a rank subordinate to lieutenant general (as a lieutenant outranks a sergeant major). In contrast, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
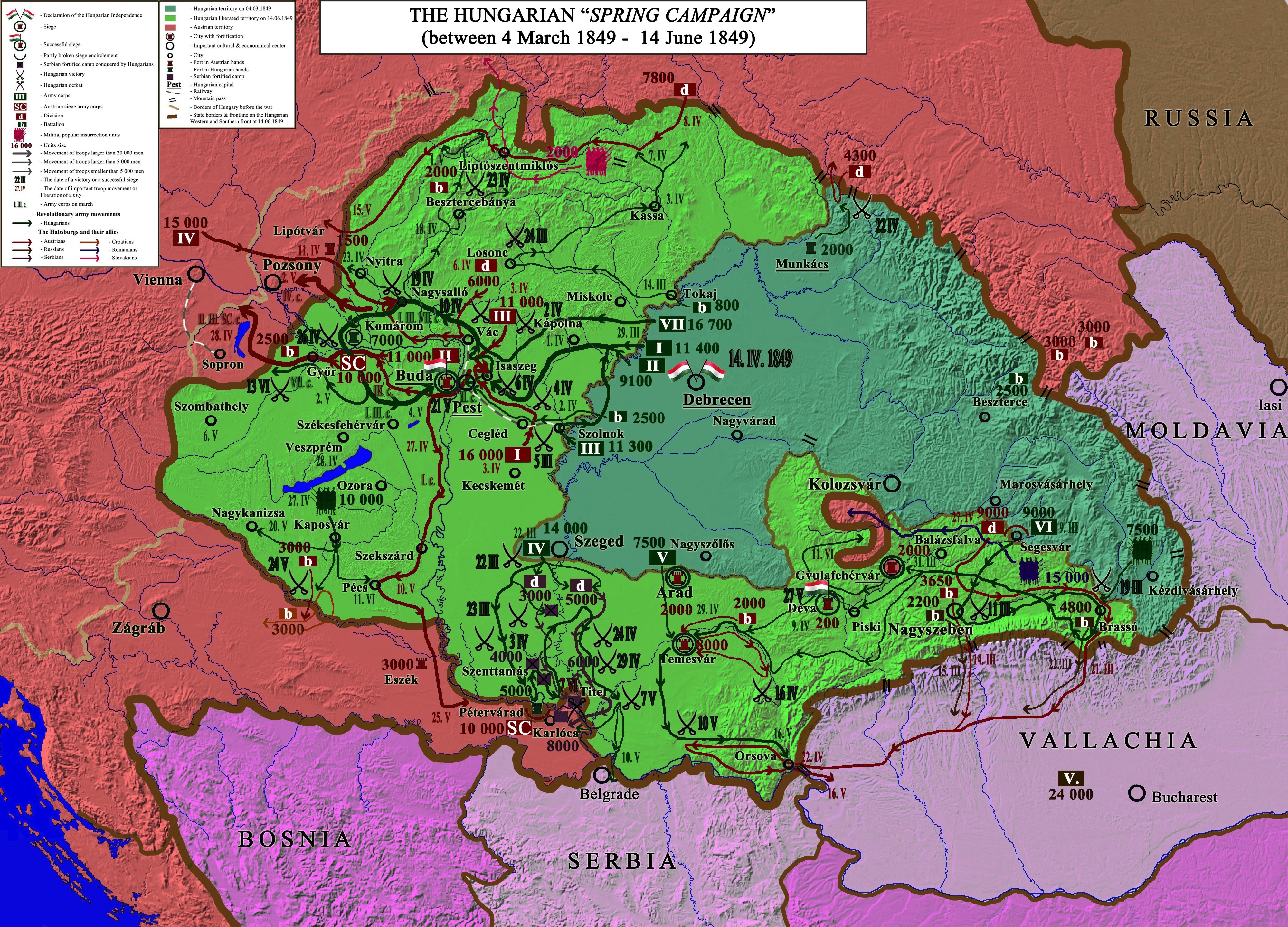
Spring Campaign
The Spring CampaignIstván Lázár, An illustrated history of Hungary, Corvina, 1999, p. 90, ( hu, tavaszi hadjárat), named also the ''Glorious Spring Campaign''Tarján Tamás1849. április 26. , A komáromi csata Rubicon ( hu, dicsőséges tavaszi hadjárat) is the military campaign of the Hungarian Revolutionary Army against the forces of the Habsburg Empire in Middle and Western Hungary during the Hungarian Revolution of 1848 between 2 April and 21 May 1849, which resulted in the liberation of almost the whole territory of Hungary from the Habsburg forces. The spring campaign's commander-in-chief was General Artúr Görgey, whose army (47 500 men, 198 cannons) defeated the numerically, technologically and tactically superior (55 000 soldiers and 214 cannons and rockets) imperial armies led by Alfred I, Prince of Windisch-Grätz and after his dismissal, Ludwig von Welden, in a series of victories. The Hungarians won the battles of Hatvan (2nd of April), Tápióbicske (4th of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)