|
Battle Of La Rochelle (other)
Battle of La Rochelle or Siege of La Rochelle may refer to: * Siege of La Rochelle (1224) between the Capetians and the Plantagenets * Battle of La Rochelle (1372) between the Castilians and the English in a naval battle off La Rochelle * Battle of La Rochelle (1419) between the Castilians and a joint Flemish-Hanseatic fleet off La Rochelle * Siege of La Rochelle (1572–1573) between the Huguenots and the Catholics during the Wars of Religion * Siege of La Rochelle (1627–1628) between the Royalists and the Huguenots * Allied siege of La Rochelle (1944–1945) between the Allies and the Germans during the Second World War See also * Blockade of La Rochelle (1621-1622) * History of La Rochelle * * * La Rochelle (other) La Rochelle is a city in Charente-Maritime, France. La Rochelle may also refer to: Places *La Rochelle, Manitoba, Canada * Arrondissement of La Rochelle, Charente-Maritime, France *La Rochelle-1, La Rochelle-2, etc.; nine cantons in Charente-Mari ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of La Rochelle (1224)
The siege of La Rochelle of 1224 was the decisive engagement in the campaign between the Capetians and the Plantagenets for control of Poitou. French royal forces commanded by Capetian king Louis VIII laid siege to the strategic port of La Rochelle and its garrison of Poitevin and English soldiers commanded by Savari de Mauléon. The port had long been a staging ground for Plantagenet efforts to regain their continental lands lost to the French crown since 1203. The siege lasted from July to August 1224, and resulted in La Rochelle's citizens surrendering the city to Louis after the failure of English relief to emerge. The siege of La Rochelle was the crowning event of the Capetian conquest of Poitou from the Plantagenets. With Poitou in Capetian hands, only Gascony remained under Plantagenet rule on the continent. Background The city of La Rochelle came under Plantagenet rule with the rest of Aquitaine in 1152, when Eleanor of Aquitaine married Henry Plantagenet, the duke of Anjo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of La Rochelle
The Battle of La Rochelle was a naval battle fought on 22 and 23 June 1372 between a Castilian fleet commanded by the Castilian Ambrosio Boccanegra and an English fleet commanded by John Hastings, 2nd Earl of Pembroke. The Castilian fleet had been sent to attack the English at La Rochelle, which was being besieged by the French. Besides Boccanegra, other Castilian commanders were Cabeza de Vaca, Fernando de Peón and Ruy Díaz de Rojas. Pembroke had been dispatched to the town with a small retinue of 160 soldiers, £12,000 and instructions to use the money to recruit an army of 3,000 soldiers around Aquitaine for at least four months. The strength of the fleet is estimated as between the 12 galleys given by the Castilian chronicler and naval captain López de Ayala and the 40 sailing ships, of which three ships were warships and 13 barges mentioned by the French chronicler Jean Froissart. Probably it consisted of 22 ships, mainly galleys and some (carracks) three- or four-ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of La Rochelle (1419)
The naval Battle of La Rochelle 1419 was a battle between a Castilian and an allied Flemish-Hanseatic fleet. The Castillian victory resulted in their naval supremacy in the Bay of Biscay. but also led to a protracted conflict with County of Flanders, Flanders and the Hanseatic League that ended in 1443 with further commercial concessions to Crown of Castile, Castile. The battle was notable for the use of guns by the Castilian fleet. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Battle Of La Rochelle (1419) Naval battles of the Hundred Years' War, La Rochelle Conflicts in 1419, La Rochelle 1419 in England Naval battles involving the Hanseatic League, La Rochelle Naval battles involving Castile, La Rochelle La Rochelle 1410s in France 14th century in Castile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of La Rochelle (1572–1573)
The siege of La Rochelle of 1572–1573 was a massive military assault on the Huguenot city of La Rochelle by Catholic troops during the fourth phase of the French Wars of Religion, following the August 1572 St. Bartholomew's Day massacre. The conflict began in November 1572 when inhabitants of the city refused to receive Armand de Gontaut, baron de Biron, as royal governor. Beginning on 11 February 1573, the siege was led by the Duke of Anjou (the future Henry III). Political considerations following the duke's election to the throne of Poland in May 1573 resulted in negotiations, culminating on 24 June 1573, that lifted the siege on 6 July 1573. The Edict of Boulogne signed shortly thereafter brought an end to this phase of the civil war. The siege of La Rochelle was contemporaneous with Catholic assaults on the cities of Sommières (led by Henri I de Montmorency) and Sancerre. Background Since 1568, La Rochelle had been the main base of the Huguenots in France. A c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of La Rochelle
The siege of La Rochelle (, or sometimes ) was a result of a war between the French royal forces of Louis XIII of France and the Huguenots of La Rochelle in 1627–28. The siege marked the height of the struggle between the Catholics and the Protestants in France, and ended with a complete victory for King Louis XIII and the Catholics. Background The 1598 Edict of Nantes that ended the French Wars of Religion granted Protestants, commonly known as Huguenots, a large degree of autonomy and self-rule. La Rochelle was the centre of Huguenot seapower, and a key point of resistance against the Catholic royal government. The assassination of Henry IV of France in 1610 led to the appointment of Marie de' Medici as regent for her nine-year-old son, Louis XIII. Her removal in 1617 caused a series of revolts by powerful regional nobles, both Catholic and Protestant, while religious tensions were heightened by the outbreak of the 1618 to 1648 Thirty Years War. In 1621, Louis re-estab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allied Siege Of La Rochelle
The Allied siege of La Rochelle occurred during the Second World War in 1944–45, when Allied troops invaded France. La Rochelle was an important German naval base on the Atlantic for surface ships and submarines, from which U-boat campaigns were launched. La Rochelle and other harbours such as Royan and Saint-Nazaire, became " Atlantic pockets" still occupied by the Germans, which were bypassed by the main thrust of the Allied invasion, as was Dunkirk on the North Sea. The city was liberated only at the very end of the war, nine months after the Liberation of Paris, after the general German capitulation on 8 May 1945. Siege The Allied siege of the pocket of La Rochelle lasted from September 1944 to May 1945, without heavy bombardment. La Rochelle remained in German hands until the end of the war, like other Atlantic pockets such as Saint-Nazaire and Lorient. Just surrounding the city was considered wiser than conducting a frontal attack, as the city would ultimately fall anyw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
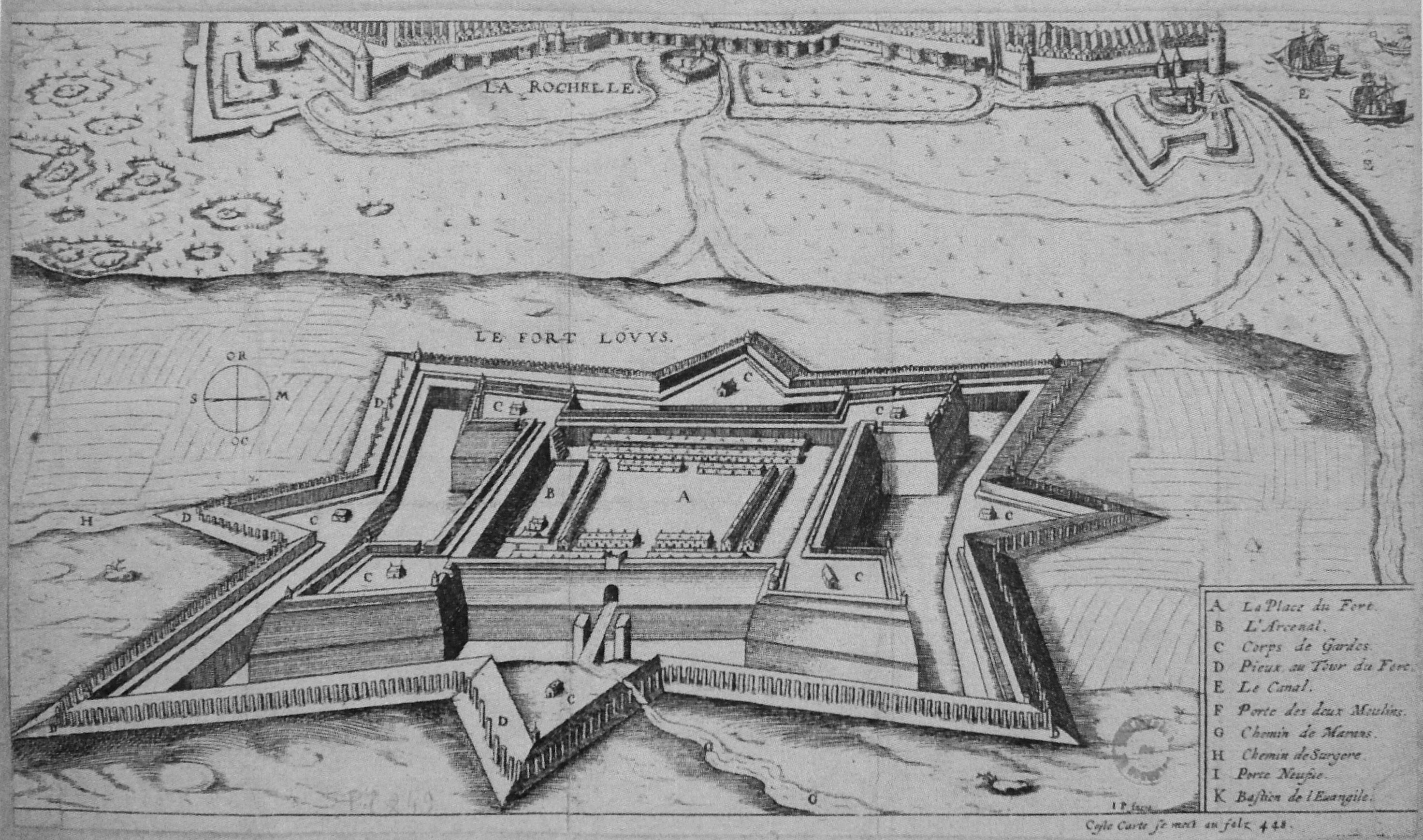
Blockade Of La Rochelle
The Blockade of La Rochelle (French: ''Blocus de La Rochelle'') took place in 1621-1622 during the repression of the Huguenot rebellion by the French king Louis XIII. In June 1621, Louis XIII besieged and captured Saint-Jean d'Angély, a strategic city controlling the approaches to the Huguenot stronghold of La Rochelle. Louis XIII chose however to move south with his main force for the Siege of Montauban. The blockade Meanwhile, Louis XIII ordered the Duke of Épernon to blockade La Rochelle by sea as well as by land. On the sea, however, efforts were ineffective, as many small ships could easily go through ships of the Royal Navy and the Huguenots generally had mastery of the sea. At one point they attacked the harbour of Brouage and attempted to block it by sinking ships filled with stones at its entrance. In July 1621, d'Épernon established his headquarters on land in La Jarrie, in the vicinity of La Rochelle. In August, the shipowner Jean Guiton was named by the City Counc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of La Rochelle
La Rochelle (, , ; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''La Rochéle''; oc, La Rochèla ) is a city on the west coast of France and a seaport on the Bay of Biscay, a part of the Atlantic Ocean. It is the capital of the Charente-Maritime department. With 75,735 inhabitants in 2017, La Rochelle is the most populated commune in the department and ranks fifth in the New Aquitaine region after Bordeaux, the regional capital, Limoges, Poitiers and Pau. Its inhabitants are called "les Rochelaises" and "les Rochelais". Situated on the edge of the Atlantic Ocean the city is connected to the Île de Ré by a bridge completed on 19 May 1988. Since the Middle-Ages the harbour has opened onto a protected strait, the Pertuis d'Antioche and is regarded as a "Door océane" or gateway to the ocean because of the presence of its three ports (fishing, trade and yachting). The city has a strong commercial tradition, having an active port from very early on in its history. La Rochelle underwent susta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |