|
Battle Of Issos
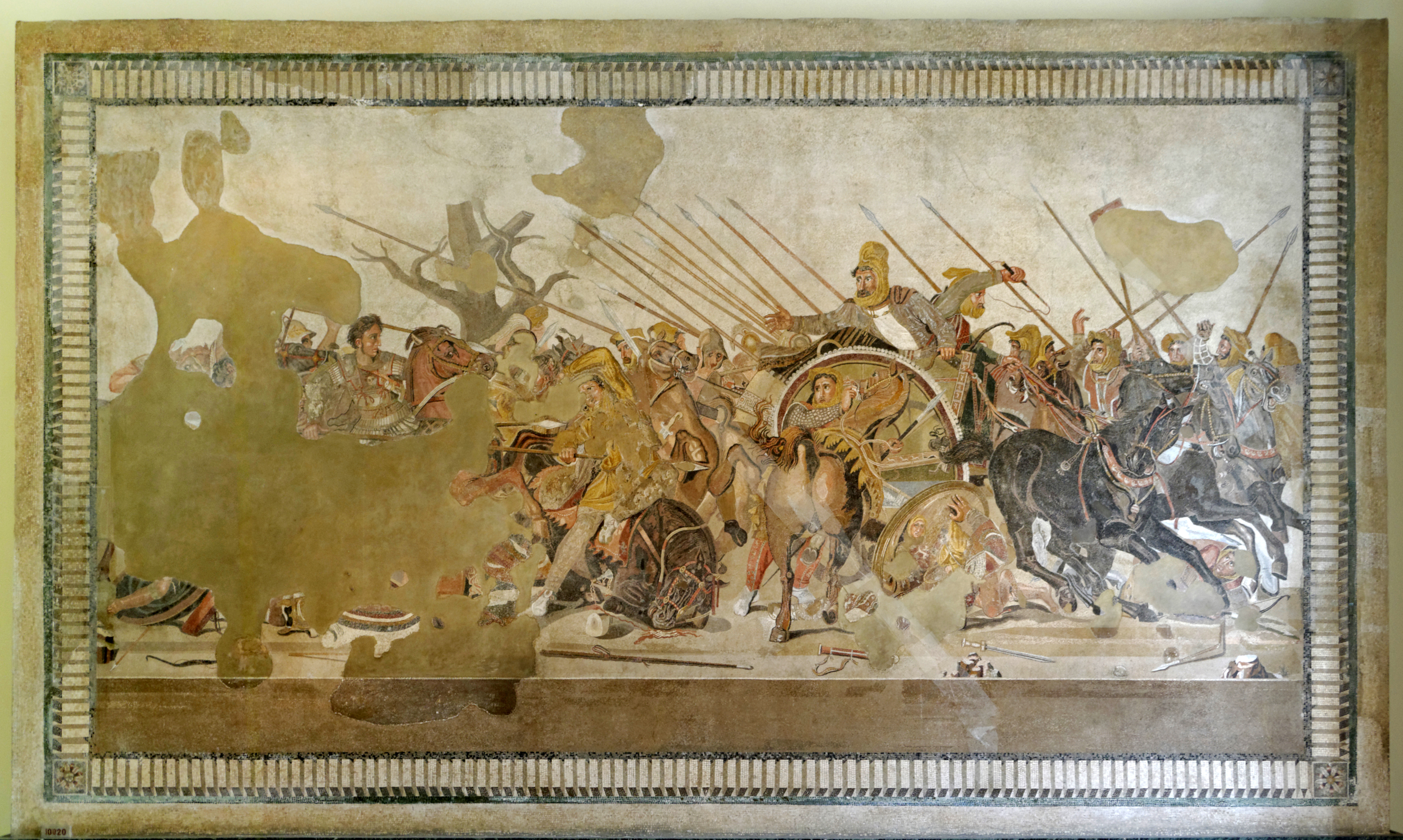
The Battle of Issus (also Issos) occurred in southern Anatolia, on November 5, 333 BC between the Hellenic League led by Alexander the Great and the Achaemenid Empire, led by Darius III. It was the second great battle of Alexander's conquest of Asia, and the first encounter between Darius III and Alexander the Great. The battle resulted in the Macedonian troops defeating the Persian forces. After the Hellenic League soundly defeated the Persian satraps of Asia Minor (led by Greek mercenary Memnon of Rhodes) at the Battle of the Granicus, Darius took personal command of his army. He gathered reinforcements and proceeded to lead his men in a surprise march behind the Hellenic advance, in order to cut off their line of supply. Alexander was forced to countermarch, and the stage was set for the battle near the mouth of the Pinarus River and the town of Issus. Location The battle took place south of the ancient town Issus, which is close to the present-day Turkish town of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naples National Archaeological Museum
The National Archaeological Museum of Naples ( it, Museo Archeologico Nazionale di Napoli, italic=no, sometimes abbreviated to MANN) is an important Italian archaeological museum, particularly for ancient Roman remains. Its collection includes works from Greek, Roman and Renaissance times, and especially Roman artifacts from the nearby Pompeii, Stabiae and Herculaneum sites. From 1816 to 1861, it was known as Real Museo Borbonico ("the Royal Bourbon Museum"). Building The building was built as a cavalry barracks in 1585. From 1616 to 1777 it was the seat of the University of Naples. During the 19th century, after it became a museum, it suffered many changes to the main structure. Collections The museum hosts extensive collections of Greek and Roman antiquities. Their core is from the Farnese Collection, which includes a collection of engraved gems (including the Farnese Cup, a Ptolemaic bowl made of sardonyx agate and the most famous piece in the "Treasure of the Magnifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hephaestion
Hephaestion ( grc, Ἡφαιστίων ''Hephaistíon''; c. 356 BC – October 324 BC), son of Amyntor, was an ancient Macedonian nobleman and a general in the army of Alexander the Great. He was "by far the dearest of all the king's friends; he had been brought up with Alexander and shared all his secrets."Curtius 3.12.16 This relationship lasted throughout their lives, and was compared, by others as well as themselves, to that of Achilles and Patroclus. His military career was distinguished. A member of Alexander the Great's personal bodyguard, he went on to command the Companion cavalry and was entrusted with many other tasks throughout Alexander's ten-year campaign in Asia, including diplomatic missions, the bridging of major rivers, sieges and the foundation of new settlements. Besides being a soldier, engineer and diplomat, he corresponded with the philosophers Aristotle and Xenocrates and actively supported Alexander in his attempts to integrate th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypaspists
A hypaspist ( el, Ὑπασπιστής "shield bearer" or "shield covered") is a squire, man at arms, or "shield carrier". In Homer, Deiphobos advances "" () or under cover of his shield. By the time of Herodotus (426 BC), the word had come to mean a high status soldier as is strongly suggested by Herodotus in one of the earliest known uses: A similar usage occurs in Euripides's play '' Rhesus'' and another in his ''Phoenissae''. Xenophon was deserted by his horse in a particularly sticky situation. A hypaspist would differ from a skeuophoros in most cases because the "shield bearer" is a free warrior and the "baggage carrier" was probably usually a slave. The word may have had Homeric and heroic connotations that led Philip II of Macedon to use it for an elite military unit. This unit, known as the Hypaspistai, or hypaspists, was probably armed in the hoplite manner, with a large concave shield ( Aspis) and a spear (Dory), in addition to spolas or linothorax body-armor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phalangites
The Macedonian phalanx ( gr, Μακεδονική φάλαγξ) was an infantry formation developed by Philip II from the classical Greek phalanx, of which the main innovation was the use of the sarissa, a 6 meter pike. It was famously commanded by Philip's son Alexander the Great during his conquest of the Achaemenid Empire between 334 and 323 BC. The Macedonian phalanx model then spread throughout the Hellenistic world, where it became the standard battle formation for pitched battles. During the Macedonian Wars against the Roman Republic (214–148 BC), the phalanx appeared obsolete against the more manoeuvrable Roman legions. Development In 359 BC, following the Macedonian defeat by the Illyrians, which killed the majority of Macedonia's army and King Perdiccas III of Macedon, Perdiccas' brother Philip II took the throne. Philip II was a hostage in Thebes for much of his youth (367–360), where he witnessed the combat tactics of the general Epaminondas, which then influence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabaces
Sabaces (name variants: Sabakes, Sauaces; Sataces; Sathaces; Diodorus Siculus calls him Tasiaces; Aramaic: 𐡎𐡅𐡉𐡊 SWYK, died in 333 BC) was an Achaemenid Persian satrap of the Achaemenid Thirty-first Dynasty of Egypt during the reign of king Darius III of Persia. Resistance to Alexander the Great Some time before the Battle of Issus (modern-day Turkey), Sabaces left Egypt with his army to join Darius III in Syria and support him in his fight against Alexander the Great. When the Battle of Issus took place (November 333 BC) Alexander and his horsemen fought their way through the enemy troops until they came in close vicinity to Darius III, whose life was therefore threatened. Darius III was protected by the most noble Persians, among them also Sabaces, who was killed:Arrian, ''Anabasis Alexandri'' 2.11.8; Diodorus Siculus, ''Bibliotheca historica'' 17.34.5; Quintus Curtius Rufus, ''Historiae Alexandri Magni'' 3.11.10 and 4.1.28 The Persian king fled because he feared f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atizyes
Atizyes was a Persian satrap of Greater Phrygia under the Achaemenids in 334 BC, when Alexander the Great began his campaign. He is not mentioned in the council of Zelea where the satrap coalition was formed against the invasion, so it is not sure whether he took part in the battle of the Granicus. After the battle, he appears to be in the capital of Greater Phrygia, Celaenae where he had a garrison force of 1,000 Carians and 100 Greek mercenaries. He himself went to Syria to join the army of Darius III and fell in the battle of Issus (modern-day Turkey) at 333 BC. After Phrygia fell to Alexander, he appointed his general Antigonus Monophthalmus Antigonus I Monophthalmus ( grc-gre, Ἀντίγονος Μονόφθαλμος , 'the One-Eyed'; 382 – 301 BC), son of Philip from Elimeia, was a Macedonian Greek nobleman, general, satrap, and king. During the first half of his life he serv ... as its satrap.Arrian ''Anabasis'' 1.29.3 References Sources * External linksOrigina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheomithres
Rheomithres (Old Persian: ; Ancient Greek: ) was a Persian noble. He was father of several children, including Phrasaortes whom Alexander the Great appointed satrap of Persis in 330 BC. He joined in the Great Satraps' Revolt of the western Persian provinces from Artaxerxes II, in 362 BC, and was employed by his confederates to go to Tachos, pharaoh of Egypt, for aid. He came back with 500 talents and 50 warships and he is supposed to have left his wife and his children to Tachos as a guarantee for his assistance. Nevertheless, Rheomithres betrayed the rebels and he invited a number of them in a meeting. On their arrival, he arrested them, and despatched them in chains to Artaxerxes to receive the bounties, thus making his own peace at court. Rheomithres took part in the battle of the Granicus, in 334 BC, where he was in command of a body of 2,000 cavalry on the right wing, between 1,000 Medes and 2,000 Bactrians. He survived the battle and the next year he joined Darius at the bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arsames (satrap Of Cilicia)
Arsames (Old Persian ''Aršāma'', el, Ἀρσάμης) was an Achaemenid Persian people, Persian satrap of Cilicia (satrapy), Cilicia in 334/3 BC. He succeeded Mazaeus in this position. He took part in the Battle of Granicus where he fought with his cavalry on the left wing, along with Arsites and Memnon of Rhodes. He was able to survive that battle and flee to the capital of Cilicia Tarsus, Mersin, Tarsus. There he was planning a scorched-earth policy according to that of Memnon which caused the native Cilician soldiers to abandon their posts. He also decided to burn Tarsus to the ground so as not to fall in the hands of Alexander but was prevented from doing so by the speedy arrival of Parmenion with the light armored units who took the city. After that, Arsames fled to Darius III, Darius who was at this time in Syria (region), Syria. He was slain at the battle of Issus (modern-day Turkey) in 333 BC.Alexander of Macedon, 356-323 B.C.: a historical biography By Peter Green He wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darius III
Darius III ( peo, 𐎭𐎠𐎼𐎹𐎺𐎢𐏁 ; grc-gre, Δαρεῖος ; c. 380 – 330 BC) was the last Achaemenid King of Kings of Persia, reigning from 336 BC to his death in 330 BC. Contrary to his predecessor Artaxerxes IV Arses, Darius was a distant member of the Achaemenid dynasty. During his early career, he was reportedly an obscure figure among his peers and first rose to prominence during the Cadusian expedition of Artaxerxes III in the 350s BC. As a reward for his bravery, he was given the Satrapy of Armenia. Around 340 BC, he was placed in charge of the royal "postal service," a high-ranking position. In 338 BC, Artaxerxes III met an abrupt end after being poisoned by the court eunuch and chiliarch (''hazahrapatish'') Bagoas, who installed his youngest son Arses on the throne. He only reigned for a few years, until Bagoas had him poisoned as well. Darius was subsequently installed on the throne and soon forced Bagoas to drink his poison after discovering that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balacrus
Balakros ( el, Bάλακρoς), also Balacrus, the son of Nicanor, one of Alexander the Great's "Somatophylakes" (bodyguards), was appointed satrap of Cilicia after the Battle of Issus, 333 BC. He succeeded to the last Achaemenid satrap of Cilicia, Arsames. Career Balakros completed the conquest of Asia Minor together with Calas, satrap of Hellespontine Phrygia, and Antigonus, satrap of Phrygia. It was probably this Balacrus who married Phila, the daughter of Antipater, and subsequently the wife of Craterus. He was probably supervised by Menes from 331 BC, who held the position of ''Hyparch'' or ''Strategoi'' for the area from Babylon to the satrapies of Syria, Phoenicia, and Cilicia. He fell in battle against the Pisidians in the lifetime of Alexander. His death is variously placed circa 328 BC or 323 BC. Coinage Balacrus is among several Hellenistic satraps who continued to use an Achaemenid type for their coinage, complete with the local deity of Tarsus, Baal. His coi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menes Of Pella
Menes of Pella ( grc, Μένης), son of Dionysius, was one of the Greek officers of Alexander the Great; and after the Battle of Issus (333 BC) was admitted by the king into the number of his somatophylakes, in the place of Balacrus, who was promoted to the satrapy of Cilicia. In 331 BC, after Alexander had occupied Susa, he sent Menes down to the Mediterranean to take the government of Syria, Phoenicia, and Cilicia, entrusting him at the same time with 3000 talents, a portion of which he was to transmit to Antipater for his war with the Lacedaemonians. He was a ''Hyparch'', and in this position, he may have been responsible for overseeing the existing administration as far as Cilicia. Apollodorus of Amphipolis Apollodorus ( el, Ἀπολλόδωρος) from Amphipolis was one of the cavalry generals of Alexander the Great, who commanded the force Alexander left behind with the Babylonian governor Mazaeus. He was entrusted in 331 BCE, together with Menes o ... was joined wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |