|
Battle Of Elasa
The Battle of Elasa was fought in April 160 BCE during the Maccabean Revolt between Judean rebels led by Judas Maccabeus (Judah Maccabee) and an army of the Seleucid Empire under the command of Bacchides. The battle resulted in the triumph of the Greek Syrian forces, the defeat of the Maccabees, and the death of Judas Maccabeus. Leadership of the Maccabees would pass to Judas's brother Jonathan Apphus (Yonatan), who would continue to fight against Bacchides for the remainder of 160 BCE. The Seleucids largely triumphed; control of the cities was restored to them including Jerusalem, hostages of important Jewish families were taken, and Greek-aligned garrisons were placed around Judea. Despite this setback, unrest continued in the countryside. The Hasmonean sons of Mattathias continued to oppose the government in the following eight years, and would eventually succeed in gaining allies both among Seleucid rulers and the Romans that would allow for autonomy. Judas's brother ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maccabean Revolt
The Maccabean Revolt ( he, מרד החשמונאים) was a Jewish rebellion led by the Maccabees against the Seleucid Empire and against Hellenistic influence on Jewish life. The main phase of the revolt lasted from 167–160 BCE and ended with the Seleucids in control of Judea, but conflict between the Maccabees, Hellenized Jews, and the Seleucids continued until 134 BCE, with the Maccabees eventually attaining independence. Seleucid King Antiochus IV Epiphanes launched a massive campaign of repression against the Jewish religion in 168 BCE. The reason he did so is not entirely clear, but it seems to have been related to the King mistaking an internal conflict among the Jewish priesthood as a full-scale rebellion. Jewish practices were banned, Jerusalem was placed under direct Seleucid control, and the Second Temple in Jerusalem was made the site of a syncretic Pagan-Jewish cult. This repression triggered exactly the revolt that Antiochus IV had feared, with a group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philoi
''Philoi'' ( grc, φίλοι; plural of φίλος ''philos'' "friend") is a word that roughly translates to "friend." This type of friendship is based on the characteristically Greek value for reciprocity as opposed to a friendship that exists as an end to itself. Characteristics Reciprocity There is no exact translation for ''philoi'' other than the word "friend" (separate from '' xenos'', or "guest-friend," often used to describe a stranger one is kind or respectful to). The meaning of the word ''philoi'' is deeply rooted in the concept of reciprocity; encompassing the exchange of favors and support, in addition to a profound sense of duty to each other. ''Philoi'' typically encompassed family members foremost, with the addition of friends or members of society with whom obligations, loyalty or other established ties existed. Greek value-system Within the Greek value-system there was an explicit distinction between friend (''philoi'') and the enemy (''echthroi Echthroi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eleazar Avaran
Eleazar Avaran, also known as Eleazar Maccabeus, Eleazar Hachorani/Chorani (Hebrew: אלעזר המכבי ''Eleazar HaMakabi'', אלעזר החורני ''Eleazar HaChorani''; died 162 BC) was the fourth son of Mattathias and the younger brother of Judas Maccabeus. He was killed at the Battle of Beth-zechariah () during the Maccabean revolt. Little is known about Eleazar, except his heroic death as was told. According to the scroll of Antiochus, his father saw in him a Zealot among zealots, like Pinhas. In it is told that Eleazar read from the Tanakh in front of the people just before the last battle began in . Death According to , during the Battle of Beit Zechariah, Eleazar identified a war elephant that he believed to carry the Seleucid King Antiochus V, due to the special armor the elephant wore. He decided to endanger his life by attacking the elephant and thrusting a spear into its belly. The dead elephant then collapsed upon Eleazar, killing him as well. Despite this h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judaean Mountains
The Judaean Mountains, or Judaean Hills ( he, הרי יהודה, translit=Harei Yehuda) or the Hebron Mountains ( ar, تلال الخليل, translit=Tilal al-Khalīl, links=, lit=Hebron Mountains), is a mountain range in Palestine and Israel where Jerusalem, Hebron and several other biblical cities are located. The mountains reach a height of . The Judean Mountains can be separated to a number of sub-regions, including the Mount Hebron ridge, the Jerusalem ridge and the Judean slopes. The Judaean Mountains formed the heartland of the Kingdom of Judah (930-586 BCE), where the earliest Jewish settlements emerged, and from which Jews are generally descended. Geography The Judaean mountains are part of a more extended range that runs in a north-south direction. The ridge consists of the Samarian Hills in its northern part, and of the Judaean mountains in its southern part, the two segments meeting at the latitude of Ramallah. The westward descent from the hard limestone count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tall Asur
Tall Asur ( ar, تل العاصور), known in Hebrew as Ba'al Hazor ( he, בַּעַל חָצוֹר, link=no), is a hill and one of the highest points in the West Bank, with an altitude of 1,016 metres (3,333 ft). It is surrounded by the Palestinian villages of Silwad, Taybeh, Kafr Malik and Al-Mazra'a ash-Sharqiya and the Israeli settlement of Ofra. In modern times it was identified with the biblical site of Baal-hazor, a place in Samaria on the border of Ephraim and Benjamin where Absalom held the feast of sheep-shearing when Amnon was assassinated, according to . It is probably identical with Hazor mentioned in . If that is correct, the modern Arabic place name preserves the original Biblical name. The mountain has two peaks, one of which is an IDF base. See also * Geography of the Palestinian territories Geography of the State of Palestine refers to the geographic, climatic and other properties of the areas claimed by State of Palestine. Physiographic re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baal-hazor
Baal-hazor ( he, בַּעַל חָצוֹר, link=, lit=Baal's village) is a place on the border of Ephraim and Benjamin where Absalom held the feast of sheep-shearing when Amnon was assassinated, according to . It is probably identical with Hazor mentioned in . Baal-hazor is identified with Tell Asur, a 1,016 meters high mountain 8 km north-east of Bethel. It is the highest mountain in Samaria and one of the highest mountains in the West Bank The West Bank ( ar, الضفة الغربية, translit=aḍ-Ḍiffah al-Ġarbiyyah; he, הגדה המערבית, translit=HaGadah HaMaʽaravit, also referred to by some Israelis as ) is a landlocked territory near the coast of the Mediter .... See also * Hazor (other) Hebrew Bible places Absalom Books of Samuel {{Tanakh-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Adasa
The Battle of Adasa was fought during the Maccabean revolt on the 13th of the month Adar (late winter, equivalent to March), 161 BC at Adasa ( he, חדשה), near Beth-horon. It was a battle between the rebel Maccabees of Judas Maccabeus (Judah Maccabee) and the Seleucid Empire, whose army was led by Nicanor. The Maccabees won the battle after killing Nicanor early in the fighting. The battle came after a period of political maneuvering over several months where the peace deal established a year earlier by Lysias was tested by new High Priest Alcimus, new military governor Nicanor, and Maccabee leader Judas Maccabeus. The date of the battle in the Hebrew calendar, 13 Adar, was celebrated as ''Yom Nicanor'' (Day of Nicanor) to commemorate the victory. Primary sources Nicanor's military governance of Judea, the Battle of Caphar-salama, and the Battle of Adasa are recorded in the book of 1 Maccabees (), the book of 2 Maccabees (, ), and in Josephus's ''Antiquities of the Jews' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
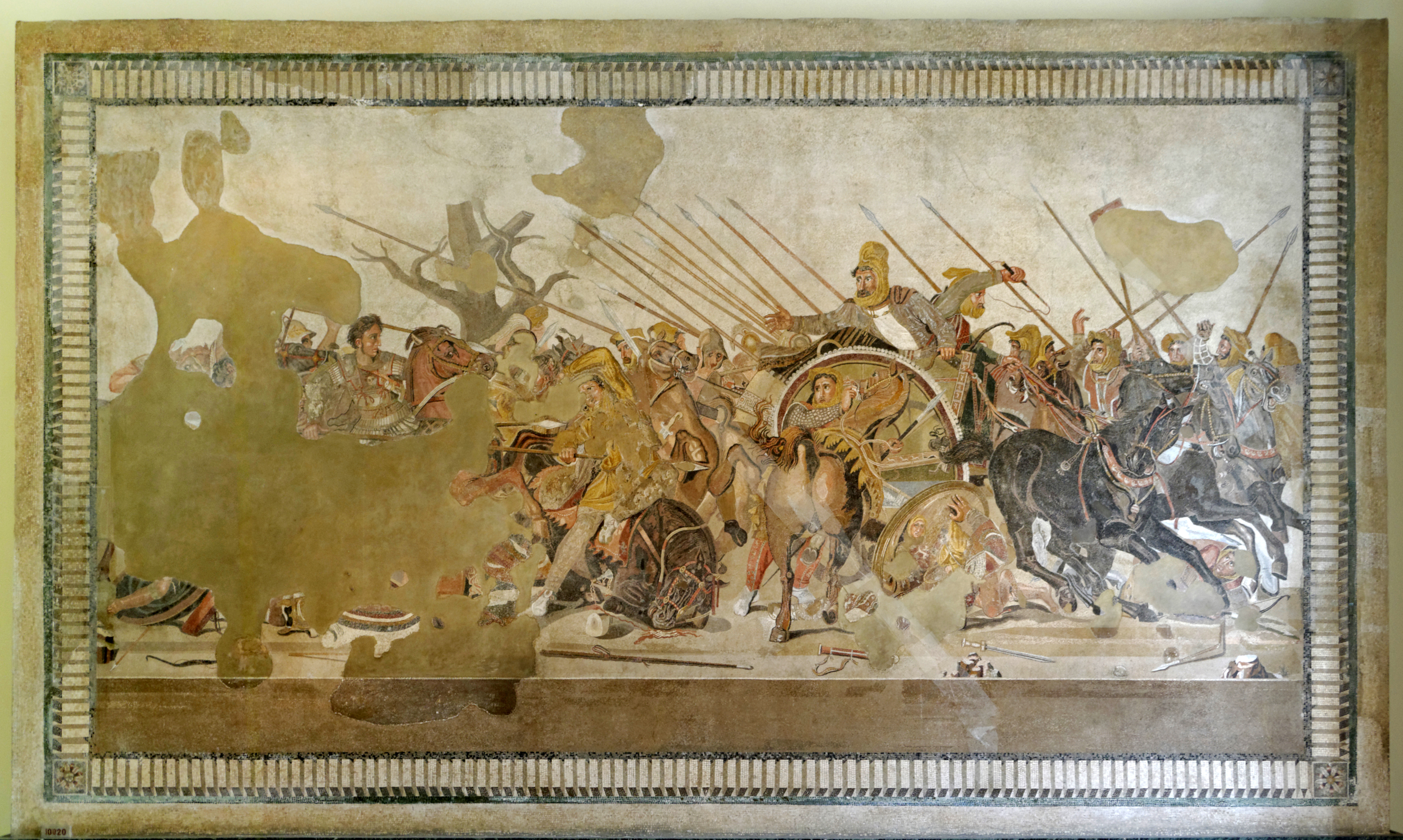
Companion Cavalry
The Companions ( el, , ''hetairoi'') were the elite cavalry of the Macedonian army from the time of king Philip II of Macedon, achieving their greatest prestige under Alexander the Great, and regarded as the first or among the first shock cavalry used in Europe. Chosen Companions, or Hetairoi, formed the elite guard of the king (Somatophylakes). Etymology The name of the military unit derives from Greek ''Hetairoi'', those near the king. The Hetairoi (Companions) could be members of the Macedonian aristocracy or commoners of any origin who enjoyed the trust and friendship of the Macedonian regent. The Hetairideia, a festival pertaining to the sacred relationship which bound the king and his companions together was celebrated and even Euripides, the famed Athenian playwright, was honoured as an ''hetairos'' of the king Archelaus. The Royal friends ( Philoi) or the king's Companions (basilikoi hetairoi) were named for life by the king among the Macedonian aristocracy. Uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sling (weapon)
A sling is a projectile weapon typically used to throw a blunt projectile such as a stone, clay, or lead " sling-bullet". It is also known as the shepherd's sling or slingshot (in British English). Someone who specializes in using slings is called a slinger. A sling has a small cradle or ''pouch'' in the middle of two retention cords. A projectile is placed in the pouch. There is a loop on the end of one side of the retention cords. Depending on the design of the sling, either the middle finger or the wrist is placed through a loop on the end of one cord, and a tab at the end of the other cord is placed between the thumb and forefinger. The sling is swung in an arc, and the tab released at a precise moment. This action releases the projectile to fly to the target. The sling is much more than merely an extension of a human arm. By its double-pendulum kinetics, the sling enables stones (or spears) to be thrown much further than they could be by hand alone. The sling is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archery
Archery is the sport, practice, or skill of using a bow to shoot arrows.Paterson ''Encyclopaedia of Archery'' p. 17 The word comes from the Latin ''arcus'', meaning bow. Historically, archery has been used for hunting and combat. In modern times, it is mainly a competitive sport and recreational activity. A person who practices archery is typically called an archer, bowman, or toxophilite. History Origins and ancient archery The oldest known evidence of the bow and arrow comes from South African sites such as Sibudu Cave, where the remains of bone and stone arrowheads have been found dating approximately 72,000 to 60,000 years ago.Backwell L, d'Errico F, Wadley L.(2008). Middle Stone Age bone tools from the Howiesons Poort layers, Sibudu Cave, South Africa. Journal of Archaeological Science, 35:1566–1580. Backwell L, Bradfield J, Carlson KJ, Jashashvili T, Wadley L, d'Errico F.(2018). The antiquity of bow-and-arrow technology: evidence from Middle Stone Age laye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phalanx
The phalanx ( grc, φάλαγξ; plural phalanxes or phalanges, , ) was a rectangular mass military formation, usually composed entirely of heavy infantry armed with spears, pikes, sarissas, or similar pole weapons. The term is particularly used to describe the use of this formation in ancient Greek warfare, although the ancient Greek writers used it to also describe any massed infantry formation, regardless of its equipment. Arrian uses the term in his ''Array against the Alans'' when he refers to his legions. In Greek texts, the phalanx may be deployed for battle, on the march, or even camped, thus describing the mass of infantry or cavalry that would deploy in line during battle. They marched forward as one entity. The term itself, as used today, does not refer to a distinctive military unit or division (e.g., the Roman legion or the contemporary Western-type battalion), but to the type of formation of an army's troops. Therefore, this term does not indicate a standar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Bireh
Al-Bireh, al-Birah, or el-Bira ( ar, البيرة; also known historically as Castrum Mahomeria, Magna Mahomeria, Mahomeria Major, Birra, or Beirothah) is a Palestinian city in the central West Bank, north of Jerusalem. It is the capital of the Ramallah and al-Bireh Governorate of the State of Palestine. It is situated on the central ridge running through the West Bank and is above sea level, covering an area of . Al-Bireh is under the administration of the Palestinian National Authority (as part of Area A). Because of its location Al-Bireh served as an economic crossroad between the north and south, along the caravan route between Jerusalem and Nablus. According to the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics (PCBS), the city had a population of approximately 39,202 in the 2007 census. In 1114, the gift was re-confirmed by Baldwin I of Jerusalem. In 1156, 92 people from ''Mahomeria'' pledged their allegiance to the Church of the Holy Sepulchre, and a further 50 names were add ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
