|
Bathory Cave
The Bathory Cave () is a cave located just below the top of (Great Linden Hill), on the northeast side of the mountain. It is located within the Danube-Ipoly National Park and the 2nd district of Budapest. The cave gets its name from Pauline monk, László Báthory who used the cave as a hermitage for twenty years. Background Geothermal springs carved the cave from Dachstein limestone probably during the Pliocene era. The upper portions of the cave extend into the Hárshegy sandstone. The cave consists of several cupola-like carved from the stone. There are horizontal passages connected by steep shafts. There are speleothem formations of various shapes and colors, and a small number of stalactites are found inside. There are formations of hematite and limonite inside the cave. Names of the cave halls and passages include the Great Stairs, Pyramid Branch, Tavas Hall, Hall of Loyalty, Hármas termi, Saint Laszlo Hall, Dome Hall, Triple Hall, Small-Staircase, Y-branch, Vorte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buda Hills
The Buda Hills ( Hungarian: ''Budai-hegység'') are a low mountain range of numerous hills which dot the Buda side of Budapest, capital of Hungary. The most famous ones located within city limits are Gellért Hill, Castle Hill, Rózsadomb, , János Hill, and Eagle Hill. These hills consist of both nature and residential areas. Geology The Budaörs dolomite of Anisian-Carnian age (Triassic period) is the oldest formation which crops out in the Buda Hills. Younger Triassic succession is composed of cherty dolomite and limestone (basin facies), and dolomite combined with limestone (platform facies). The Trassic surface is composed of karstified carbonates, which are overlain by an Upper Eocene succession made of conglomerate beds. During the period from the terminal Cretaceous to Priabonian, the area was a karstic terrestrial environment displaying distinct relief differences. It was also the time when Triassic formations were eroded. The continental period (ended by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
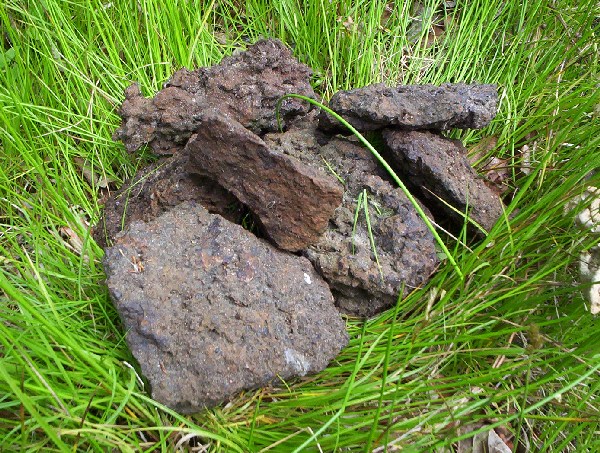
Limonite
Limonite () is an iron ore consisting of a mixture of hydrated iron(III) oxide-hydroxides in varying composition. The generic formula is frequently written as FeO(OH)·H2O, although this is not entirely accurate as the ratio of oxide to hydroxide can vary quite widely. Limonite is one of the three principal iron ores, the others being hematite and magnetite, and has been mined for the production of iron since at least 2500 BP. Names Limonite is named for the Greek word λειμών (/leː.mɔ̌ːn/), meaning "wet meadow", or λίμνη (/lím.nɛː/), meaning “marshy lake” as an allusion to its occurrence as '' bog iron ore'' in meadows and marshes. In its brown form it is sometimes called brown hematite or brown iron ore. Characteristics Limonite is relatively dense with a specific gravity varying from 2.7 to 4.3.Northrop, Stuart A. (1959) "Limonite" ''Minerals of New Mexico'' (revised edition) University of New Mexico Press, Albuquerque, New Mexico, pp. 329–333, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In Hungary
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2nd District Of Budapest
The 2nd district of Budapest is a district of Budapest, Hungary. It has an area of 36.34 km² and is situated to the south of the 3rd district and to the north of the 1st district and the 12th district. Notable places * Széll Kálmán tér, one of the city's biggest transport interchanges. * Mammut shopping centre * Central Statistical Office Library, one of the largest public libraries in Budapest * Millenáris Park * Church of Our Lady of Sarlós, a historic Roman Catholic church built in the 18th century Politics The current mayor of II. District of Budapest is Gergely Örsi (MSZP). The District Assembly, elected at the 2019 local government elections, is made up of 21 members (1 Mayor, 14 Individual constituencies MEPs and 6 Compensation List MEPs) divided into this political parties and alliances: List of mayors Twin towns ''2nd district of Budapest is twinned with:'' * Tököl, Hungary * Mosbach, Germany * Żoliborz of Warsaw, Poland * Grottaz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Budapest
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population of 1,752,286 over a land area of about . Budapest, which is both a city and county, forms the centre of the Budapest metropolitan area, which has an area of and a population of 3,303,786; it is a primate city, constituting 33% of the population of Hungary. The history of Budapest began when an early Celtic settlement transformed into the Roman town of Aquincum, the capital of Lower Pannonia. The Hungarians arrived in the territory in the late 9th century, but the area was pillaged by the Mongols in 1241–42. Re-established Buda became one of the centres of Renaissance humanist culture by the 15th century. The Battle of Mohács, in 1526, was followed by nearly 150 years of Ottoman rule. After the reconquest of Buda in 1686, the region en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Budapest Children's Railway
The Gyermekvasút ( en, Children's Railway) or Line 7 is a narrow gauge railway line in Budapest, which connects and Hűvösvölgy and is long. The former name of the line was ''Úttörővasút'' (''Pioneer Railway'', in reference to the communist scouts), and now the official designation is ''MÁV Zrt. Széchenyi-hegy Gyermekvasút''. Except the train driver, all of the posts are operated by children aged 10–14 under adult supervision. It is the world's largest children's railway. The Széchenyihegy terminus of the Gyermekvasút is a walk from the upper terminus of the Budapest Cog Railway, whilst the Hűvösvölgy terminus is adjacent to the Budapest tram terminus of the same name. History In 1947, the Hungarian State Railways (MÁV) company decided that a railway operated by children would be built. For the railway construction several sites were considered, including the neighbourhood of the Gödöllő Palace, Margaret Island, and the Népliget Népliget or Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermitage (religious Retreat)
A hermitage most authentically refers to a place where a hermit lives in seclusion from the world, or a building or settlement where a person or a group of people lived religiously, in seclusion. Particularly as a name or part of the name of properties its meaning is often imprecise, harking to a distant period of local history, components of the building material, or recalling any former sanctuary or holy place. Secondary churches or establishments run from a monastery were often called "hermitages". In the 18th century, some owners of English country houses adorned their gardens with a "hermitage", sometimes a Gothic ruin, but sometimes, as at Painshill Park, a romantic hut which a "hermit" was recruited to occupy. The so-called Ermita de San Pelayo y San Isidoro is the ruins of a Romanesque church of Ávila, Spain that ended up several hundred miles away, to feature in the Buen Retiro Park in Madrid. Western Christian tradition A hermitage is any type of domestic dwelli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monastery Of St Lawrence At Buda
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone (hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer which may be a chapel, church, or temple, and may also serve as an oratory, or in the case of communities anything from a single building housing only one senior and two or three junior monks or nuns, to vast complexes and estates housing tens or hundreds. A monastery complex typically comprises a number of buildings which include a church, dormitory, cloister, refectory, library, balneary and infirmary, and outlying granges. Depending on the location, the monastic order and the occupation of its inhabitants, the complex may also include a wide range of buildings that facilitate self-sufficiency and service to the community. These may include a hospice, a school, and a range of agricultural and manufacturing buildings such as a barn, a forge, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Deer
The red deer (''Cervus elaphus'') is one of the largest deer species. A male red deer is called a stag or hart, and a female is called a hind. The red deer inhabits most of Europe, the Caucasus Mountains region, Anatolia, Iran, and parts of western Asia. It also inhabits the Atlas Mountains of Northern Africa; its early ancestors are thought to have crossed over to Morocco, then to Algeria, Libya and Tunisia via the Strait of Gibraltar, becoming the only species of true deer (Cervidae) to inhabit Africa. Red deer have been introduced to other areas, including Australia, New Zealand, the United States, Canada, Peru, Uruguay, Chile and Argentina. In many parts of the world, the meat (venison) from red deer is used as a food source. Red deer are ruminants, characterized by a four-chambered stomach. Genetics, Genetic evidence indicates that the red deer, as traditionally defined, is a species group, rather than a single species, though exactly how many species the group includes rem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woolly Rhinoceros
The woolly rhinoceros (''Coelodonta antiquitatis'') is an extinct species of rhinoceros that was common throughout Europe and Asia during the Pleistocene epoch and survived until the end of the last glacial period. The woolly rhinoceros was a member of the Pleistocene megafauna. The woolly rhinoceros was covered with long, thick hair that allowed it to survive in the extremely cold, harsh mammoth steppe. It had a massive hump reaching from its shoulder and fed mainly on herbaceous plants that grew in the steppe. Mummified carcasses preserved in permafrost and many bone remains of woolly rhinoceroses have been found. Images of woolly rhinoceroses are found among cave paintings in Europe and Asia. Taxonomy Woolly rhinoceros remains have been known long before the species was described, and were the basis for some mythical creatures. Native peoples of Siberia believed their horns were the claws of giant birds. A rhinoceros skull was found in Kl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of settlement. It began about 12,000 years ago when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East, and later in other parts of the world. The Neolithic lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BC), marked by the development of metallurgy, leading up to the Bronze Age and Iron Age. In other places the Neolithic followed the Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age) and then lasted until later. In Ancient Egypt, the Neolithic lasted until the Protodynastic period, 3150 BC.Karin Sowada and Peter Grave. Egypt in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)






