|
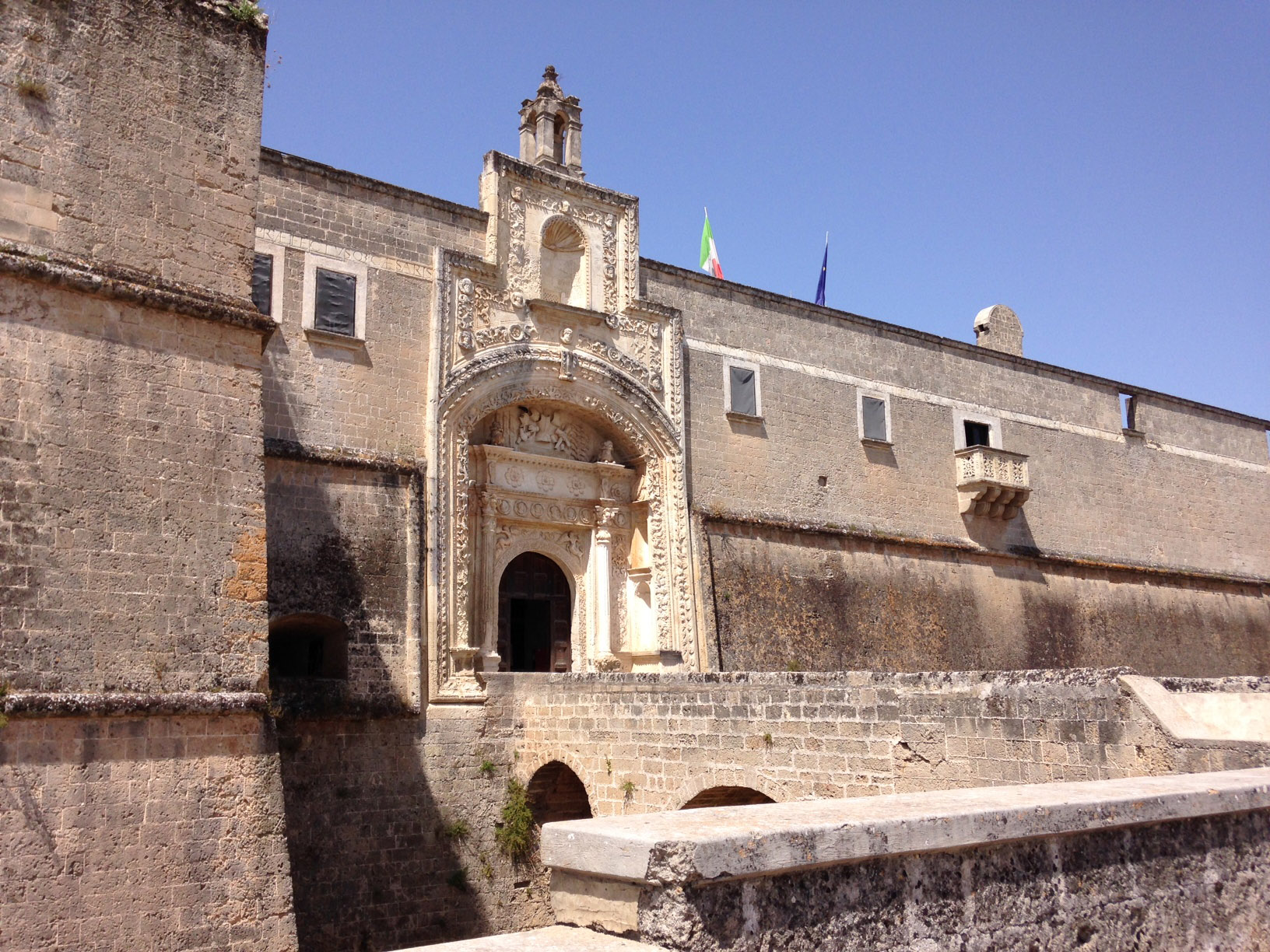
Bastion Of San Salvatore
A bastion or bulwark is a structure projecting outward from the curtain wall of a fortification, most commonly angular in shape and positioned at the corners of the fort. The fully developed bastion consists of two faces and two flanks, with fire from the flanks being able to protect the curtain wall and the adjacent bastions. Compared with the medieval fortified towers they replaced, bastion fortifications offered a greater degree of passive resistance and more scope for ranged defence in the age of gunpowder artillery. As military architecture, the bastion is one element in the style of fortification dominant from the mid 16th to mid 19th centuries. Evolution By the middle of the 15th century, artillery pieces had become powerful enough to make the traditional medieval round tower and curtain wall obsolete. This was exemplified by the campaigns of Charles VII of France who reduced the towns and castles held by the English during the latter stages of the Hundred Years Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bastion (PSF)
A bastion or bulwark is a structure projecting outward from the Curtain wall (fortification), curtain wall of a fortification, most commonly angular in shape and positioned at the corners of the fort. The fully developed bastion consists of two faces and two flanks, with fire from the flanks being able to protect the curtain wall and the adjacent bastions. Compared with the medieval fortified towers they replaced, bastion fortifications offered a greater degree of passive resistance and more scope for ranged defence in the age of Gunpowder artillery in the Middle Ages, gunpowder artillery. As Military engineering, military architecture, the bastion is one element in the style of fortification dominant from the mid 16th to mid 19th centuries. Evolution By the middle of the 15th century, artillery pieces had become powerful enough to make the traditional medieval round tower and curtain wall obsolete. This was exemplified by Hundred Years War#Fall of Gascony, the campaigns of Cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Komárno - Castle
Komárno, ( hu, Komárom, german: Komorn, sr, Коморан, translit=Komoran), colloquially also called ''Révkomárom, Öregkomárom, Észak-Komárom'' in Hungarian; is a town in Slovakia at the confluence of the Danube and the Váh rivers. Historically it was formed by the "old town" on the left bank of Danube, present day Komárno in Slovakia, and by a "new town" on the right bank, present day Komárom in Hungary, which were historically one administrative unit. Following World War I and the Treaty of Trianon, the border of the newly created Czechoslovakia cut the historical, unified town in half, creating two new independent towns in two countries. Komárno and Komárom are connected by the Elisabeth Bridge, which used to be an official border crossing between Slovakia and Hungary until border checks were lifted due to the Schengen Area rules. In 2020, a new road bridge was opened. Komárno is Slovakia's principal port on the Danube. It is also the center of the Hungarian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
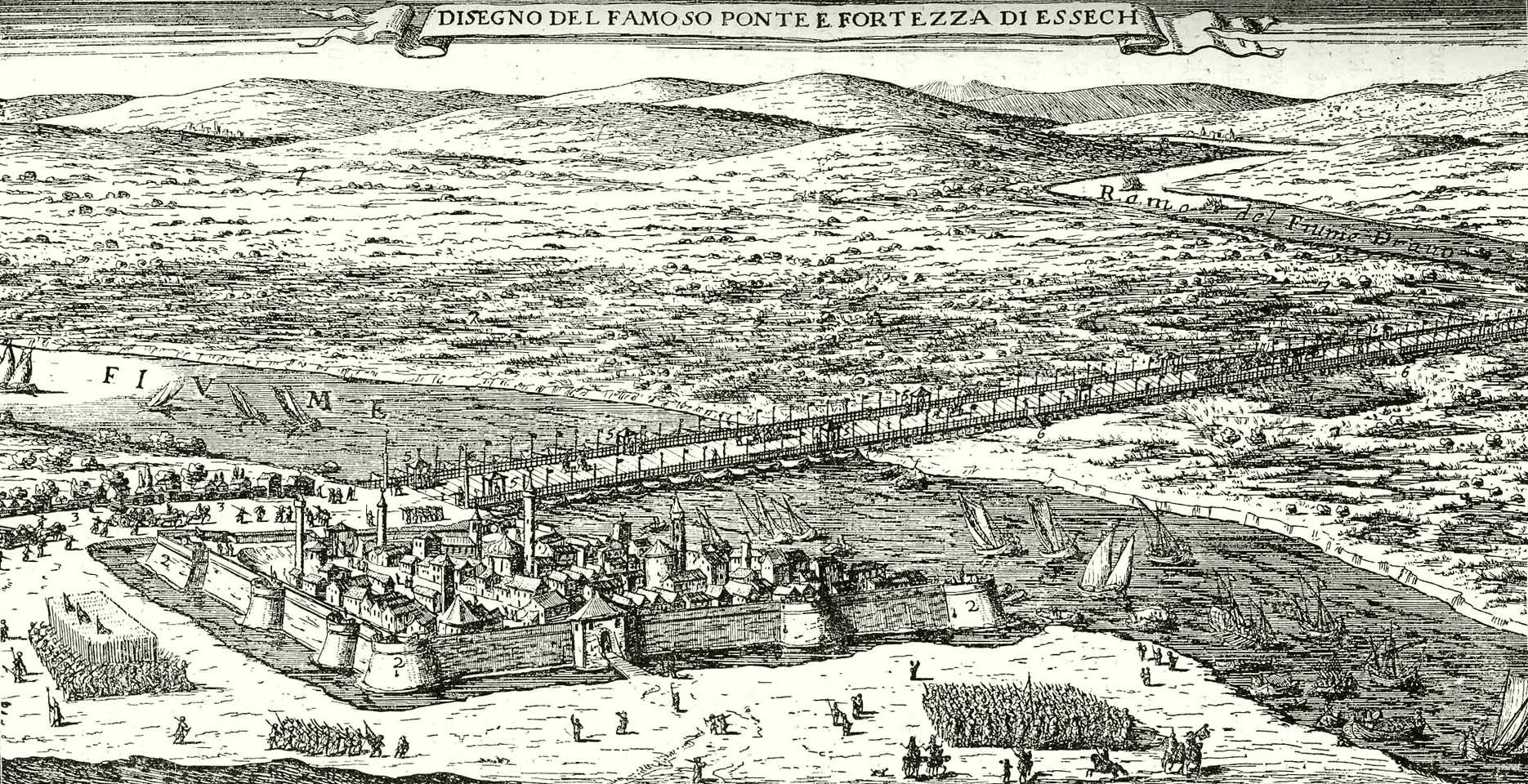
Osijek
Osijek () is the fourth-largest city in Croatia, with a population of 96,848 in 2021. It is the largest city and the economic and cultural centre of the eastern Croatian region of Slavonia, as well as the administrative centre of Osijek-Baranja County. Osijek is located on the right bank of the Drava River, upstream of its confluence with the Danube, at an elevation of . Name The name was given to the city due to its position on elevated ground, which prevented the city being flooded by the local swamp waters. Its name "Osijek" derives from the Croatian word ''oseka'', which means "ebb tide". Due to its history within the Habsburg monarchy and briefly in the Ottoman Empire, as well as the presence of German, Hungarian, and Serbian minorities throughout its history, Osijek has (or had) its names in other languages, Осек/Osek or Осијек/Osijek in Serbian, Hungarian: ''Eszék'', german: link=no, Esseg or Essegg, tr, Ösek, la, Essek. It is also spelled ''Esgek''. Its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tvrđa
Tvrđa (''Citadel'') is the old town of the city of Osijek in Croatia. It is the best-preserved and largest ensemble of Baroque buildings in Croatia and consists of a Habsburg star fort built on the right bank of the River Drava. Tvrđa has been described by the World Monuments Fund as "a unique example of an eighteenth-century baroque military, administrative, and commercial urban center". The star fort was constructed in the immediate vicinity of medieval Osijek after the defeat of the Ottoman forces in 1687, due to Osijek's strategic importance. Constructed starting in 1712 to plans by Mathias von Kaiserfeld and then Maximilian Gosseau de Henef, all five planned bastions and two gates were complete by 1715. By 1735, the inner town was finished and three northern bastions had been added. When complete, it was the largest and most advanced Habsburg fortress on the border with the Ottoman Empire, consisting of eight bastions and featuring armories, depots, a garrison headquar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geneva
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevra ; rm, Genevra is the List of cities in Switzerland, second-most populous city in Switzerland (after Zürich) and the most populous city of Romandy, the French-speaking part of Switzerland. Situated in the south west of the country, where the Rhône exits Lake Geneva, it is the capital of the Canton of Geneva, Republic and Canton of Geneva. The city of Geneva () had a population 201,818 in 2019 (Jan. estimate) within its small municipal territory of , but the Canton of Geneva (the city and its closest Swiss suburbs and exurbs) had a population of 499,480 (Jan. 2019 estimate) over , and together with the suburbs and exurbs located in the canton of Vaud and in the French Departments of France, departments of Ain and Haute-Savoie the cross-border Geneva metropolitan area as officially defined by Eurostat, which extends over ,As of 2020, the Eurostat-defined Functional Urban Area of Geneva was made up of 9 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical region. Italy is also considered part of Western Europe, and shares land borders with France, Switzerland, Austria, Slovenia and the enclaved microstates of Vatican City and San Marino. It has a territorial exclave in Switzerland, Campione. Italy covers an area of , with a population of over 60 million. It is the third-most populous member state of the European Union, the sixth-most populous country in Europe, and the tenth-largest country in the continent by land area. Italy's capital and largest city is Rome. Italy was the native place of many civilizations such as the Italic peoples and the Etruscans, while due to its central geographic location in Southern Europe and the Mediterranean, the country has also historically been home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copertino
Copertino (; historical en, Cupertino, italic=yes; scn, label=Salentino, Cupirtinu ), also known in English as Cupertino, is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Lecce in the Apulia region of south-east Italy. History Following Charles of Anjou's successful campaign in 1266, the Hohenstaufen tower of Copertino was held first by the de Pratis family and then by Walter VI of Brienne, Duke of Athens, Count of Lecce and Grand Constable of France. Copertino became the centre of a County under the Enghiens, who were sovereigns of the land of Galatone, Leverano and Veglie. With the marriage of Mary of Enghien, Countess of Lecce and Copertino (later Queen of Naples and titular Queen of Sicily, Jerusalem, and Hungary) to Raimondo del Balzo Orsini, the county became part of the principality of Taranto. The French knight Tristan Chiaromonte (de Clermont-Lodeve) led the development of the county capital, having assumed power over the territory on his marriage to Caterina, daughter of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petersberg Citadel
Petersberg Citadel (German:''Zitadelle Petersberg'') in Erfurt, central Germany, is one of the largest and best-preserved town fortresses in Europe.Stadtverwaltung Erfurt (17 November 2017) ''Petersberg'' Retrieved 23 December 2017 The citadel was built on Petersberg hill, in the north-western part of the old town centre from 1665, when Erfurt was governed by the Electorate of Mainz.Kogel, Kristina (2011). ''Erfurt an einem Tag. Ein Stadtrundgang''. Leipzig: Lehmstadt Verlag It is surrounded by over two kilometres of stone walls and is 36 hectares in size.Erfurt Tourismus & MarketinPetersberg Citadel (pdf). Retrieved 2 January 2013 Erfurt has also been ruled by Sweden, Prussia, Napoleon, the German Empire, the Nazis, and post-World War II Soviet occupying forces, and it was part of the German Democratic Republic (East Germany). All of these regimes used Petersberg Citadel and had an influence on its development. The baroque fortress was in military use until 1963.Steffen Raßloff ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castillo De San Marcos
The Castillo de San Marcos (Spanish for "St. Mark's Castle") is the oldest masonry fort in the continental United States; it is located on the western shore of Matanzas Bay in the city of St. Augustine, Florida. It was designed by the Spanish engineer Ignacio Daza, with construction beginning in 1672, 107 years after the city's founding by Spanish Admiral and conquistador Pedro Menéndez de Avilés, when Florida was part of the Spanish Empire. The fort's construction was ordered by Governor Francisco de la Guerra y de la Vega after a raid by the English privateer Robert Searles in 1668 that destroyed much of St. Augustine and damaged the existing wooden fort. Work proceeded under the administration of Guerra's successor, Manuel de Cendoya in 1671, and the first '' coquina'' stones were laid in 1672. The construction of the core of the current fortress was completed in 1695, though it would undergo many alterations and renovations over the centuries. Though built in part by bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crownwork
A crownwork is an element of the trace italienne system of fortification and is effectively an expanded hornwork (a type of outwork). It consists of a full bastion with the walls on either side ending in half bastions from which longer flank walls run back towards the main fortress. The crownwork was used to extend the fortified area in a particular direction, often in order to defend a bridge, prevent the enemy occupying an area of high ground, or simply strengthen the overall fortifications in the expected direction of attack. See also * The Kronverk The Kronverk (russian: Кронверк, from the German word for "crownwork") is a ground fortification for the Sts. Peter and Paul Fortress in Saint Petersburg, Russia. The Kronverk is situated on Petrogradsky Island, across the small island ..., St Petersburg, Russia Notes References * * {{Fortifications Fortification (architectural elements) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hornwork
A hornwork is an element of the Italian bastion system of fortification. Its face is flanked with a pair of demi-bastions. It is distinguished from a crownwork, because crownworks contain full bastions at their centers. They are both outwork An outwork is a minor fortification built or established outside the principal fortification limits, detached or semidetached. Outworks such as ravelins, lunettes (demilunes), flèches and caponiers to shield bastions and fortification curtains ...s. References Fortifications {{Fort-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorge (fortification)
A gorge in field fortification is the "unexposed side of a fieldwork", typically the rear of an independent fieldwork or detached outwork in front of the main fortress or defensive position. Outworks with open gorges Straith describes three commonly used classes of field work: "works open at the gorge, works enclosed all round and lines." He lists the following as works open at the gorge: * Redan * Lunette * Redan with flanks * Double Redan * Tenaille-head * Bastion-head Closed works are the redoubt, star fort and bastion A bastion or bulwark is a structure projecting outward from the curtain wall of a fortification, most commonly angular in shape and positioned at the corners of the fort. The fully developed bastion consists of two faces and two flanks, with fi ...ed fort. Gorges of 'half-closed works' were usually closed either by a parapet or stockade. References Literature * * * {{Fortifications Fortification (architectural elements) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)