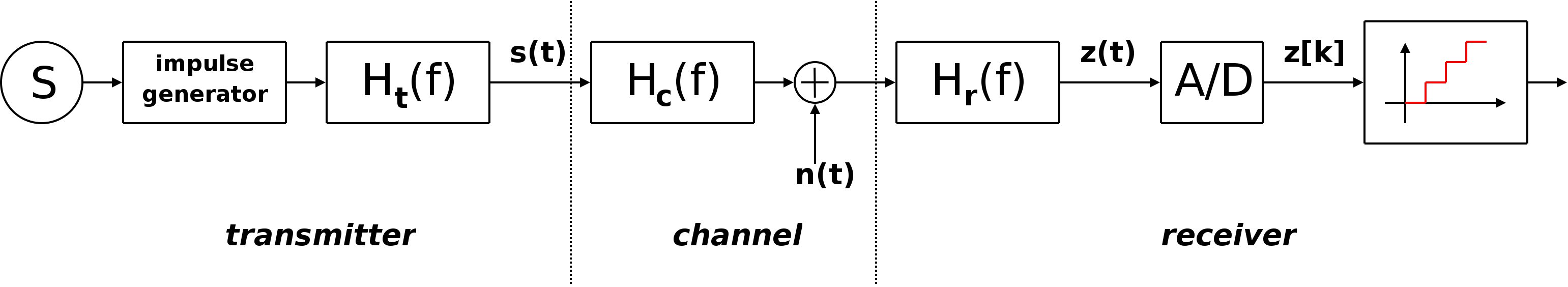
|
Baseband Signal
In telecommunications and signal processing, baseband is the range of frequencies occupied by a signal that has not been modulated to higher frequencies. Baseband signals typically originate from transducers, converting some other variable into an electrical signal. For example, the output of a microphone is a baseband signal that is an analog of the applied voice audio. In conventional analog radio broadcasting the baseband audio signal is used to modulate an RF carrier signal of a much higher frequency. A baseband signal may have frequency components going all the way down to DC, or at least it will have a high ratio bandwidth. A modulated baseband signal is called a passband signal. This occupies a higher range of frequencies and has a lower ratio and fractional bandwidth. Various uses Baseband signal A ''baseband signal'' or ''lowpass signal'' is a signal that can include frequencies that are very near zero, by comparison with its highest frequency (for example, a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bandlimited2
Bandlimiting is the limiting of a signal's frequency domain representation or spectral density to zero above a certain finite frequency. A band-limited signal is one whose Fourier transform or spectral density has bounded support. A bandlimited signal may be either random (stochastic) or non-random (deterministic). In general, infinitely many terms are required in a continuous Fourier series representation of a signal, but if a finite number of Fourier series terms can be calculated from that signal, that signal is considered to be band-limited. Sampling bandlimited signals A bandlimited signal can be fully reconstructed from its samples, provided that the sampling rate exceeds twice the maximum frequency in the bandlimited signal. This minimum sampling rate is called the Nyquist rate. This result, usually attributed to Nyquist and Shannon, is known as the Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem. An example of a simple deterministic bandlimited signal is a sinusoid of the for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Area Network
A local area network (LAN) is a computer network that interconnects computers within a limited area such as a residence, school, laboratory, university campus or office building. By contrast, a wide area network (WAN) not only covers a larger geographic distance, but also generally involves leased telecommunication circuits. Ethernet and Wi-Fi are the two most common technologies in use for local area networks. Historical network technologies include ARCNET, Token Ring and AppleTalk. History The increasing demand and usage of computers in universities and research labs in the late 1960s generated the need to provide high-speed interconnections between computer systems. A 1970 report from the Lawrence Radiation Laboratory detailing the growth of their "Octopus" network gave a good indication of the situation. A number of experimental and early commercial LAN technologies were developed in the 1970s. Cambridge Ring was developed at Cambridge University starting in 1974. Ethe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase-shift Keying
Phase-shift keying (PSK) is a digital modulation process which conveys data by changing (modulating) the phase of a constant frequency reference signal (the carrier wave). The modulation is accomplished by varying the sine and cosine inputs at a precise time. It is widely used for wireless LANs, RFID and Bluetooth communication. Any digital modulation scheme uses a finite number of distinct signals to represent digital data. PSK uses a finite number of phases, each assigned a unique pattern of binary digits. Usually, each phase encodes an equal number of bits. Each pattern of bits forms the symbol that is represented by the particular phase. The demodulator, which is designed specifically for the symbol-set used by the modulator, determines the phase of the received signal and maps it back to the symbol it represents, thus recovering the original data. This requires the receiver to be able to compare the phase of the received signal to a reference signal such a system is termed c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amplitude-shift Keying
Amplitude-shift keying (ASK) is a form of amplitude modulation that represents digital data as variations in the amplitude of a carrier wave. In an ASK system, a symbol, representing one or more bits, is sent by transmitting a fixed-amplitude carrier wave at a fixed frequency for a specific time duration. For example, if each symbol represents a single bit, then the carrier signal could be transmitted at nominal amplitude when the input value is 1, but transmitted at reduced amplitude or not at all when the input value is 0. Any digital modulation scheme uses a finite number of distinct signals to represent digital data. ASK uses a finite number of amplitudes, each assigned a unique pattern of binary digits. Usually, each amplitude encodes an equal number of bits. Each pattern of bits forms the symbol that is represented by the particular amplitude. The demodulator, which is designed specifically for the symbol-set used by the modulator, determines the amplitude of the received si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carrier Frequency
In telecommunications, a carrier wave, carrier signal, or just carrier, is a waveform (usually sinusoidal) that is modulated (modified) with an information-bearing signal for the purpose of conveying information. This carrier wave usually has a much higher frequency than the input signal does. The purpose of the carrier is usually either to transmit the information through space as an electromagnetic wave (as in radio communication), or to allow several carriers at different frequencies to share a common physical transmission medium by frequency division multiplexing (as in a cable television system). The term originated in radio communication, where the carrier wave creates the waves which carry the information (modulation) through the air from the transmitter to the receiver. The term is also used for an unmodulated emission in the absence of any modulating signal. In music production, carrier signals can be controlled by a modulating signal to change the sound property of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Navigation
A satellite navigation or satnav system is a system that uses satellites to provide autonomous geo-spatial positioning. It allows satellite navigation devices to determine their location (longitude, latitude, and altitude/elevation) to high precision (within a few centimetres to metres) using time signals transmitted along a line of sight by radio from satellites. The system can be used for providing position, navigation or for tracking the position of something fitted with a receiver (satellite tracking). The signals also allow the electronic receiver to calculate the current local time to a high precision, which allows time synchronisation. These uses are collectively known as Positioning, Navigation and Timing (PNT). One set of critical vulnerabilities in satellite communications are the signals that govern positioning, navigation and timing (PNT). Failure to properly secure these transmissions could not only disrupt satellite networks but wreak havoc on a host of dependent s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baseband Processor
A baseband processor (also known as baseband radio processor, BP, or BBP) is a device (a chip or part of a chip) in a network interface controller that manages all the radio functions (all functions that require an antenna); however, this term is generally not used in reference to Wi-Fi and Bluetooth radios. A baseband processor typically uses its own RAM and firmware. Baseband processors are typically fabricated using CMOS (complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor) or RF CMOS technology, and are widely used in radio-frequency (RF) and wireless communications. Overview Baseband processors typically run a real-time operating system (RTOS) as their firmware, such as ENEA's OSE, Nucleus RTOS (iPhone 3G/3GS/iPad), ThreadX (iPhone 4), and VRTX. There are more than a few significant manufacturers of baseband processors, including Broadcom, Icera, Intel Mobile Communications (former Infineon wireless division), MediaTek, Qualcomm, Spreadtrum, and ST-Ericsson. The rational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Line Code
In telecommunication, a line code is a pattern of voltage, current, or photons used to represent digital data transmitted down a communication channel or written to a storage medium. This repertoire of signals is usually called a constrained code in data storage systems. Some signals are more prone to error than others as the physics of the communication channel or storage medium constrains the repertoire of signals that can be used reliably. Common line encodings are unipolar, polar, bipolar, and Manchester code. Transmission and storage After line coding, the signal is put through a physical communication channel, either a transmission medium or data storage medium.Karl Paulsen"Coding for Magnetic Storage Mediums".2007. The most common physical channels are: * the line-coded signal can directly be put on a transmission line, in the form of variations of the voltage or current (often using differential signaling). * the line-coded signal (the ''baseband signal'') underg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1000BASE-SX
In computer networking, Gigabit Ethernet (GbE or 1 GigE) is the term applied to transmitting Ethernet frames at a rate of a gigabit per second. The most popular variant, 1000BASE-T, is defined by the IEEE 802.3ab standard. It came into use in 1999, and has replaced Fast Ethernet in wired local networks due to its considerable speed improvement over Fast Ethernet, as well as its use of cables and equipment that are widely available, economical, and similar to previous standards. History Ethernet was the result of research conducted at Xerox PARC in the early 1970s, and later evolved into a widely implemented physical and link layer protocol. Fast Ethernet increased the speed from 10 to 100 megabits per second (Mbit/s). Gigabit Ethernet was the next iteration, increasing the speed to 1000 Mbit/s. * The initial standard for Gigabit Ethernet was produced by the IEEE in June 1998 as IEEE 802.3z, and required optical fiber. 802.3z is commonly referred to as 1000BASE-X, whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
100BASE-TX
In computer networking, Fast Ethernet physical layers carry traffic at the nominal rate of 100 Mbit/s. The prior Ethernet speed was 10 Mbit/s. Of the Fast Ethernet physical layers, 100BASE-TX is by far the most common. Fast Ethernet was introduced in 1995 as the IEEE 802.3u standard and remained the fastest version of Ethernet for three years before the introduction of Gigabit Ethernet. The acronym ''GE/FE'' is sometimes used for devices supporting both standards. Nomenclature The "100" in the media type designation refers to the transmission speed of 100 Mbit/s, while the "BASE" refers to baseband signaling. The letter following the dash ("T" or "F") refers to the physical medium that carries the signal (twisted pair or fiber, respectively), while the last character ("X", "4", etc.) refers to the line code method used. Fast Ethernet is sometimes referred to as 100BASE-X, where "X" is a placeholder for the FX and TX variants. General design Fast Ethernet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10BASE5
10BASE5 (also known as thick Ethernet or thicknet) was the first commercially available variant of Ethernet. The technology was standardized in 1982 as IEEE 802.3. 10BASE5 uses a thick and stiff coaxial cable up to in length. Up to 100 stations can be connected to the cable using vampire taps and share a single collision domain with 10 megabit per second, Mbit/s of Bandwidth (computing), bandwidth shared among them. The system is difficult to install and maintain. 10BASE5 was superseded by much cheaper and more convenient alternatives: first by 10BASE2 based on a thinner coaxial cable, and then, once Ethernet over twisted pair was developed, by 10BASE-T and its successors 100BASE-TX and 1000BASE-T. In 2003, the IEEE 802.3 working group deprecated 10BASE5 for new installations. Name origination The name ''10BASE5'' is derived from several characteristics of the physical medium. The ''10'' refers to its transmission speed of 10 Mbit/s. The ''BASE'' is short for baseb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethernet Physical Layer
The physical-layer specifications of the Ethernet family of computer network standards are published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), which defines the electrical or optical properties and the transfer speed of the physical connection between a device and the network or between network devices. It is complemented by the MAC layer and the logical link layer. The Ethernet physical layer has evolved over its existence starting in 1980 and encompasses multiple physical media interfaces and several orders of magnitude of speed from 1 Mbit/s to 400 Gbit/s. The physical medium ranges from bulky coaxial cable to twisted pair and optical fiber with a standardized reach of up to 80 km. In general, network protocol stack software will work similarly on all physical layers. Many Ethernet adapters and Network switch, switch ports support multiple speeds by using autonegotiation to set the speed and Duplex (telecommunications), duplex for the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |