|
Base Effect (inflation)
The base effect relates to inflation in the corresponding period of the previous year, if the inflation rate was too low in the corresponding period of the previous year, even a smaller rise in the Price Index will arithmetically give a high rate of inflation now. On the other hand, if the price index had risen at a high rate in the corresponding period of the previous year and recorded high inflation rate, a similar absolute increase in the price index now will show a lower inflation rate now. An example of the base effect: :The Price Index is 100, 150, and 200 in each of three consecutive periods, called 1, 2, and 3, respectively. The increase of 50 from period 1 to period 2 gives a percentage increase of 50%, but the increase from period 2 to period 3, despite being the same as the previous increase in absolute terms, gives a percentage increase of only 33.33%. This is due to the relatively large difference in the bases on which the percentages are calculated (100 vs 150). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy. When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation corresponds to a reduction in the purchasing power of money. The opposite of inflation is deflation, a sustained decrease in the general price level of goods and services. The common measure of inflation is the inflation rate, the annualized percentage change in a general price index. As prices do not all increase at the same rate, the consumer price index (CPI) is often used for this purpose. The employment cost index is also used for wages in the United States. Most economists agree that high levels of inflation as well as hyperinflation—which have severely disruptive effects on the real economy—are caused by persistent excessive growth in the money supply. Views on low to moderate rates of inflation are more varied. Low or moderate inflation may be a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
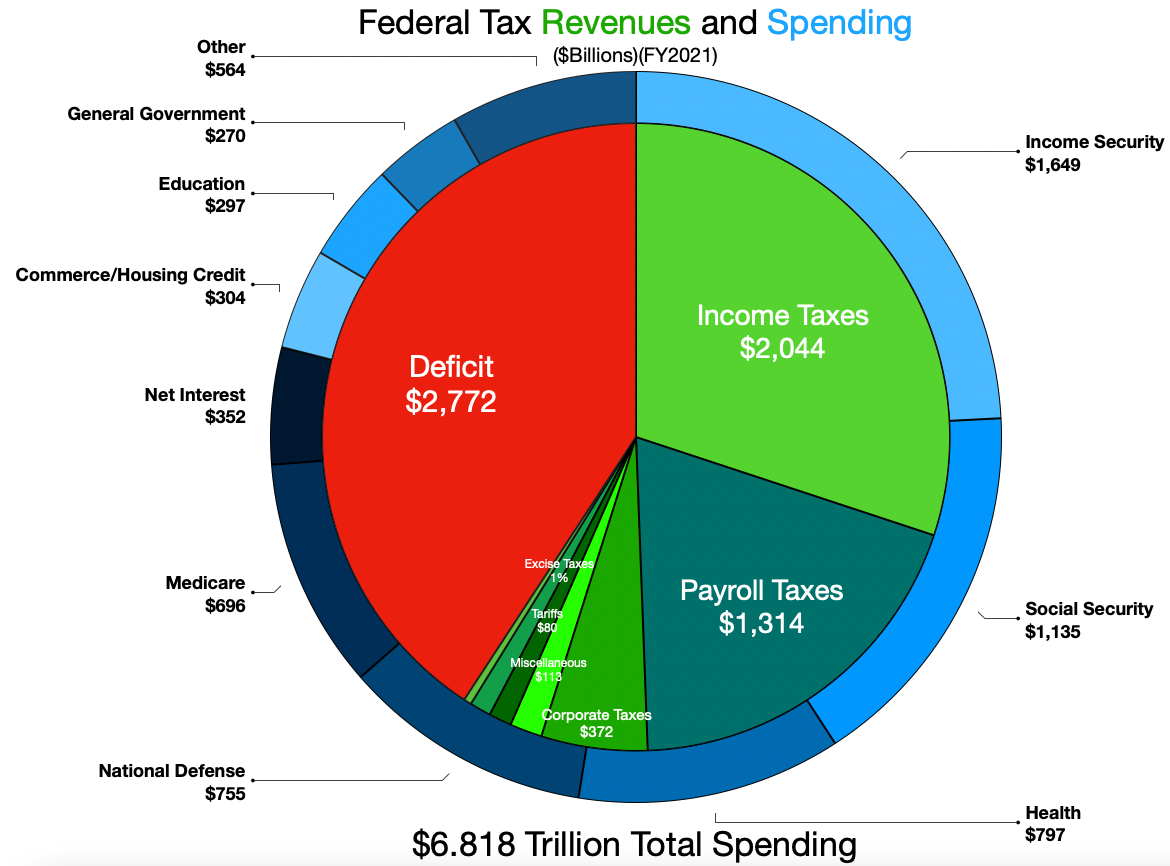
Fiscal Year
A fiscal year (or financial year, or sometimes budget year) is used in government accounting, which varies between countries, and for budget purposes. It is also used for financial reporting by businesses and other organizations. Laws in many jurisdictions require company financial reports to be prepared and published on an annual basis but generally not the reporting period to align with the calendar year (1 January to 31 December). Taxation laws generally require accounting records to be maintained and taxes calculated on an annual basis, which usually corresponds to the fiscal year used for government purposes. The calculation of tax on an annual basis is especially relevant for direct taxes, such as income tax. Many annual government fees—such as council tax and license fees, are also levied on a fiscal year basis, but others are charged on an anniversary basis. Some companies, such as Cisco Systems, end their fiscal year on the same day of the week each year: the day that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compound Annual Growth Rate
Compound annual growth rate (CAGR) is a business and investing specific term for the geometric progression ratio that provides a constant rate of return over the time period. CAGR is not an accounting term, but it is often used to describe some element of the business, for example revenue, units delivered, registered users, etc. CAGR dampens the effect of volatility of periodic returns that can render arithmetic means irrelevant. It is particularly useful to compare growth rates from various data sets of common domain such as revenue growth of companies in the same industry or sector. CAGR is equivalent to the more generic exponential growth rate when the exponential growth interval is one year. Formula CAGR is defined as: :\mathrm(t_0,t_n) = \left( \frac \right)^\frac - 1 where V(t_0) is the initial value, V(t_n) is the end value, and t_n - t_0 is the number of years. Actual or normalized values may be used for calculation as long as they retain the same mathematical propo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Path Dependence
Path dependence is a concept in economics and the social sciences, referring to processes where past events or decisions constrain later events or decisions. It can be used to refer to outcomes at a single point in time or to long-run equilibria of a process. Path dependence has been used to describe institutions, technical standards, patterns of economic or social development, organizational behavior, and more. In common usage, the phrase can imply two types of claims. The first is the broad concept that "history matters", often articulated to challenge explanations that pay insufficient attention to historical factors. This claim can be formulated simply as "the future development of an economic system is affected by the path it has traced out in the past" or "particular events in the past can have crucial effects in the future." The second is a more specific claim about how past events or decisions affect future events or decisions in significant or disproportionate ways, throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volatility Tax
The volatility tax is a mathematical finance term, formalized by hedge fund manager Mark Spitznagel, describing the effect of large investment losses (or volatility) on compound returns.Not all risk mitigation is created equal ''Pensions & Investments'', November 20, 2017 It has also been called volatility drag, volatility decay or variance drain. This is not literally a tax in the sense of a levy imposed by a government, but the mathematical difference between geometric averages compared to arithmetic averages. This difference resembles a tax due to the mathematics which impose a lower compound return when returns vary over time, compared to a simple sum of returns. This diminishment of returns is in increasing proportion to volatility, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |