|
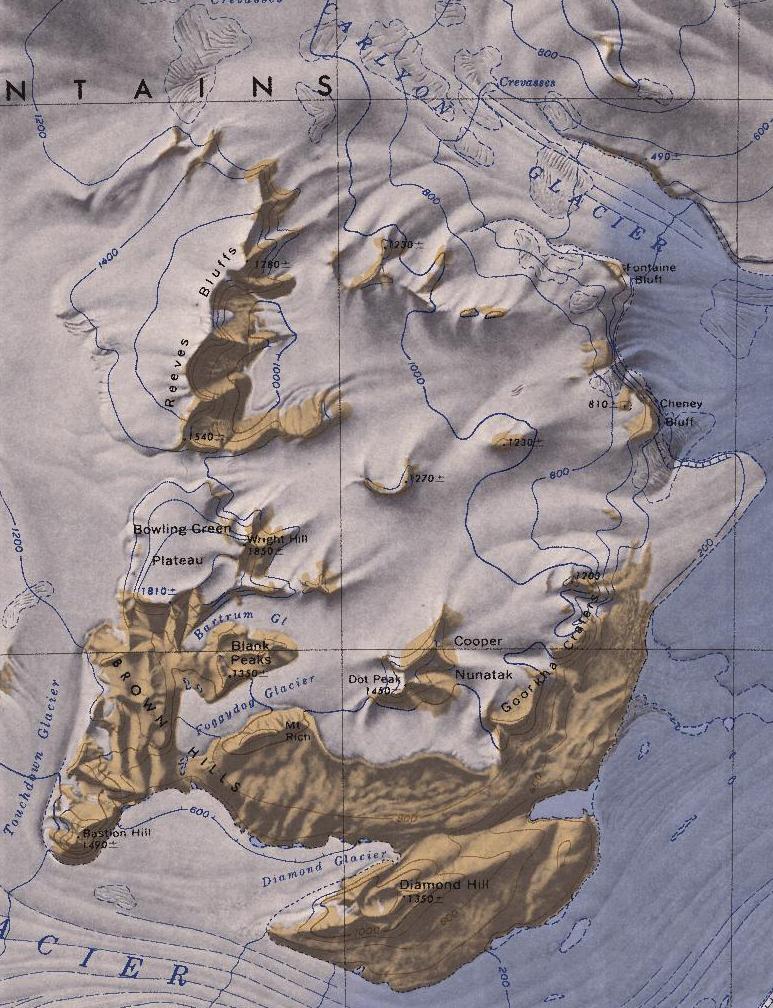
Bartrum Glacier
Bartrum Glacier () is a small steeply crevassed glacier in the Brown Hills, flowing west between Bowling Green Plateau and Blank Peaks. It was mapped by the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition (1962–63), and named after J.A. Bartrum (1885–1949), Professor of Geology at the University of Auckland, New Zealand. See also * Erewhon Basin * List of glaciers in the Antarctic * Glaciology Glaciology (; ) is the scientific study of glaciers, or more generally ice and natural phenomena that involve ice. Glaciology is an interdisciplinary Earth science that integrates geophysics, geology, physical geography, geomorphology, climato ... References * Glaciers of Oates Land {{OatesLand-glacier-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brown Hills
The Brown Hills () are a group of mainly snow-free hills in the Cook Mountains of Antarctica. Location The Brown Hills lie north of the lower reaches of Darwin Glacier. They are north of Diamond Hill and are adjacent to Diamond Glacier, a distributary of the Darwin Glacier. To the east they are bordered by the Ross Ice Shelf. On the west side, the Touchdown Glacier flows south to the Darwin Glacier between Roadend Nunatak and the Brown Hills. Reeves Bluffs are to the north of the hills. The hills were named for their color by the Darwin Glacier Party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (1956–58). Geology During glacial periods, Diamond Glacier would probably have flowed over the Brown Hills to the Ross Ice Shelf. Exposure ages of five glacial erratics from the Brown Hills range from 7,000 to 205,000 years ago, which implies that until 7,000 years ago the Brown Hills saddle was ice-covered. Simpson 2002 proposes that the Darwin calcic suite, a K-series, I-ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its Ablation#Glaciology, ablation over many years, often Century, centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as Crevasse, crevasses and Serac, seracs, as it slowly flows and deforms under stresses induced by its weight. As it moves, it abrades rock and debris from its substrate to create landforms such as cirques, moraines, or fjords. Although a glacier may flow into a body of water, it forms only on land and is distinct from the much thinner sea ice and lake ice that form on the surface of bodies of water. On Earth, 99% of glacial ice is contained within vast ice sheets (also known as "continental glaciers") in the polar regions, but glaciers may be found in mountain ranges on every continent other than the Australian mainland, including Oceania's high-latitude oceanic island countries such as New Zealand. Between lati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bowling Green Plateau
Bowling Green Plateau () is a small but prominent ice-covered plateau at the north side of the Brown Hills in the Cook Mountains in Antarctica It was named by the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition (VUWAE) (1962–63); Professor Charles C. Rich, geologist and deputy leader of the VUWAE, was affiliated with Bowling Green State University of Ohio. It is associated with the Bowling Green Col. See also *Gatson Ridge Gatson Ridge () is a jagged ridge, long with an elevation of 1158m. It runs east from the southern part of Bowling Green Plateau in the Brown Hills of the Cook Mountains, Antarctica. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names aft ... References * Plateaus of Oates Land Bowling Green State University {{OatesLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blank Peaks
Blank Peaks is a cluster of ice-free peaks occupying the isolated ridge between Bartrum and Foggydog Glacier Foggydog Glacier is a glacier between the Blank Peaks and Mount Rich in the Brown Hills of Antarctica. It was mapped by the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition (1962–63) and so named because in plan the glacier is shaped l ...s in the Brown Hills of Antarctica. Mapped by the VUWAE (1960–61) and named for H. Richard Blank, geologist with the expedition. References * Mountains of Oates Land {{OatesLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria University Of Wellington Antarctic Expedition
The Antarctic Research Centre (ARC) is part of the School of Geography, Environment and Earth Sciences at Victoria University of Wellington. Its mission is to research "Antarctic climate history and processes, and their influence on the global climate system. The current director of the Antarctic Research Centre is Associate Professor Robert McKay. Directors * 1972 - 2007: Professor Peter Barrett * 2008 - 2016: Professor Tim Naish * 2017 - 2019: Professor Andrew Mackintosh * 2020 - Present: Professor Robert McKay History In December 1957, geology students Barrie McKelvey and Peter Webb along with biologist Ron Balham conducted an expedition to the then unexplored McMurdo Dry Valleys via the Royal New Zealand Navy Antarctic support ship HMNZS ''Endeavour''. This expedition formed the basic for the annual Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expeditions, which continue to the present day. Since this first expedition, over 400 staff and students have travelled to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Auckland
, mottoeng = By natural ability and hard work , established = 1883; years ago , endowment = NZD $293 million (31 December 2021) , budget = NZD $1.281 billion (31 December 2021) , chancellor = Cecilia Tarrant , vice_chancellor = Dawn Freshwater , city = Auckland , country = New Zealand (Māori: ''Tāmaki Makaurau, Aotearoa'') , academic_staff = 2,402 (FTE, 2019) , administrative_staff = 3,567 (FTE, 2019) , students = 34,521 (EFTS, 2019) , undergrad = 25,200 (EFTS, 2019) , postgrad = 8,630 (EFTS, 2019) , type = Public flagship research university , campus = Urban,City Campus: 16 ha (40 acres)Total: 40 ha (99 acres) , free_label = Student Magazine , free = Craccum , colours = Auckland Dark Blue and White , affiliations = ACU, APAIE, APRU, Universitas 21, WUN , website Auckland.ac.nz, logo = File:University of Auckland.svg The University of Auckland is a public research university based in Auckland, New Zealand. It is the largest, most comprehen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island country by area, covering . New Zealand is about east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps, owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and then developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. In 1840, representatives of the United Kingdom and Māori chiefs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erewhon Basin
Erewhon Basin () is an extensive ice-free area in Antarctica. It forms a basin in the Brown Hills separating the snouts of Foggydog Glacier and Bartrum Glacier from the northern edge of the Darwin Glacier. It was explored by the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition), 1962–63, and named from Samuel Butler's novel ''Erewhon ''Erewhon: or, Over the Range'' () is a novel by English writer Samuel Butler, first published anonymously in 1872, set in a fictional country discovered and explored by the protagonist. The book is a satire on Victorian society. The firs ...''. References Structural basins of Antarctica Landforms of Oates Land {{OatesLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Glaciers In The Antarctic
There are many glaciers in the Antarctic. This set of lists does not include ice sheets, ice caps or ice fields, such as the Antarctic ice sheet, but includes glacial features that are defined by their flow, rather than general bodies of ice. The lists include outlet glaciers, valley glaciers, cirque glaciers, tidewater glaciers and ice streams. Ice streams are a type of glacier and many of them have "glacier" in their name, e.g. Pine Island Glacier. Ice shelves are listed separately in the List of Antarctic ice shelves. For the purposes of these lists, the Antarctic is defined as any latitude further south than 60° (the continental limit according to the Antarctic Treaty System). List by letters * List of glaciers in the Antarctic: A–H * List of glaciers in the Antarctic: I–Z See also * List of Antarctic and subantarctic islands * List of Antarctic ice rises * List of Antarctic ice shelves * List of Antarctic ice streams * List of glaciers * List of subantar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaciology
Glaciology (; ) is the scientific study of glaciers, or more generally ice and natural phenomena that involve ice. Glaciology is an interdisciplinary Earth science that integrates geophysics, geology, physical geography, geomorphology, climatology, meteorology, hydrology, biology, and ecology. The impact of glaciers on people includes the fields of human geography and anthropology. The discoveries of water ice on the Moon, Mars, Europa and Pluto add an extraterrestrial component to the field, which is referred to as "astroglaciology". Overview A glacier is an extended mass of ice formed from snow falling and accumulating over a long period of time; glaciers move very slowly, either descending from high mountains, as in valley glaciers, or moving outward from centers of accumulation, as in continental glaciers. Areas of study within glaciology include glacial history and the reconstruction of past glaciation. A glaciologist is a person who studies glaciers. A glacial geologist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |