|
Bartonella Apis
''Bartonella apis'' is a bacterium from the genus ''Bartonella''. ''Bartonella apis'' was first isolated from the gut of the honey bee (''Apis mellifera'') in 2015 by Swiss researchers at the University of Lausanne. To date, it has been found only as a gut symbiont of honey bees, including the Western honey bee (''Apis mellifera''), and the Eastern or Asiatic honey bee (''Apis cerana''). Phylogeny and characteristics ''Bartonella apis'' is a member of the order Rhizobiales and class Alphaproteobacteria. Phylogenetically, it places in the genus Bartonella through 16s rRNA genetic homology, with its nearest relative being ''Bartonella tamiae'', a human pathogen isolated initially from three patients in Thailand and an uncultured ''Bartonella'' species isolated from an ant. Like other ''Bartonellae'', ''B. apis'' is a small (1.2 to 1.8 um), gram negative rod shaped organism. Transmission Electron Microscopy revealed hair like structures on the cellular envelope as well as suspe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LPSN
List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) is an online database that maintains information on the naming and taxonomy of prokaryotes, following the taxonomy requirements and rulings of the International Code of Nomenclature of Prokaryotes The International Code of Nomenclature of Prokaryotes (ICNP) formerly the International Code of Nomenclature of Bacteria (ICNB) or Bacteriological Code (BC) governs the scientific names for Bacteria and Archaea.P. H. A. Sneath, 2003. A short hist .... The database was curated from 1997 to June 2013 by Jean P. Euzéby. From July 2013 to January 2020, LPSN was curated by Aidan C. Parte. In February 2020, a new version of LPSN was published as a service of the Leibniz Institute DSMZ, thereby also integrating the Prokaryotic Nomenclature Up-to-date service. References External links List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bartonella
''Bartonella'' is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria. It is the only genus in the family Bartonellaceae. Facultative intracellular parasites, ''Bartonella'' species can infect healthy people, but are considered especially important as opportunistic pathogens. ''Bartonella'' species are transmitted by vectors such as ticks, fleas, sand flies, and mosquitoes. At least eight ''Bartonella'' species or subspecies are known to infect humans. ''Bartonella henselae'' is the organism responsible for cat scratch disease. History ''Bartonella'' species have been infecting humans for thousands of years, as demonstrated by ''Bartonella quintana'' DNA in a 4000-year-old tooth. The genus is named for Alberto Leonardo Barton Thompson (1871–October 26, 1950), a Peruvian scientist. Infection cycle The currently accepted model explaining the infection cycle holds that the transmitting vectors are blood-sucking arthropods and the reservoir hosts are mammals. Immediately after infection, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Honey Bee
The western honey bee or European honey bee (''Apis mellifera'') is the most common of the 7–12 species of honey bees worldwide. The genus name ''Apis'' is Latin for "bee", and ''mellifera'' is the Latin for "honey-bearing" or "honey carrying", referring to the species' production of honey. Like all honey bee species, the western honey bee is eusocial, creating colonies with a single fertile female (or "queen"), many normally non-reproductive females or "workers", and a small proportion of fertile males or " drones". Individual colonies can house tens of thousands of bees. Colony activities are organized by complex communication between individuals, through both pheromones and the dance language. The western honey bee was one of the first domesticated insects, and it is the primary species maintained by beekeepers to this day for both its honey production and pollination activities. With human assistance, the western honey bee now occupies every continent except Antarctica. W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apis Cerana
''Apis cerana'', the eastern honey bee, Asiatic honey bee or Asian honey bee, is a species of honey bee native to South, Southeast and East Asia. This species is the sister species of ''Apis koschevnikovi'' and both are in the same subgenus as the western (European) honey bee, ''Apis mellifera''. Engel, M.S. (1999) The taxonomy of recent and fossil honey bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae: ''Apis''). ''Journal of Hymenoptera Research'' 8: pp. 165–196. ''A. cerana'' is known to live sympatrically along with ''Apis koschevnikovi'' within the same geographic location. ''Apis cerana'' colonies are known for building nests consisting of multiple combs in cavities containing a small entrance, presumably for defense against invasion by individuals of another nest.Nanork, P., et al. "Social parasitism by workers in queenless and queenright Apis cerana colonies." Molecular ecology 16.5 (2007): 1107-1114. The diet of this honey bee species consists mostly of pollen and nectar, or honey.Haydak, May ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphaproteobacteria
Alphaproteobacteria is a class of bacteria in the phylum Pseudomonadota (formerly Proteobacteria). The Magnetococcales and Mariprofundales are considered basal or sister to the Alphaproteobacteria. The Alphaproteobacteria are highly diverse and possess few commonalities, but nevertheless share a common ancestor. Like all ''Proteobacteria'', its members are gram-negative and some of its intracellular parasitic members lack peptidoglycan and are consequently gram variable. Characteristics The Alphaproteobacteria are a diverse taxon and comprises several phototrophic genera, several genera metabolising C1-compounds (''e.g.'', ''Methylobacterium'' spp.), symbionts of plants (''e.g.'', ''Rhizobium'' spp.), endosymbionts of arthropods (''Wolbachia'') and intracellular pathogens (''e.g. Rickettsia''). Moreover, the class is sister to the protomitochondrion, the bacterium that was engulfed by the eukaryotic ancestor and gave rise to the mitochondria, which are organelles in eukaryotic ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bartonella Henselae
''Bartonella henselae'', formerly ''Rochalimæa henselae'', is a bacterium that is the causative agent of cat-scratch disease ( bartonellosis). ''Bartonella henselae'' is a member of the genus ''Bartonella'', one of the most common types of bacteria in the world. It is a facultative intracellular microbe that targets red blood cells. One study showed it invaded the mature blood cells of humans. It infects the host cell by sticking to it using trimeric autotransporter adhesins. In the United States, about 22,000 people(per year?)are diagnosed, most under the age of 20. Most often, it is transmitted from kittens. Diagnosis ''Bartonella henselae'' is a Gram-negative rod. It can be cultured in a lysis-centrifugation blood culture. The presence of bacteria can be detected by Warthin-Starry stain, or by a similar silver stain technique performed on infected tissue. The specific name ''henselae'' honors Diane Marie Hensel (b. 1953), a clinical microbiology technologist at University ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bartonella Quintana
''Bartonella quintana'', originally known as ''Rochalimaea quintana'', and "''Rickettsia quintana''", is a bacterium transmitted by the human body louse that causes trench fever. This bacterial species caused outbreaks of trench fever affecting 1 million soldiers in Europe during World War I. Genome ''B. quintana'' had an estimated genome size of 1,700 to 2,174 kb., but the first genome sequence (of strain RM-11) contains a single circular chromosome of 1,587,646 base pairs. Background and characteristics ''B. quintana'' is a fastidious, aerobic, Gram-negative(-), pole rod-shaped (bacillus) bacterium. The infection caused by this microorganism, trench fever, was first documented in soldiers during World War I, but has now been seen Europe, Asia, and North Africa. Its primary vector is known to be ''Pediculus humanus'' variety ''corporis'', also known as the human body louse. It was first known to be isolated in axenic culture by J.W. Vinson in 1960, from a patient in Mexico Ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bartonella Bacilliformis
''Bartonella bacilliformis'' is a bacterium, Gram negative aerobic, pleomorphic, flagellated, motile, coccobacillary, 2–3 μm long, 0.2–0.5 μm wide, and a facultative intracellular bacterium. History The bacterium was discovered by Peruvian microbiologist Alberto Barton in 1905, but it was not published until 1909. Barton originally identified them as endoglobular structures, which actually were the bacteria living inside red blood cells. Until 1993, the genus ''Bartonella'' contained only one species; there are now more than 23 identified species, all of them within family Bartonellaceae. Epidemiology ''Bartonella bacilliformis'' is found only in Peru, Ecuador, and Colombia and some areas of south Florida . It is endemic in some areas of Peru, with outbreaks of the disease occurring in new epidemic areas. The bacterium is transmitted by sandflies of the genus ''Lutzomyia''. Microbiology For its isolation, special cultures are required, containing complemental soy ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
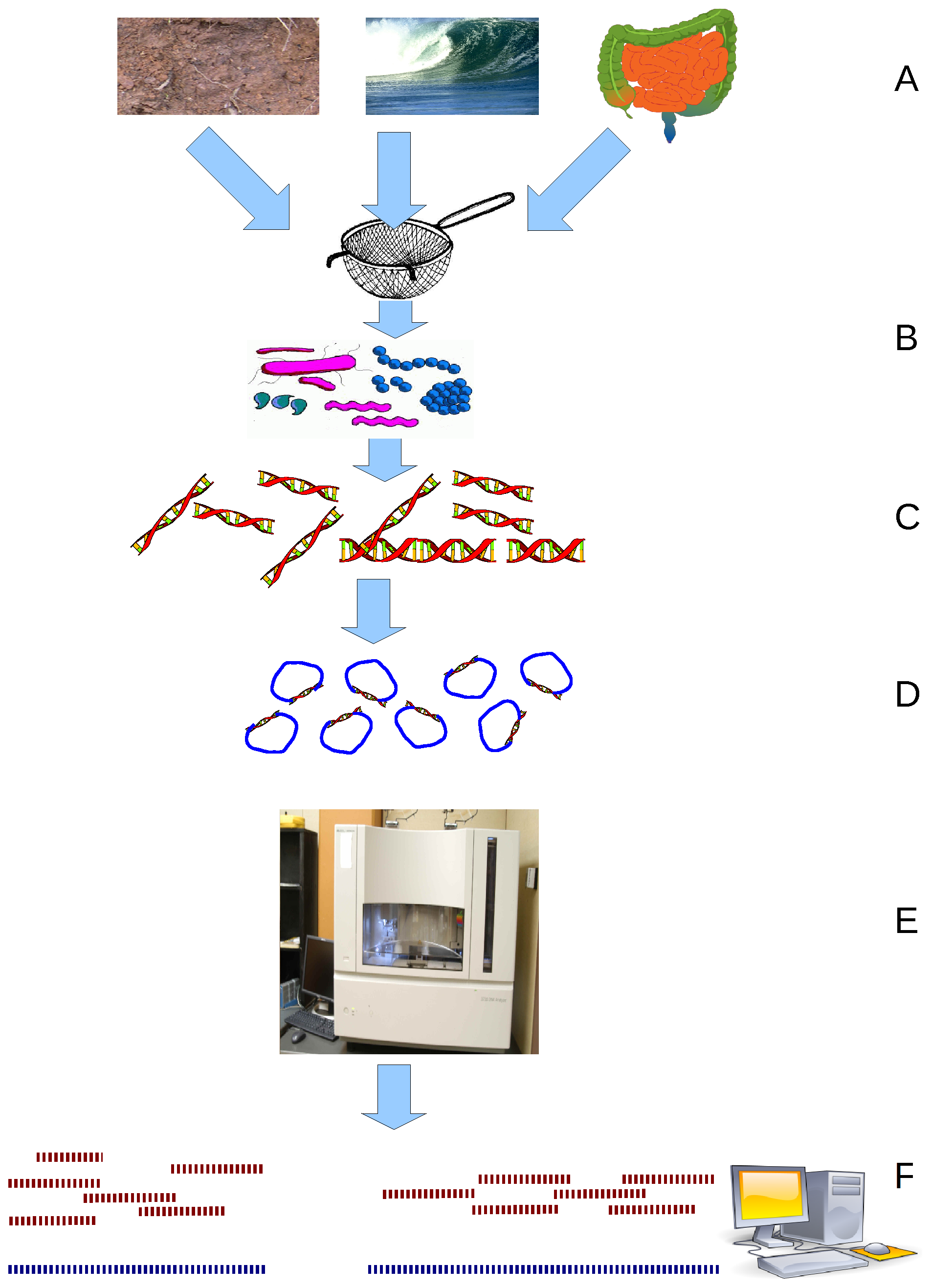
Metagenomics
Metagenomics is the study of genetic material recovered directly from environmental or clinical samples by a method called sequencing. The broad field may also be referred to as environmental genomics, ecogenomics, community genomics or microbiomics. While traditional microbiology and microbial genome sequencing and genomics rely upon cultivated clonal cultures, early environmental gene sequencing cloned specific genes (often the 16S rRNA gene) to produce a profile of diversity in a natural sample. Such work revealed that the vast majority of microbial biodiversity had been missed by cultivation-based methods. Because of its ability to reveal the previously hidden diversity of microscopic life, metagenomics offers a powerful lens for viewing the microbial world that has the potential to revolutionize understanding of the entire living world. As the price of DNA sequencing continues to fall, metagenomics now allows microbial ecology to be investigated at a much greater scale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colony Collapse Disorder
Colony collapse disorder (CCD) is an abnormal phenomenon that occurs when the majority of worker bees in a honey bee colony disappear, leaving behind a queen, plenty of food, and a few nurse bees to care for the remaining immature bees. While such disappearances have occurred sporadically throughout the history of apiculture, and have been known by various names (including disappearing disease, spring dwindle, May disease, autumn collapse, and fall dwindle disease), the syndrome was renamed colony collapse disorder in early 2007 in conjunction with a drastic rise in reports of disappearances of western honey bee (''Apis mellifera'') colonies in North America. Beekeepers in most European countries had observed a similar phenomenon since 1998, especially in Southern and Western Europe; the Northern Ireland Assembly received reports of a decline greater than 50%. The phenomenon became more global when it affected some Asian and African countries as well. Colony collapse disorder co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimicrobial Resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from the effects of antimicrobials. All classes of microbes can evolve resistance. Fungi evolve antifungal resistance. Viruses evolve antiviral resistance. Protozoa evolve antiprotozoal resistance, and bacteria evolve antibiotic resistance. Those bacteria that are considered extensively drug resistant (XDR) or totally drug-resistant (TDR) are sometimes called "superbugs".A.-P. Magiorakos, A. Srinivasan, R. B. Carey, Y. Carmeli, M. E. Falagas, C. G. Giske, S. Harbarth, J. F. Hinndler ''et al''Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria... Clinical Microbiology and Infection, Vol 8, Iss. 3 first published 27 July 2011 ia Wiley Online Library Retrieved 28 August 2020 Although antimicrobial resistance is a naturally-occurring process, it is often the result of improper usage of the drugs and management of the infections. Antibiotic resistance is a major subset o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxytetracycline
Oxytetracycline is a broad-spectrum tetracycline antibiotic, the second of the group to be discovered. Oxytetracycline works by interfering with the ability of bacteria to produce essential proteins. Without these proteins, the bacteria cannot grow, multiply and increase in numbers. Oxytetracycline therefore stops the spread of the infection and the remaining bacteria are killed by the immune system or eventually die. Oxytetracycline is a broad-spectrum antibiotic, active against a wide variety of bacteria. However, some strains of bacteria have developed resistance to this antibiotic, which has reduced its effectiveness for treating some types of infections. Oxytetracycline is used to treat infections caused by ''Chlamydia'' (e.g. the chest infection psittacosis, the eye infection trachoma, and the genital infection urethritis) and infections caused by ''Mycoplasma'' organisms (e.g. pneumonia). Oxytetracycline is also used to treat acne, due to its activity against the bact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |