|
Barrah Bint Abdul Uzza
Barrah bint Abd al-Uzza ( ar, برة بنت عبد العزى) ibn Uthman ibn Abd-al-Dar ibn Qusai ibn Kilab (of the Banu Abd ad-Dar), was the maternal grandmother of Islamic prophet Muhammad. Family The mother of Barrah was Um Habib bint Asad ibn Abd-al-Uzza ibn Qusai ibn Kilab and her father was Abdul Uzza ibn Othman ibn Abd-al-Dar ibn Qusai. Therefore, Barrah's mother and father were second cousins. Moreover, Barra was a cousin of Khadija (first wife of the Prophet Muhammad) since her mother, Um Habib, was a sister of Khadija's father, Khuwaylid ibn Asad. Furthermore, the mother of Um Habib was Barrah bint Awf ibn Abid ibn Awij ibn Adiy ibn Ka'ab ibn Lu'ay ibn Ghalib; this was the maternal grandmother of Barrah bint Abdul Uzza. See also *Family tree of Muhammad This family tree is about the relatives of the Islamic prophet Muhammad known as a family member of the family of Hashim and the Qurayshs tribe which is ‘Adnani. "The ‘arabicised or arabicising Arabs’, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prophets Of Islam
Prophets in Islam ( ar, الأنبياء في الإسلام, translit=al-ʾAnbiyāʾ fī al-ʾIslām) are individuals in Islam who are believed to spread God's message on Earth and to serve as models of ideal human behaviour. Some prophets are categorized as messengers ( ar, رسل, rusul, sing. , ), those who transmit divine revelation, most of them through the interaction of an angel. Muslims believe that many prophets existed, including many not mentioned in the Quran. The Quran states: "And for every community there is a messenger." Belief in the Islamic prophets is one of the six articles of the Islamic faith. Muslims believe that the first prophet was also the first human being, Adam, created by God. Many of the revelations delivered by the 48 prophets in Judaism and many prophets of Christianity are mentioned as such in the Quran but usually with Arabic versions of their names; for example, the Jewish Elisha is called Alyasa', Job is Ayyub, Jesus is 'Isa, etc. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khadija Bint Khuwaylid
Khadijah bint Khuwaylid ( ar, خَدِيجَة بِنْت خُوَيْلِد, Khadīja bint Khuwaylid, 555 – November 619 CE) was the first wife and is considered to be the first follower of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. Khadija was the daughter of Khuwaylid ibn Asad, a leader of the Quraysh tribe in Makkah and a successful businesswoman. Khadija is often referred to by Muslims as "The Mother of Believers". In Islam, she is an important female figure as one of the four 'ladies of heaven', alongside Asiya, Maryam, and her daughter Fatimah.Encyclopaedia of the Quran. Leidan: Brill, 2001. Print. Muhammad ibn Abdullah was monogamously married to her for 25 years. Before marrying Muhammad Family Khadija's mother, Fatima bint Za'idah, who died in 575, was a member of the Amir ibn Luayy clan of the Quraysh and a third cousin of Muhammad's mother. Khadija's father, Khuwaylid ibn Asad, was a merchant and leader. According to some accounts, he died in the Sacrilegious War, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th-century Women
The 6th century is the period from 501 through 600 in line with the Julian calendar. In the West, the century marks the end of Classical Antiquity and the beginning of the Middle Ages. The collapse of the Western Roman Empire late in the previous century left Europe fractured into many small Germanic kingdoms competing fiercely for land and wealth. From the upheaval the Franks rose to prominence and carved out a sizeable domain covering much of modern France and Germany. Meanwhile, the surviving Eastern Roman Empire began to expand under Emperor Justinian, who recaptured North Africa from the Vandals and attempted fully to recover Italy as well, in the hope of reinstating Roman control over the lands once ruled by the Western Roman Empire. In its second Golden Age, the Sassanid Empire reached the peak of its power under Khosrau I in the 6th century.Roberts, J: "History of the World.". Penguin, 1994. The classical Gupta Empire of Northern India, largely overrun by the Huna, ended in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Unknown
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Death Unknown
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year (the mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th-century Deaths
The 6th century is the period from 501 through 600 in line with the Julian calendar. In the West, the century marks the end of Classical Antiquity and the beginning of the Middle Ages. The collapse of the Western Roman Empire late in the previous century left Europe fractured into many small Germanic kingdoms competing fiercely for land and wealth. From the upheaval the Franks rose to prominence and carved out a sizeable domain covering much of modern France and Germany. Meanwhile, the surviving Eastern Roman Empire began to expand under Emperor Justinian, who recaptured North Africa from the Vandals and attempted fully to recover Italy as well, in the hope of reinstating Roman control over the lands once ruled by the Western Roman Empire. In its second Golden Age, the Sassanid Empire reached the peak of its power under Khosrau I in the 6th century.Roberts, J: "History of the World.". Penguin, 1994. The classical Gupta Empire of Northern India, largely overrun by the Huna, ended i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibn Hisham
Abū Muḥammad ʿAbd al-Malik ibn Hishām ibn Ayyūb al-Ḥimyarī al-Muʿāfirī al-Baṣrī ( ar, أبو محمد عبدالملك بن هشام ابن أيوب الحميري المعافري البصري; died 7 May 833), or Ibn Hisham, edited the biography of Islamic prophet Muhammad written by Ibn Ishaq. The ''nisba'' Al-Baṣrī means "of Basra", in modern Iraq. Life Ibn Hisham has been said to have grown up in Basra and moved afterwards to Egypt.Mustafa al-Suqa, Ibrahim al-Abyari and Abdul-Hafidh Shalabi, ''Tahqiq Sirah an-Nabawiyyah li Ibn Hisham'', ed.: Dar Ihya al-Turath, pp. 23-4. His family was native to Basra but he himself was born in Old Cairo. He gained a name as a grammarian and student of language and history in Egypt. His family was of Himyarite origin and belongs to Banu Ma‘afir tribe of Yemen. Biography of Muḥammad ''As-Sīrah an-Nabawiyyah'' (), 'The Life of the Prophet'; is an edited recension of Ibn Isḥāq's classic ''Sīratu Rasūli l-L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
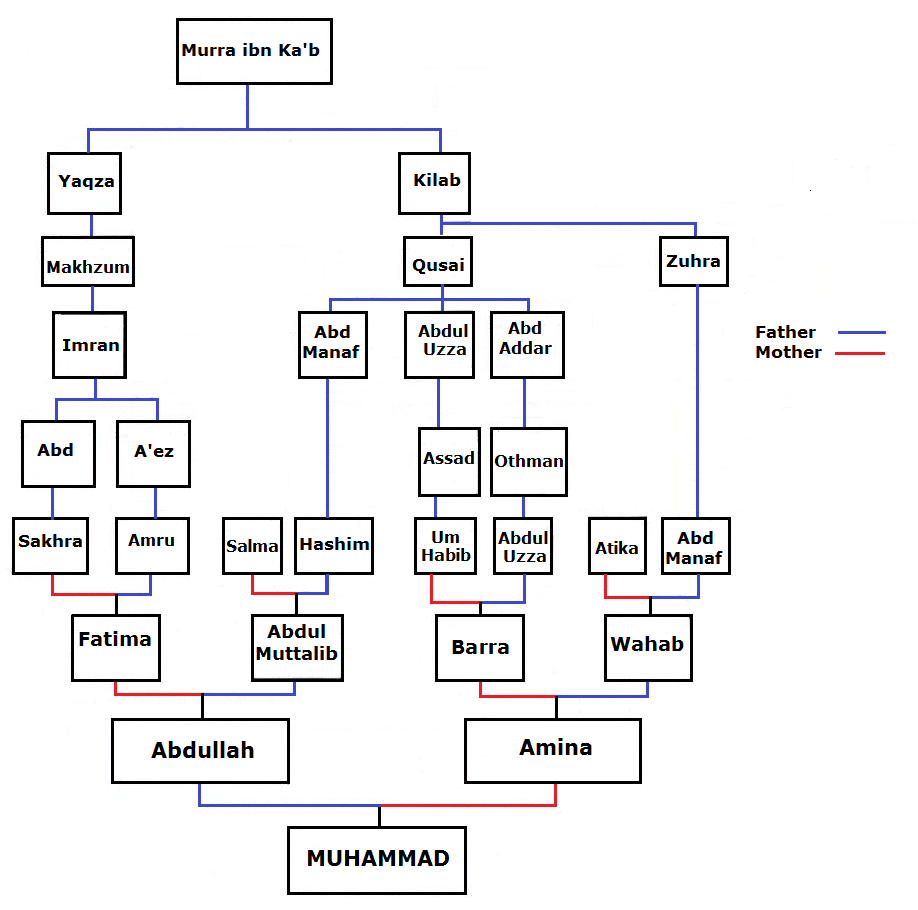
Family Tree Of Muhammad
This family tree is about the relatives of the Islamic prophet Muhammad known as a family member of the family of Hashim and the Qurayshs tribe which is ‘Adnani. "The ‘arabicised or arabicising Arabs’, on the contrary, are believed to be the descendants of Ishmael through Adnan, but in this case the genealogy does not match the Biblical line exactly. The label ‘arabicised’ is due to the belief that Ishmael spoke Hebrew until he got to Mecca, where he married a Yemeni woman and learnt Arabic. Both genealogical lines go back to Sem, son of Noah, but only Adnanites can claim Abraham as their ascendant, and the lineage of Mohammed, the Seal of Prophets (khatim al-anbiya'), can therefore be traced back to Abraham. Contemporary historiography unveiled the lack of inner coherence of this genealogical system and demonstrated that it finds insufficient matching evidence; the distinction between Qahtanites and Adnanites is even believed to be a product of the Umayyad Age, when t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lu'ay Ibn Ghalib
Lu'ayy ibn Ghalib () was an ancestor of Islamic prophet Muhammad of Arabia. He is the son of Ghalib ibn Fihr who lived in Makkah. History The tradition states that Muhammad was the son of 'Abdullah, b. 'Abdu'I-Muttalib (whose name was Shayba), b. Hashim (whose name was 'Amr), b. Abd Manaf (whose name was al-Mughira), b. Qusay (whose name was Zayd), b. Kilab, b. Murrah, b. Ka'b, b. ''Lu'ayy'', b. Ghalib, b. Fihr, b. Malik, b. al-Nadr, b. Kinana, b. Khuzayma, b. Mudrika (whose name was 'Amir), b. Ilyas , b. Mudar, b. Nizar, b. Ma'ad, b. Adnan, b. Udd (or Udad),....b. Ya'rub, b. Yashjub, b. Qedar, b. Isma'il, b. Ibrahim, the friend of the Compassionate. Ibn Ishaq's account In Ibn Ishaq's ''Biography of the Prophet Muhammad'' (as translated by Alfred Guillaume) he reports these stories: "A soothsayer Shafi' b. Kulayb al-Sadafi had come to Yemen King Tubba' and lived with him, and when he wished to bid him farewell Tubba' asked him whether he had anything of importance to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khuwaylid Ibn Asad
Khuwaylid ibn Asad ( ar, خويلد بن أسد) was a member of the Arab Banu Quraysh tribe and is recognized for being the father of Khadijah bint Khuwaylid, the wife of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. Family He was the son of Asad ibn Abd-Al-Uzza ibn Qusai ibn Kilab and a cousin of Abdul-Muttalib as his grandfather (Abd-al-Uzza ibn Qusai) and Abdul-Muttalib's grandfather ('Abd Manaf ibn Qusai) were brothers. Khuwaylid married Fatima bint Za'idah, who was a member of the Amir ibn Luayy clan of the Quraysh and a third cousin of Muhammad's mother, Aminah bint Wahb. Some of their children would become prominent people in early Islamic history And lead to an overall better Islam e.g.: *Awwam ibn Khuwaylid *Halah bint Khuwailid *Khadijah bint Khuwaylid * Hizam ibn Khuwaylid From another marriage he had a son Nawfal ibn Khuwaylid Nawfal ibn Khuwaylid ibn Asad was one of the non-Muslims who interacted with the Islamic prophet Muhammad. Biography Nawfal was the son of Khuwaylid ibn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Cousins
Most generally, in the lineal kinship system used in the English-speaking world, a cousin is a type of familial relationship in which two relatives are two or more familial generations away from their most recent common ancestor. Commonly, "cousin" refers to a first cousin – a relative of the same generation whose most recent common ancestor with the subject is a grandparent. Degrees and removals are separate measures used to more precisely describe the relationship between cousins. ''Degree'' measures the separation, in generations, from the most recent common ancestor(s) to a parent of one of the cousins (whichever is closest), while ''removal'' measures the difference in generations between the cousins themselves, relative to their most recent common ancestor(s). To illustrate usage, a second cousin is a cousin with a ''degree'' of two; there are three (not two) generations from the common ancestor(s). When the degree is not specified, first cousin is assumed. A cousin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



