|
Baron De Binder (1782 Ship)
''Baron de Binder'' (or ''Baron Bender'') was launched in 1782. She made two voyages as a slave ship in the triangular trade in enslaved people. Then in 1793, she became the privateer ''Duguay-Trouin''. After one cruise, the French Navy requisitioned her, and she served as a corvette for almost three years. The navy returned her to her owners, who sailed her as a privateer again. In 1798. the British Royal Navy captured her. Career Slave ship 1st voyage transporting enslaved people (1782–1783): Captain Daniel Deslands sailed from Saint-Malo on 31 December 1782. ''Baron de Binder'' gathered 840 captives at Cabinda and sailed from Africa on 22 July 1783. She arrived at Cap Français on 13 September with 804 captives. It is currently not clear what ''Baron de Binder'' did between her two voyages transporting enslaved people. 2nd voyage transporting enslaved people (1789–1790): On 15 June 1789, Captain Toussaint Le Forestier sailed from Saint-Malo. ''Baron de Binder'' ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of France (1814–1830)
The national flag of France (french: link=no, drapeau français) is a tricolour featuring three vertical bands coloured blue ( hoist side), white, and red. It is known to English speakers as the ''Tricolour'' (), although the flag of Ireland and others are also so known. The design was adopted after the French Revolution; while not the first tricolour, it became one of the most influential flags in history. The tricolour scheme was later adopted by many other nations in Europe and elsewhere, and, according to the '' Encyclopædia Britannica'' has historically stood "in symbolic opposition to the autocratic and clericalist royal standards of the past". Before the tricolour was adopted the royal government used many flags, the best known being a blue shield and gold fleur-de-lis (the Royal Arms of France) on a white background, or state flag. Early in the French Revolution, the Paris militia, which played a prominent role in the storming of the Bastille, wore a cockade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brest (France)
Brest (; ) is a port city in the Finistère department, Brittany. Located in a sheltered bay not far from the western tip of the peninsula, and the western extremity of metropolitan France, Brest is an important harbour and the second French military port after Toulon. The city is located on the western edge of continental France. With 142,722 inhabitants in a 2007 census, Brest forms Western Brittany's largest metropolitan area (with a population of 300,300 in total), ranking third behind only Nantes and Rennes in the whole of historic Brittany, and the 19th most populous city in France; moreover, Brest provides services to the one million inhabitants of Western Brittany. Although Brest is by far the largest city in Finistère, the ''préfecture'' (regional capital) of the department is the much smaller Quimper. During the Middle Ages, the history of Brest was the history of its castle. Then Richelieu made it a military harbour in 1631. Brest grew around its arsenal until t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
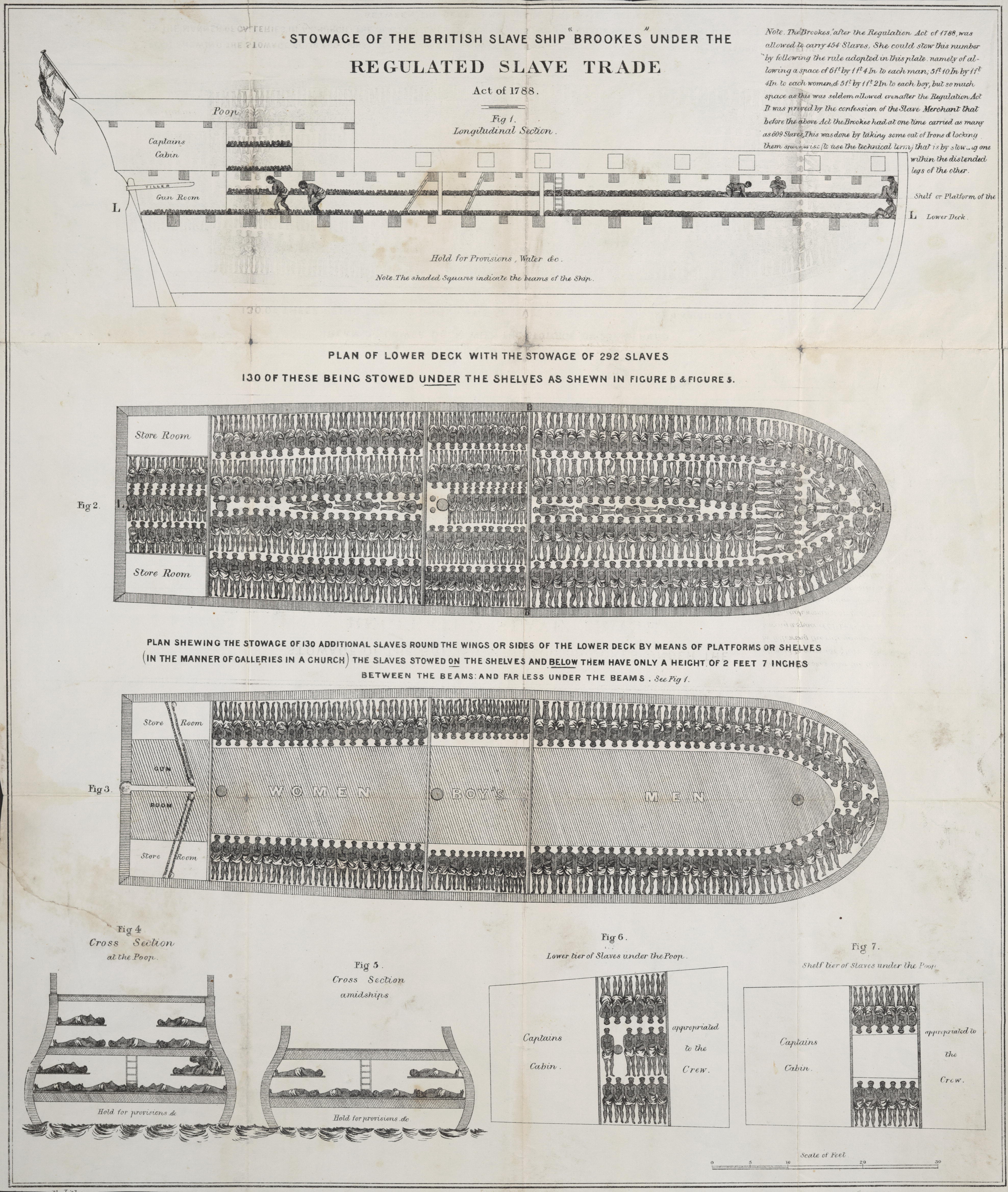
Slave Ships
Slave ships were large cargo ships specially built or converted from the 17th to the 19th century for transporting slaves. Such ships were also known as "Guineamen" because the trade involved human trafficking to and from the Guinea coast in West Africa. Atlantic slave trade In the early 1600s, more than a century after the arrival of Europeans to the Americas, demand for unpaid labor to work plantations made slave-trading a profitable business. The Atlantic slave trade peaked in the last two decades of the 18th century, during and following the Kongo Civil War. To ensure profitability, the owners of the ships divided their hulls into holds with little headroom, so they could transport as many slaves as possible. Unhygienic conditions, dehydration, dysentery and scurvy led to a high mortality rate, on average 15% and up to a third of captives. Often the ships carried hundreds of slaves, who were chained tightly to plank beds. For example, the slave ship ''Henrietta Marie'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merchant Ships Of France
A merchant is a person who trades in commodities produced by other people, especially one who trades with foreign countries. Historically, a merchant is anyone who is involved in business or trade. Merchants have operated for as long as industry, commerce, and trade have existed. In 16th-century Europe, two different terms for merchants emerged: referred to local traders (such as bakers and grocers) and ( nl, koopman) referred to merchants who operated on a global stage, importing and exporting goods over vast distances and offering added-value services such as credit and finance. The status of the merchant has varied during different periods of history and among different societies. In modern times, the term ''merchant'' has occasionally been used to refer to a businessperson or someone undertaking activities (commercial or industrial) for the purpose of generating profit, cash flow, sales, and revenue using a combination of human, financial, intellectual and physical capital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ships Built In France
A ship is a large watercraft that travels the world's oceans and other sufficiently deep waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research, and fishing. Ships are generally distinguished from boats, based on size, shape, load capacity, and purpose. Ships have supported exploration, trade, warfare, migration, colonization, and science. After the 15th century, new crops that had come from and to the Americas via the European seafarers significantly contributed to world population growth. Ship transport is responsible for the largest portion of world commerce. The word ''ship'' has meant, depending on the era and the context, either just a large vessel or specifically a ship-rigged sailing ship with three or more masts, each of which is square-rigged. As of 2016, there were more than 49,000 merchant ships, totaling almost 1.8 billion dead weight tons. Of these 28% were oil tankers, 43% were bulk carriers, and 13% were co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1782 Ships
Year 178 ( CLXXVIII) was a common year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Scipio and Rufus (or, less frequently, year 931 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 178 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Bruttia Crispina marries Commodus, and receives the title of '' Augusta''. * Emperor Marcus Aurelius and his son Commodus arrive at Carnuntum in Pannonia, and travel to the Danube to fight against the Marcomanni. Asia * Last (7th) year of ''Xiping'' era and start of ''Guanghe'' era of the Chinese Han Dynasty. * In India, the decline of the Kushan Empire begins. The Sassanides take over Central Asia. Religion * The Montanist heresy is condemned for the first time. Births * Lü Meng, Chinese general (d. 220) * Pen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roadstead
A roadstead (or ''roads'' – the earlier form) is a body of water sheltered from rip currents, spring tides, or ocean swell where ships can lie reasonably safely at anchor without dragging or snatching.United States Army technical manual, TM 5-360. Port Construction and Rehabilitation'. Washington: United States. Government Printing Office, 1964. It can be open or natural, usually estuary-based, or may be created artificially. In maritime law, it is described as a "known general station for ships, notoriously used as such, and distinguished by the name". Definition A roadstead can be an area of safe anchorage for ships waiting to enter a port, or to form a convoy. If sufficiently sheltered and convenient, it can be used for the transshipment of goods, stores, and troops, either separately or in combination. The same applies in transfers to and from shore by Lighter (barge), lighters. In the days of sailing ships, some voyages could only easily be made with a change in wind dir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Île-d'Aix
Île-d'Aix () is a commune and an island in the Charente-Maritime department, region of Nouvelle-Aquitaine (before 2015: Poitou-Charentes), off the west coast of France. It occupies the territory of the small Isle of Aix (''île d'Aix''), in the Atlantic Ocean. It is a popular place for tourist day-trips during the summer months. Location Île-d'Aix is located at the mouth of the river Charente, between Oléron Island and the coast of mainland France. The island is also close to Fort Boyard. History During the Roman period, it seems the island was connected to the continent at low tide. It finally took its current shape around 1500. In 1067, Isembert de Châtelaillon gave the island to the order of Cluny. A small convent was established, which depended on St Martin in Île de Ré. At the end of the 12th century, France and England fought for the possession of the island. Until 1286, the island was located at the boundary between the French and the English Saintonge, formed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Livre
The livre (abbreviation: £ or ₶., French for (pound)) was the currency of Kingdom of France and its predecessor state of West Francia from 781 to 1794. Several different livres existed, some concurrently. The livre was the name of coins and of units of account. History Origin and etymology The livre was established by Charlemagne as a unit of account equal to one pound of silver. It was subdivided into 20 ''sous'' (also ''sols''), each of 12 '' deniers''. The word ''livre'' came from the Latin word ''libra'', a Roman unit of weight and still the name of a pound in modern French, and the denier comes from the Roman denarius. This system and the denier itself served as the model for many of Europe's currencies, including the British pound, Italian lira, Spanish dinero and the Portuguese dinheiro. This first livre is known as the . Only deniers were initially minted, but debasement led to larger denominations being issued. Different mints in different regions used diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Builder's Old Measurement
Builder's Old Measurement (BOM, bm, OM, and o.m.) is the method used in England from approximately 1650 to 1849 for calculating the cargo capacity of a ship. It is a volumetric measurement of cubic capacity. It estimated the tonnage of a ship based on length and maximum beam (nautical), beam. It is expressed in "tons burden" ( en-em , burthen , enm , byrthen ), and abbreviated "tons bm". The formula is: : \text = \frac where: * ''Length'' is the length, in foot (length), feet, from the stem (ship), stem to the sternpost; * ''Beam (nautical), Beam'' is the maximum beam, in feet. The Builder's Old Measurement formula remained in effect until the advent of steam propulsion. Steamships required a different method of estimating tonnage, because the ratio of length to beam was larger and a significant volume of internal space was used for boilers and machinery. In 1849, the Moorsom System was created in the United Kingdom. The Moorsom system calculates the cargo-carrying capaci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Malo
Saint-Malo (, , ; Gallo: ; ) is a historic French port in Ille-et-Vilaine, Brittany, on the English Channel coast. The walled city had a long history of piracy, earning much wealth from local extortion and overseas adventures. In 1944, the Allies heavily bombarded Saint-Malo, which was garrisoned by German troops. The city changed into a popular tourist centre, with a ferry terminal serving the Channel Islands of Jersey and Guernsey, as well as the Southern English settlements of Portsmouth, Hampshire and Poole, Dorset. The famous transatlantic single-handed yacht race Route du Rhum, which takes place every four years in November, is between Saint Malo and Pointe-à-Pitre in Guadeloupe. Population The population in 2017 was 46,097 – though this can increase to up to 300,000 in the summer tourist season. With the suburbs included, the metropolitan area's population is approximately 133,000 (2017). The population of the commune more than doubled in 1967 with the merging ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cap-Haïtien
Cap-Haïtien (; ht, Kap Ayisyen; "Haitian Cape"), typically spelled Cape Haitien in English and often locally referred to as or , is a commune of about 190,000 people on the north coast of Haiti and capital of the department of Nord. Previously named ''Cap‑Français'' ( ht, Kap-Fransè; initially ''Cap-François'' ht, Kap-Franswa) and ''Cap‑Henri'' ( ht, Kap-Enri) during the rule of Henri I, it was historically nicknamed the ''Paris of the Antilles'', because of its wealth and sophistication, expressed through its architecture and artistic life. It was an important city during the colonial period, serving as the capital of the French Colony of Saint-Domingue from the city's formal foundation in 1711 until 1770 when the capital was moved to Port-au-Prince. After the Haitian Revolution, it became the capital of the Kingdom of Haiti under King Henri I until 1820. Cap-Haïtien's long history of independent thought was formed in part by its relative distance from Port-au-Pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |