|
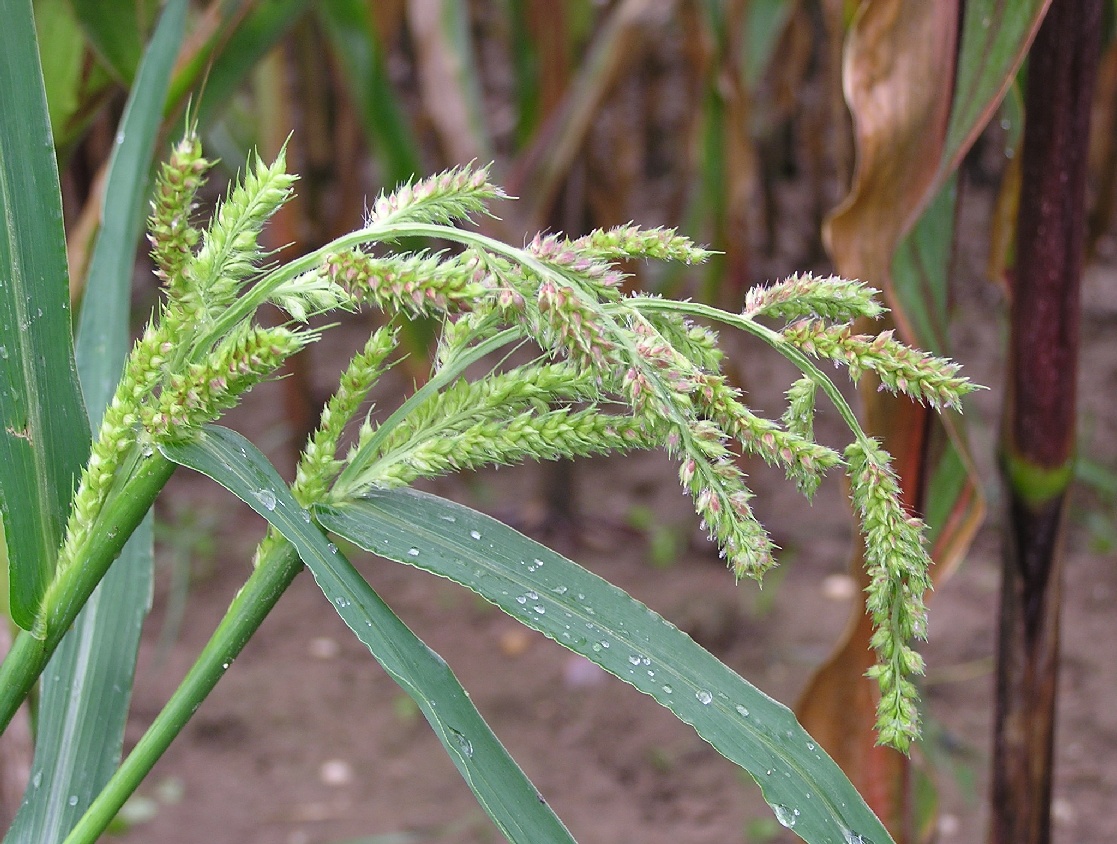
Barnyard Millet
''Echinochloa'' is a very widespread genus of plants in the grass family and tribe Paniceae. Some of the species are known by the common names barnyard grass or cockspur grass. Some of the species within this genus are millets that are grown as cereal or fodder crops. The most notable of these are Japanese millet (''E. esculenta'') in East Asia, Indian barnyard millet (''E. frumentacea'') in South Asia, and burgu millet (''E. stagnina'') in West Africa. Collectively, the members of this genus are called barnyard grasses (though this may also refer to '' E. crus-galli'' specifically), and are also known as barnyard millets or billion-dollar grasses. When not grown on purpose, these grasses may become a nuisance to farmers. In particular, common barnyard grass (''E. crus-galli'') is notorious as a weed. It is not easily suppressed with living mulches such as velvet bean (''Mucuna pruriens'' var. ''utilis''). Early barnyard grass (''E. oryzoides'') is a well-known example of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echinochloa Crus-galli
''Echinochloa crus-galli'' is a type of wild grass originating from tropical Asia that was formerly classified as a type of panicum grass. It is commonly known as cockspur (or cockspur grass), barnyard millet, Japanese millet, water grass, common barnyard grass, or simply "barnyard grass" (which may refer to any species of ''Echinochloa'' or the genus as a whole however). This plant can grow to 60" (1.5 m) in height and has long, flat leaves which are often purplish at the base. Most stems are upright, but some will spread out over the ground. Stems are flattened at the base. The seed heads are a distinctive feature, often purplish, with large millet-like seeds in crowded spikelets. Considered one of the world's worst weeds, it reduces crop yields and causes forage crops to fail by removing up to 80% of the available soil nitrogen. It acts as a host for several mosaic virus diseases.Heuzé V., Thiollet H., Tran G., Lebas F., 2017. Cockspur grass (Echinochloa crus-galli) forage. Fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echinochloa Crus-galli
''Echinochloa crus-galli'' is a type of wild grass originating from tropical Asia that was formerly classified as a type of panicum grass. It is commonly known as cockspur (or cockspur grass), barnyard millet, Japanese millet, water grass, common barnyard grass, or simply "barnyard grass" (which may refer to any species of ''Echinochloa'' or the genus as a whole however). This plant can grow to 60" (1.5 m) in height and has long, flat leaves which are often purplish at the base. Most stems are upright, but some will spread out over the ground. Stems are flattened at the base. The seed heads are a distinctive feature, often purplish, with large millet-like seeds in crowded spikelets. Considered one of the world's worst weeds, it reduces crop yields and causes forage crops to fail by removing up to 80% of the available soil nitrogen. It acts as a host for several mosaic virus diseases.Heuzé V., Thiollet H., Tran G., Lebas F., 2017. Cockspur grass (Echinochloa crus-galli) forage. Fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Reservoir
In infectious disease ecology and epidemiology, a natural reservoir, also known as a disease reservoir or a reservoir of infection, is the population of organisms or the specific environment in which an infectious pathogen naturally lives and reproduces, or upon which the pathogen primarily depends for its survival. A reservoir is usually a living host of a certain species, such as an animal or a plant, inside of which a pathogen survives, often (though not always) without causing disease for the reservoir itself. By some definitions a reservoir may also be an environment external to an organism, such as a volume of contaminated air or water. Because of the enormous variety of infectious microorganisms capable of causing disease, precise definitions for what constitutes a natural reservoir are numerous, various, and often conflicting. The reservoir concept applies only for pathogens capable of infecting more than one host population and only with respect to a defined target popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rice Hoja Blanca Virus
''Rice hoja blanca tenuivirus'' (RHBV), meaning "white leaf rice virus", is a plant virus in the family ''Phenuiviridae.'' RHBV causes Hoja blanca disease (HBD), which affects the leaves of the rice plant ''Oryza sativa'', stunting the growth of the plant or killing it altogether. RHBV is carried by an insect vector, ''Tagosodes orizicolus'', a type of planthopper. The virus is found in South America, Mexico, throughout Central America, the Caribbean region, and the southern United States. In South America, the disease is endemic to Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Peru, Suriname, French Guiana and Guyana. Virology Viral Classification RHBV is a single stranded, negative-sense RNA virus of the genus ''Tenuivirus'', derived from the Latin "''tenui"'', meaning thin or weak. This comes from the nature of ''Tenuiviruses'' to form thin, filamentous viral particles. Other viruses in the genus ''Tenuivirus'' include maize stripe virus (MSV), rice stripe virus (RSV), and rice grassy stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cochliobolus Sativus
The fungus ''Cochliobolus sativus'' is the teleomorph (sexual stage) of ''Bipolaris sorokiniana'' (anamorph) which is the causal agent of a wide variety of cereal diseases. The pathogen can infect and cause disease on roots (where it is known as common root rot), leaf and stem, and head tissue. ''C. sativus'' is extremely rare in nature and thus it is the asexual or anamorphic stage which causes infections. The two most common diseases caused by ''B. sorokiniana'' are spot blotch and common root rot, mainly on wheat and barley crops. Identification The mycelium of ''B. sorokiniana'' is usually deep olive-brown. New cultures produce abundant simple conidiophores, which may be single or clustered and measure 6–10 x 110–220 μm with septations. Conidia develop laterally from pores beneath each conidiophore septum. Conidia are olive-brown and ovate to oblong, with rounded ends and a prominent basal scar. They measure 15–28 x 40–120 μm and are 3- to 10-septate. Some may b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sac Fungus
Ascomycota is a phylum of the kingdom Fungi that, together with the Basidiomycota, forms the subkingdom Dikarya. Its members are commonly known as the sac fungi or ascomycetes. It is the largest phylum of Fungi, with over 64,000 species. The defining feature of this fungal group is the " ascus" (), a microscopic sexual structure in which nonmotile spores, called ascospores, are formed. However, some species of the Ascomycota are asexual, meaning that they do not have a sexual cycle and thus do not form asci or ascospores. Familiar examples of sac fungi include morels, truffles, brewers' and bakers' yeast, dead man's fingers, and cup fungi. The fungal symbionts in the majority of lichens (loosely termed "ascolichens") such as ''Cladonia'' belong to the Ascomycota. Ascomycota is a monophyletic group (it contains all descendants of one common ancestor). Previously placed in the Deuteromycota along with asexual species from other fungal taxa, asexual (or anamorphic) ascom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Pathogen
Plant pathology (also phytopathology) is the scientific study of diseases in plants caused by pathogens (infectious organisms) and environmental conditions (physiological factors). Organisms that cause infectious disease include fungi, oomycetes, bacteria, viruses, viroids, virus-like organisms, phytoplasmas, protozoa, nematodes and parasitic plants. Not included are ectoparasites like insects, mites, vertebrate, or other pests that affect plant health by eating plant tissues. Plant pathology also involves the study of pathogen identification, disease etiology, disease cycles, economic impact, plant disease epidemiology, plant disease resistance, how plant diseases affect humans and animals, pathosystem genetics, and management of plant diseases. Overview Control of plant diseases is crucial to the reliable production of food, and it provides significant problems in agricultural use of land, water, fuel and other inputs. Plants in both natural and cultivated populat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific American
''Scientific American'', informally abbreviated ''SciAm'' or sometimes ''SA'', is an American popular science magazine. Many famous scientists, including Albert Einstein and Nikola Tesla, have contributed articles to it. In print since 1845, it is the oldest continuously published magazine in the United States. ''Scientific American'' is owned by Springer Nature, which in turn is a subsidiary of Holtzbrinck Publishing Group. History ''Scientific American'' was founded by inventor and publisher Rufus Porter (painter), Rufus Porter in 1845 as a four-page weekly newspaper. The first issue of the large format newspaper was released August 28, 1845. Throughout its early years, much emphasis was placed on reports of what was going on at the United States Patent and Trademark Office, U.S. Patent Office. It also reported on a broad range of inventions including perpetual motion machines, an 1860 device for buoying vessels by Abraham Lincoln, and the universal joint which now can be found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weed Control
Weed control is a type of pest control, which attempts to stop or reduce growth of weeds, especially noxious weeds, with the aim of reducing their competition with desired flora and fauna including domesticated plants and livestock, and in natural settings preventing non native species competing with native species. Weed control is important in agriculture. Methods include hand cultivation with hoes, powered cultivation with cultivators, smothering with mulch, lethal wilting with high heat, burning, and chemical control with herbicides (weed killers). Need for control Weeds compete with productive crops or pasture, they can be poisonous, distasteful, produce burrs, thorns or otherwise interfere with the use and management of desirable plants by contaminating harvests or interfering with livestock. Weeds compete with crops for space, nutrients, water and light. Smaller, slower growing seedlings are more susceptible than those that are larger and more vigorous. Onions are one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima ''Oryza glaberrima'', commonly known as African rice, is one of the two domesticated rice species. It was first domesticated and grown in West Africa around 3,000 years ago. In agriculture, it has largely been replaced by higher-yielding Asian r ...'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera ''Zizania (genus), Zizania'' and ''Porteresia'', both wild and domesticated, although the term may also be used for primitive or uncultivated varieties of ''Oryza''. As a cereal, cereal grain, domesticated rice is the most widely consumed staple food for over half of the world's World population, human population,Abstract, "Rice feeds more than half the world's population." especially in Asia and Africa. It is the agricultural commodity with the third-highest worldwide production, after sugarcane and maize. Since sizable portions of sugarcane and ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation tends to exist within any given population as a result of genetic mutation and recombination. Evolution occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection (including sexual selection) and genetic drift act on this variation, resulting in certain characteristics becoming more common or more rare within a population. The evolutionary pressures that determine whether a characteristic is common or rare within a population constantly change, resulting in a change in heritable characteristics arising over successive generations. It is this process of evolution that has given rise to biodiversity at every level of biological organisation, including the levels of species, individual organisms, and molecules. The theory of evolution by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vavilovian Mimicry
In plant biology, Vavilovian mimicry (also crop mimicry or weed mimicry) is a form of mimicry in plants where a weed evolves to share one or more characteristics with a domesticated plant through generations of artificial selection. It is named after Nikolai Vavilov, a prominent Russian plant geneticist. Selection against the weed may occur by killing a young or adult weed, separating its seeds from those of the crop (winnowing), or both. This has been done manually since Neolithic times, and in more recent years by agricultural machinery. Vavilovian mimicry is a good illustration of unintentional selection by humans. Although the human selective agents might be conscious of their impact on the local weed gene pool, such effects go against the goals of those growing crops. Weeders do not want to select for weeds that are increasingly similar to the cultivated plant, yet the only other option is to let the weeds grow and compete with crops for sunlight and nutrients. Similar s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_W2_IMG_0528.jpg)